标签:
我的linux 环境是windows8.1 + VMware6.5.1+ Fedora14,参考书籍:第六章
我利用一个SSH软件SSH Secure File Transfer Client 来从Linux传输文件
来张虚拟机运行Fedora的图:
下面步入正题:
IO最基本操作:
1 //hello.c 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <sys/types.h> 4 #include <sys/stat.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #define MAXSIZE 10 int main(void) 11 { 12 int i,fd,size,len; 13 char *buf ="hello! I‘m wirting to this file!"; 14 char buf_r[10]; 15 len= strlen(buf); 16 if((fd = open("/tmp/hello2.txt",O_CREAT |O_TRUNC | O_RDWR,0666))<0)//打开文件 17 { 18 perror("open:"); 19 exit(1); 20 }else 21 { 22 printf("open file :hello2.txt %d\n",fd); 23 } 24 if((size = write( fd, buf,len))<0)//写固定长度数据,buf 25 { 26 perror("write:"); 27 exit(1); 28 }else 29 { 30 printf("Wirte %s size=%d\n",buf,size); 31 } 32 lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);//文件指针定位到文件头 33 if((size = read(fd,buf_r,10))<0)//读10个字节的数据,这里没有考虑字符串最后一个字节为‘\0‘,要完善 34 { 35 perror("read:"); 36 exit(1); 37 }else 38 { 39 printf("read from file:%s size=%d\n",buf_r,size); 40 } 41 if( close(fd) < 0)//别忘记关闭 42 { 43 perror("Close:"); 44 exit(1); 45 }else 46 { 47 printf("Close hello2.txt\n"); 48 } 49 exit(0); 50 }
文件的访问涉及到进程间同步、互斥问题,采用Linux的fcntl()函数来加锁。
1 //function lock_set 2 void lock_set(int fd,int type) 3 { 4 struct flock lock; 5 lock.l_whence = SEEK_SET; 6 lock.l_start = 0; 7 lock.l_len = 0; 8 while(1) 9 { 10 lock.l_type = type; 11 if(fcntl(fd, F_SETLK,&lock) == 0) //如果要操作的文件已经加"写入锁"则fcntl() 返回非0值 12 { 13 if(lock.l_type == F_RDLCK) 14 printf("read lock set by %d\n",getpid()); 15 else if (lock.l_type == F_WRLCK) 16 printf("write lock set by %d\n",getpid()); 17 else if (lock.l_type == F_UNLCK) 18 printf("release lock by %d\n",getpid()); 19 return ; 20 } 21 fcntl(fd, F_GETLK,&lock);//上锁失败说明文件被锁住,则用"F_GETLK"来获取该锁的类型,包括上锁线程ID 22 if(lock.l_type != F_UNLCK) 23 { 24 if(lock.l_type == F_RDLCK) 25 printf("read lock already set by %d\n", 26 lock.l_pid); 27 else if(lock.l_type == F_WRLCK) 28 printf("write lock already set by %d\n", 29 lock.l_pid); 30 getchar(); 31 } 32 } 33 }
下面演示A进程给文件上"写入锁",然后B进程给文件上"读锁"的实验现象:
Souce Code of A :
1 //hello3.c 即A 进程 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <sys/file.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <stdio.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 //function lock_set 9 //... 10 int main(void) 11 { 12 int fd; 13 fd=open("/tmp/hello3.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0666); 14 if(fd < 0) 15 { 16 perror("open"); 17 exit(1); 18 } 19 //lock "write" 20 lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);//给"hello3.txt"文件上"写入锁" 21 getchar();//等待,(按回车继续执行程序) 22 //then unlock 23 lock_set(fd,F_UNLCK);//去锁 24 getchar(); 25 close(fd); 26 exit(0); 27 }
