标签:
一,开篇分析
Hi,大家好!大熊君又和大家见面了,(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……,这系列文章主要是学习Html5相关的知识点,以学习API知识点为入口,由浅入深的引入实例,
让大家一步一步的体会"h5"能够做什么,以及在实际项目中如何去合理的运用达到使用自如,完美驾驭O(∩_∩)O~,好了,废话不多说,直接进入今天的主题,
今天主要讲的是“requestAnimationFrame API”及在客户端浏览器中的作用,并且会引入一个实际的例子做为讲解的原型范例,让我们先来看看“requestAnimationFrame API”:
其实在web开发中,我们实现动画效果的可选方案已经很多了:
1,你可以用CSS3的animattion+keyframes。
2,你也可以用css3的transition。
3,你还可以用通过在canvas上作图来实现动画,也可以借助jQuery动画相关的API方便地实现。
4,你还可以使用最原始的“window.setTimout()”或者“window.setInterval()”通过不断更新元素的状态位置等来实现动画,前提是画面的更新频率要达到每秒60次才能让肉眼看到流畅的动画效果。
5,哈哈哈!现在又多了一种实现动画的方案,那就是还在草案当中的“window.requestAnimationFrame()”方法。

requestAnimationFrame是什么?
在浏览器动画程序中,我们通常使用一个定时器来循环每隔几毫秒移动目标物体一次,来让它动起来。如今有一个好消息,浏览器开发商们决定:“嗨,为什么我们不在浏览器里提供这样一个API呢,
这样一来我们可以为用户优化他们的动画。”所以,这个requestAnimationFrame()函数就是针对动画效果的API,你可以把它用在DOM上的风格变化或画布动画好或WebGL中。
使用requestAnimationFrame有什么好处?
浏览器可以优化并行的动画动作,更合理的重新排列动作序列,并把能够合并的动作放在一个渲染周期内完成,从而呈现出更流畅的动画效果。
比如,通过requestAnimationFrame(),JS动画能够和CSS动画/变换或SVG SMIL动画同步发生。另外,如果在一个浏览器标签页里运行一个动画,当这个标签页不可见时,
浏览器会暂停它,这会减少CPU,内存的压力,节省电池电量。
requestAnimationFrame的用法
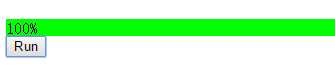
先来看一个简单的小栗子:
模拟一个进度条动画,初始div宽度为1px,在step函数中将进度加1然后再更新到div宽度上,在进度达到100之前,一直重复这一过程。
<div id="test" style="width:1px;height:17px;background:#0f0;">0%</div>
<input type="button" value="Run" id="run"/>
window.requestAnimationFrame = window.requestAnimationFrame || window.mozRequestAnimationFrame || window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame || window.msRequestAnimationFrame;
var start = null;
var ele = document.getElementById("test");
var progress = 0;
function step(timestamp) {
progress += 1;
ele.style.width = progress + "%";
ele.innerHTML=progress + "%";
if (progress < 100) {
requestAnimationFrame(step);
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(step);
document.getElementById("run").addEventListener("click", function() {
ele.style.width = "1px";
progress = 0;
requestAnimationFrame(step);
}, false);
运行效果如下:
二,深入requestAnimationFrame
我们对动画的要求苛刻吗?
对于时间要求苛刻的动画,永远不要使用 setTimeout() 或 setInterval()。
时间间隔设置为 1000/60 毫秒,这相当于大约每秒 60 帧。这个数字是我对最佳帧速率的最佳估值,它可能不是一个很好的值,但是,因为 setInterval() 和 setTimeout() 完全不了解动画,所以由我指定帧速率。
浏览器肯定比我更了解何时绘制下一个动画帧,因此,如果改为由浏览器指定帧速率,会产生更好的结果。
使用 setTimeout 和 setInterval() 甚至有一个更严重的缺陷。虽然您传递以毫秒为单位指定的这些方法的时间间隔,但这些方法没有精确到毫秒。事实上,根据 HTML 规范,
这些方法(为了节约资源)慷慨地拉长您指定的时间间隔。
使用 setTimeout 和 setInterval() 甚至有一个更严重的缺陷。虽然您传递以毫秒为单位指定的这些方法的时间间隔,但这些方法没有精确到毫秒;事实上,根据 HTML 规范,这些方法(为了节约资源)慷慨地拉长您指定的时间间隔。
为了避免这些缺陷,对于时间要求苛刻的动画,不应使用 setTimeout() 和 setInterval(),而是应该使用 ”requestAnimationFrame()“。
我们要做两件实际的事:
(1),兼容处理,不同浏览器厂商肯定内部实现有区别
window.requestAnimFrame = (function(){
return window.requestAnimationFrame ||
window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.mozRequestAnimationFrame ||
function( callback ){
window.setTimeout(callback, 1000 / 60);
};
})();
(2),另一种方式实现
(function() {
var lastTime = 0;
var vendors = [‘webkit‘, ‘moz‘];
for(var x = 0; x < vendors.length && !window.requestAnimationFrame; ++x) {
window.requestAnimationFrame = window[vendors[x]+‘RequestAnimationFrame‘];
window.cancelAnimationFrame =
window[vendors[x]+‘CancelAnimationFrame‘] || window[vendors[x]+‘CancelRequestAnimationFrame‘];
}
if (!window.requestAnimationFrame)
window.requestAnimationFrame = function(callback, element) {
var currTime = new Date().getTime();
var timeToCall = Math.max(0, 16 - (currTime - lastTime));
var id = window.setTimeout(function() { callback(currTime + timeToCall); },
timeToCall);
lastTime = currTime + timeToCall;
return id;
};
if (!window.cancelAnimationFrame)
window.cancelAnimationFrame = function(id) {
clearTimeout(id);
};
}());
三,相关分享
(1),Tween.js
