标签:优先级 linux about ps top centos
在Linux下进程查看和进程管理是经常使用的命令,我们可以使用ps来查看上一个状态中,各进程的信息,也可以通过top命令来实时的查看进程的属性信息。可以通过kill来管理进程运行,通过调整renice值来调整进程的优先级。
而htop、dstat、glances则是非常优秀Linux的系统监控命令,接下来就一步一步介绍他们的使用。
ps的使用
查看ps是shell内置的命令还是外部命令
[root@kvm ~]# type ps
ps is /bin/ps
由上可知ps是外部命令,外部命令基本都可以通过command --help查看命令的简短帮助信息
查看ps命令的详细使用,man ps
ps: 显示进程状态的命令,快照式、一次性
ps - report a snapshot of the current processes.
SYNOPSIS
ps [options]
DESCRIPTION
ps displays information about a selection of the active processes. If you want a
repetitive(重复)update of the selection and the displayed information, use top(1) instead.
支持两种风格:SysV, BSD
This version of ps accepts several kinds of options:
1 UNIX options, which may be grouped and must be preceded by a dash.
UNIX的选项,这可能是分组之前,必须用一个破折号。
2 BSD options, which may be grouped and must not be used with a dash.
BSD选项,这可能是分组,不得使用破折号。
3 GNU long options, which are preceded by two dashes.
ps命令把进程分为两类:
与终端相关的进程: a ps a
a Lift the BSD-style "only yourself" restriction, which is imposed upon the set of all processes when some BSD-style (without "-") options are used or when the personality setting is BSD-like. The set of processes selected in this manner is in addition to the set of processes selected by other means. An alternate description is that this option causes ps to list all processes with a terminal (tty), or to list all processes when used together with the x option.
与终端无关的进程:x ps x
x Lift the BSD-style "must have a tty" restriction, which is imposed upon the set of all processes when some BSD-style (without "-") options are used or when the ps personality setting is BSD-like. The set of processes selected in this manner is in addition to the set of processes selected by other means. An alternate description is that this option causes ps to list all processes owned by you (same EUID as ps), or to list all processes when used together with the a option.
u display user-oriented format
常用组合:ps aux
USER 那个用户启动的
PID 进程号
pid PID process ID number of the process.
%CPU cpu占用百分比
%cpu %CPU cpu utilization of the process in "##.#" format. Currently, it is the CPU time used divided by the time the process has been running (cputime/realtime ratio), expressed as a percentage. It will not add up to 100% unless you are lucky. (alias pcpu).
%MEM 内存占用百分比
%mem %MEM ratio of the process’s resident set size to the physical memory on the machine,expressed as a percentage. (alias pmem).
VSZ: Virtual memory SiZe 线性地址空间所占用的大小
vsz VSZ virtual memory size of the process in KiB (1024-byte units). Device mappings are currently excluded; this is subject to change. (alias vsize).
RSS: 常驻内存集 使用过程中不能交换出去的内存空间
rss RSS resident set size, the non-swapped physical memory that a task has used
(in kiloBytes). (alias rssize, rsz).
TTY 跟哪个终端相关
STAT状态: 进程的状态
R: running 运行态
R Running or runnable (on run queue)
S: 可中断睡眠
S Interruptible sleep (waiting for an event to complete)
D:不可中断睡眠
D Uninterruptible sleep (usually IO)
T:stopped 停止态
T Stopped, either by a job control signal or because it is being traced.
Z:zombie 僵死态
Z Defunct ("zombie") process, terminated but not reaped by its parent.
s: session leader 会话的领导者
s is a session leader
+:前台进程
+ is in the foreground process group
l: 多线程进程
l is multi-threaded (using CLONE_THREAD, like NPTL pthreads do)
N:低优先级进程
N low-priority (nice to other users)
<: 高优先级进程
< high-priority (not nice to other users)
COMMAND:包含在方括号中的进程表示为内核线程
[kthreadd] 加了[]说明是内核线程
常用组合:ps -ef
-e: 显示所有进程
-e Select all processes. Identical to -A.
-f: 显示完整格式的信息
-f does full-format listing. This option can be combined with many other UNIX-style
options to add additional columns. It also causes the command arguments to be printed. When used with -L, the NLWP (number of threads) and LWP (thread ID)columns will be added. See the c option, the format keyword args, and the format keyword comm.
ppid PPID parent process ID. 父进程的id.
c C processor utilization. Currently, this is the integer value of the percent usage over the lifetime of the process. (see %cpu).
C pcpu cpu utilization cpu使用率
常用组合:ps -eFH
-F: 显示额外信息
-F extra full format. See the -f option, which -F implies.