Souce Code of B:
1 //hello4.c 即B进程 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <sys/file.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <stdio.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 //function lock_set 9 //... 10 int main(void) 11 { 12 int fd; 13 fd=open("/tmp/hello3.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0666); 14 if(fd < 0) 15 { 16 perror("open"); 17 exit(1); 18 } 19 //lock "read" 20 lock_set(fd,F_RDLCK);//给我文件hello3.txt上"读锁" 21 getchar(); 22 //then unlock 23 lock_set(fd,F_UNLCK); 24 getchar(); 25 close(fd); 26 exit(0); 27 }
运行效果,
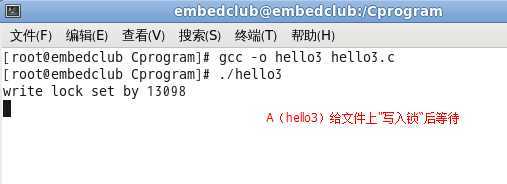
Step1:运行A进程(./hello3):
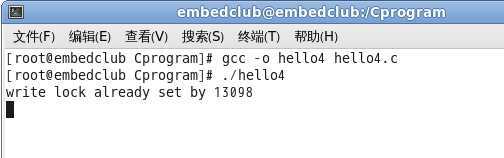
Step2:打开另一终端,运行B进程(./hello4):
Step3:A进程对应终端中按下回车键:
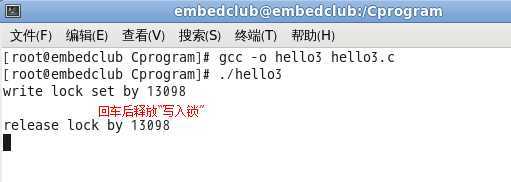
Step4:B进程终端中按下回车键:
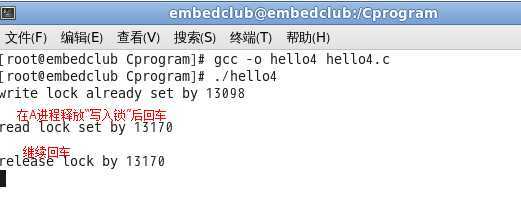
OK,读写锁实验结束。
下面再了解下IO多路复用(用select),这个对我来说有点难理解,贴上代码和效果图,以后斟酌。
1 //select.c 2 #include <fcntl.h> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 #include <time.h> 7 int main(void) 8 { 9 int fds[2]; 10 char buf[7]; 11 int i,rc,maxfd; 12 fd_set inset1,inset2; 13 struct timeval tv; 14 if((fds[0] = open("/tmp/hello5.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0666))<0) 15 perror("open hello5"); 16 if((fds[1] = open("/tmp/hello50.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0666))<0) 17 perror("open hello50"); 18 if((rc = write(fds[0],"hello!\n",7))) 19 printf("rc=%d\n",rc); 20 lseek(fds[0],0,SEEK_SET); 21 maxfd = fds[0]>fds[1] ? fds[0] : fds[1]; 22 FD_ZERO(&inset1); 23 FD_SET(fds[0],&inset1); 24 FD_ZERO(&inset2); 25 FD_SET(fds[1],&inset2); 26 tv.tv_sec=2; 27 tv.tv_usec=0; 28 while(FD_ISSET(fds[0],&inset1) || FD_ISSET(fds[1],&inset2)) 29 { 30 if(select(maxfd+1,&inset1,&inset2,NULL,&tv)<0) 31 perror("select"); 32 else 33 { 34 if(FD_ISSET(fds[0],&inset1)) 35 { 36 rc = read(fds[0],buf,7); 37 if(rc>0) 38 { 39 buf[rc]=‘\0‘; 40 printf("read %s\n",buf); 41 }else 42 perror("read"); 43 } 44 if(FD_ISSET(fds[1],&inset2)) 45 { 46 rc = write(fds[1],buf,7); 47 if(rc>0) 48 { 49 buf[rc]=‘\0‘; 50 printf("rc=%d,write:%s\n",rc,buf); 51 }else 52 perror("write"); 53 sleep(10); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 exit(0); 58 }
效果图:
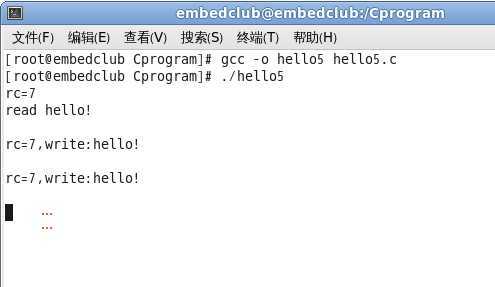
感谢您的阅读,boyang987 。转载请注明出处。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/boyang987/p/4226856.html