1 var Tween = { 2 Linear: function(t, b, c, d) { return c*t/d + b; }, 3 Quad: { 4 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 5 return c * (t /= d) * t + b; 6 }, 7 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 8 return -c *(t /= d)*(t-2) + b; 9 }, 10 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 11 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t + b; 12 return -c / 2 * ((--t) * (t-2) - 1) + b; 13 } 14 }, 15 Cubic: { 16 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 17 return c * (t /= d) * t * t + b; 18 }, 19 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 20 return c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * t + 1) + b; 21 }, 22 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 23 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t*t + b; 24 return c / 2*((t -= 2) * t * t + 2) + b; 25 } 26 }, 27 Quart: { 28 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 29 return c * (t /= d) * t * t*t + b; 30 }, 31 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 32 return -c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * t*t - 1) + b; 33 }, 34 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 35 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t * t + b; 36 return -c / 2 * ((t -= 2) * t * t*t - 2) + b; 37 } 38 }, 39 Quint: { 40 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 41 return c * (t /= d) * t * t * t * t + b; 42 }, 43 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 44 return c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * t * t * t + 1) + b; 45 }, 46 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 47 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t * t * t + b; 48 return c / 2*((t -= 2) * t * t * t * t + 2) + b; 49 } 50 }, 51 Sine: { 52 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 53 return -c * Math.cos(t/d * (Math.PI/2)) + c + b; 54 }, 55 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 56 return c * Math.sin(t/d * (Math.PI/2)) + b; 57 }, 58 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 59 return -c / 2 * (Math.cos(Math.PI * t/d) - 1) + b; 60 } 61 }, 62 Expo: { 63 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 64 return (t==0) ? b : c * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t/d - 1)) + b; 65 }, 66 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 67 return (t==d) ? b + c : c * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * t/d) + 1) + b; 68 }, 69 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 70 if (t==0) return b; 71 if (t==d) return b+c; 72 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t - 1)) + b; 73 return c / 2 * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * --t) + 2) + b; 74 } 75 }, 76 Circ: { 77 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 78 return -c * (Math.sqrt(1 - (t /= d) * t) - 1) + b; 79 }, 80 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 81 return c * Math.sqrt(1 - (t = t/d - 1) * t) + b; 82 }, 83 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 84 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return -c / 2 * (Math.sqrt(1 - t * t) - 1) + b; 85 return c / 2 * (Math.sqrt(1 - (t -= 2) * t) + 1) + b; 86 } 87 }, 88 Elastic: { 89 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d, a, p) { 90 var s; 91 if (t==0) return b; 92 if ((t /= d) == 1) return b + c; 93 if (typeof p == "undefined") p = d * .3; 94 if (!a || a < Math.abs(c)) { 95 s = p / 4; 96 a = c; 97 } else { 98 s = p / (2 * Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a); 99 } 100 return -(a * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p)) + b; 101 }, 102 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d, a, p) { 103 var s; 104 if (t==0) return b; 105 if ((t /= d) == 1) return b + c; 106 if (typeof p == "undefined") p = d * .3; 107 if (!a || a < Math.abs(c)) { 108 a = c; 109 s = p / 4; 110 } else { 111 s = p/(2*Math.PI) * Math.asin(c/a); 112 } 113 return (a * Math.pow(2, -10 * t) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p) + c + b); 114 }, 115 