-H:显示进程的层次结构
-H show process hierarchy (forest)
psr PSR processor that process is currently assigned to.在哪个cpu上运行,本实验环境是有2个cpu总共8核。
自定义要显示的信息:o
o format specify user-defined format. Identical to -o and --format.
ps axo pid,command,psr,pri,ni,.. 需要注意o需要写在后面
ni: nice值
pri: 优优级
psr: 运行的CPU
显示进程号(PID)和父进程号(PPID)运行的CPU(PRI)和优先级(PRI)
2.top的使用
top: top可以动态的显示
top - display Linux tasks
显示Linux工作任务
SYNOPSIS
top -hv | -abcHimMsS -d delay -n iterations -p pid [, pid ...]
The traditional switches ’-’ and whitespace are optional.
DESCRIPTION
The top program provides a dynamic real-time view of a running system. It can display system summary information as well as a list of tasks currently being managed by the Linux kernel. The types of system summary information shown and the types, order and size of information displayed for tasks are all user configurable and that configuration can be made persistent across restarts.
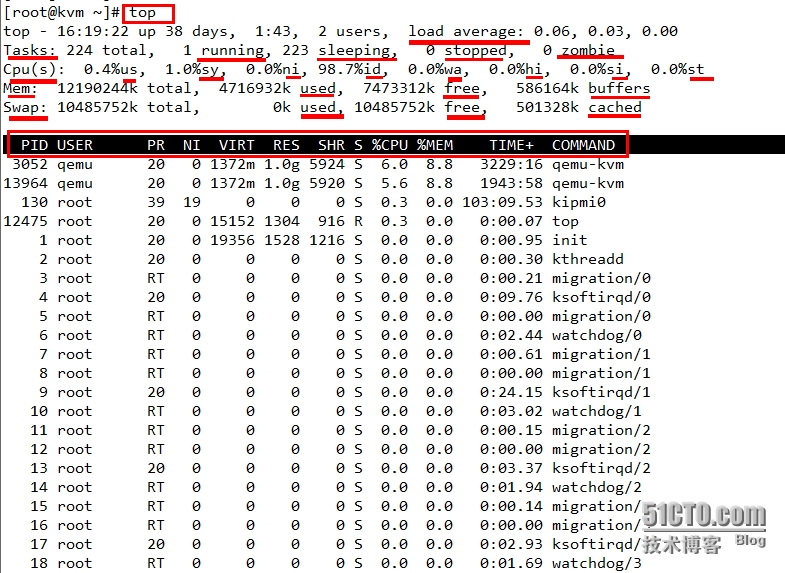
us: user space
sy: system
ni: nice值调整所占用时间百分比
id: 空闲百分比
wa: wait io cpu用于等待io事件完成所消耗的时间占据的百分比
hi: hardware interrupt
si: soft interrupt
st: 被虚拟机拿走的时间
2c. SUMMARY Area Fields
The summary area fields describing CPU statistics are abbreviated.They provide
摘要区域字段描述CPU统计数据是缩写。他们提供所花时间信息:
information about times spent in:
us = user mode
sy = system mode
ni = low priority user mode (nice)
id = idle task
wa = I/O waiting
hi = servicing IRQs
si = servicing soft IRQs
st = steal (time given to other DomU instances)
VIRT 虚拟内存集
RES 常驻内存集
SHR 共享内存大小
S 进程状态
输入字符
M: 内存百分比
P: CPU百分比
T: 累积占用的CPU时间
l: 显示或不显示负载信息
过去1分钟、5分钟、15分钟的平均负载
load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
m: 显示或不显示物理内存和交换内存的相关信息
q: 退出
k: 终止指定进程
s: 修改刷新时间间隔
后面这几个操作可以自己输入后,查看显示信息的变化,注意按对应字符后,再按一次又返回到原来的显示
常用选项:
-d #: 指定刷新时间间隔 指定刷新时间后,刷新次数就可以调整了
-b: 以批次的方式显示top的刷新,会把所有的任务都显示出来,只是是翻转的方式 只能按Ctrl+c退出
-n #: 显示的批次 显示#次后会自动退出
kill使用
[root@kvm ~]# kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX
[root@kvm ~]# kill -19 13065
通过renice来改变,运行进程的优先级
renice - alter priority of running processes
SYNOPSIS
renice [-n] priority [[-p] pid ...] [[-g] pgrp ...] [[-u] user ...]
renice -h | -v
DESCRIPTION
Renice alters the scheduling priority of one or more running processes. The following who parame-ters are interpreted as process ID’s, process group ID’s, or user names.
[root@kvm ~]# renice -10 -p 13037
13037: old priority 0, new priority -10
本文出自 “快乐就好” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://wdllife.blog.51cto.com/6615958/1604873
标签:优先级 linux about ps top centos
原文地址:http://wdllife.blog.51cto.com/6615958/1604873