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d, a, p) { 116 var s; 117 if (t==0) return b; 118 if ((t /= d / 2) == 2) return b+c; 119 if (typeof p == "undefined") p = d * (.3 * 1.5); 120 if (!a || a < Math.abs(c)) { 121 a = c; 122 s = p / 4; 123 } else { 124 s = p / (2 *Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a); 125 } 126 if (t < 1) return -.5 * (a * Math.pow(2, 10* (t -=1 )) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p)) + b; 127 return a * Math.pow(2, -10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p ) * .5 + c + b; 128 } 129 }, 130 Back: { 131 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d, s) { 132 if (typeof s == "undefined") s = 1.70158; 133 return c * (t /= d) * t * ((s + 1) * t - s) + b; 134 }, 135 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d, s) { 136 if (typeof s == "undefined") s = 1.70158; 137 return c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * ((s + 1) * t + s) + 1) + b; 138 }, 139 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d, s) { 140 if (typeof s == "undefined") s = 1.70158; 141 if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * (t * t * (((s *= (1.525)) + 1) * t - s)) + b; 142 return c / 2*((t -= 2) * t * (((s *= (1.525)) + 1) * t + s) + 2) + b; 143 } 144 }, 145 Bounce: { 146 easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) { 147 return c - Tween.Bounce.easeOut(d-t, 0, c, d) + b; 148 }, 149 easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 150 if ((t /= d) < (1 / 2.75)) { 151 return c * (7.5625 * t * t) + b; 152 } else if (t < (2 / 2.75)) { 153 return c * (7.5625 * (t -= (1.5 / 2.75)) * t + .75) + b; 154 } else if (t < (2.5 / 2.75)) { 155 return c * (7.5625 * (t -= (2.25 / 2.75)) * t + .9375) + b; 156 } else { 157 return c * (7.5625 * (t -= (2.625 / 2.75)) * t + .984375) + b; 158 } 159 }, 160 easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) { 161 if (t < d / 2) { 162 return Tween.Bounce.easeIn(t * 2, 0, c, d) * .5 + b; 163 } else { 164 return Tween.Bounce.easeOut(t * 2 - d, 0, c, d) * .5 + c * .5 + b; 165 } 166 } 167 } 168 } 169 Math.tween = Tween;
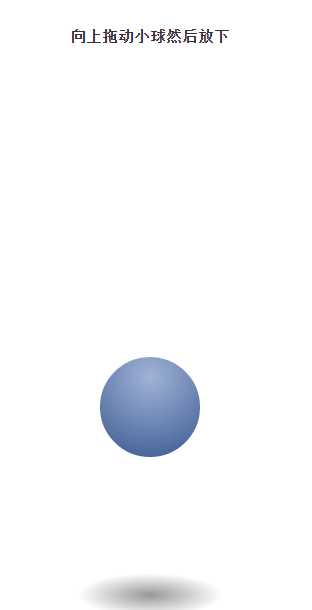
(2),ball.js
1 var ball = $("ball"), shadow = $("shadow"); 2 var objBall = {}; 3 var shadowWithBall = function(top) { 4 // 0 ~ 500 5 var top = top || parseInt(ball.css("top")), 6 scale = 1 + (500 - top) / 300; 7 opacity = 1 - (500 - top) / 300; 8 if (opacity < 0) opacity = 0; 9 shadow.css("opacity", opacity) 10 .css("WebkitTransform", "scale("+ [scale, scale].join(",") +")") 11 .css("transform", "scale("+ [scale, scale].join(",") +")"); 12 }, funFall = function() { 13 var start = 0, during = 100; 14 var _run = function() { 15 start++; 16 var top = Tween.Bounce.easeOut(start, objBall.top, 500 - objBall.top, during); 17 ball.css("top", top); 18 shadowWithBall(top); 19 if (start < during) requestAnimationFrame(_run); 20 }; 21 _run(); 22 }; 23 ball.bind("mousedown", function(event) { 24 objBall.pageY = event.pageY; 25 objBall.flagFollow = true; 26 }); 27 $(document).bind("mousemove", function(event) { 28 if (objBall.flagFollow) { 29 var pageY = event.pageY; 30 objBall.top = 500 - (objBall.pageY - pageY); 31 if (objBall.top < 0) { 32 objBall.top = 0; 33 } else if (objBall.top > 500) { 34 objBall.top = 500; 35 } 36 //cosnole.log(objBall.top); 37 ball.css("top", objBall.top); 38 shadowWithBall(objBall.top); 39 } 40 }); 41 $(document).bind("mouseup", function(event) { 42 if (objBall.flagFollow) funFall(); 43 objBall.flagFollow = false; 44 });
效果如下:
(四),最后总结
(1),理解requestAnimationFrame Api的使用方式以及具体实例中使用的目的是为了解决哪些问题。
(2),requestAnimationFrame 与 之前“setTimeout setInterval”的不同之处在哪。
(3),熟练使用requestAnimationFrame对象,不断实践与重构文章中的栗子。
哈哈哈,本篇结束,未完待续,希望和大家多多交流够沟通,共同进步。。。。。。呼呼呼……(*^__^*)
大熊君学习html5系列之------requestAnimationFrame(实现动画的另一种方案)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bigbearbb/p/4276808.html