标签:
在memcache中,作者为了专注于缓存的设计,使用了libevent来开发事件模型。memcache的时间模型同nginx的类似,拥有一个主进行(master)以及多个工作者线程(woker)。
在memcache中,是先对工作者线程进行初始化并启动,然后才会创建启动主线程。
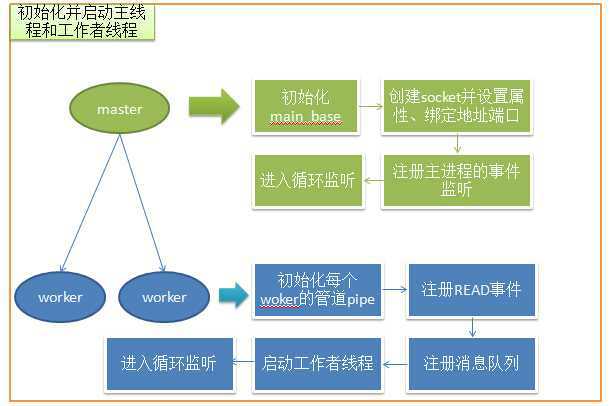
memcache对工作者线程进行初始化,参数分别为线程数量以及`main_base`,
/* start up worker threads if MT mode */ thread_init(settings.num_threads, main_base);

/* * Initializes the thread subsystem, creating various worker threads. * * nthreads Number of worker event handler threads to spawn * main_base Event base for main thread */ void thread_init(int nthreads, struct event_base *main_base) { int i; int power; pthread_mutex_init(&cache_lock, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&stats_lock, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&init_lock, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&init_cond, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&cqi_freelist_lock, NULL); cqi_freelist = NULL; /* Want a wide lock table, but don‘t waste memory */ if (nthreads < 3) { power = 10; } else if (nthreads < 4) { power = 11; } else if (nthreads < 5) { power = 12; } else { /* 8192 buckets, and central locks don‘t scale much past 5 threads */ power = 13; } item_lock_count = hashsize(power); item_lock_hashpower = power; item_locks = calloc(item_lock_count, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t)); if (! item_locks) { perror("Can‘t allocate item locks"); exit(1); } for (i = 0; i < item_lock_count; i++) { pthread_mutex_init(&item_locks[i], NULL); } pthread_key_create(&item_lock_type_key, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&item_global_lock, NULL); threads = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(LIBEVENT_THREAD)); if (! threads) { perror("Can‘t allocate thread descriptors"); exit(1); } dispatcher_thread.base = main_base; dispatcher_thread.thread_id = pthread_self(); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { int fds[2]; if (pipe(fds)) { perror("Can‘t create notify pipe"); exit(1); } threads[i].notify_receive_fd = fds[0]; threads[i].notify_send_fd = fds[1]; setup_thread(&threads[i]); /* Reserve three fds for the libevent base, and two for the pipe */ stats.reserved_fds += 5; } /* Create threads after we‘ve done all the libevent setup. */ for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { create_worker(worker_libevent, &threads[i]); } /* Wait for all the threads to set themselves up before returning. */ pthread_mutex_lock(&init_lock); wait_for_thread_registration(nthreads); pthread_mutex_unlock(&init_lock); }
在memcache中为了避免多线程共享资源的使用使用了很多锁,这里对锁不做介绍。
typedef struct { pthread_t thread_id; /* unique ID of this thread 线程ID*/ struct event_base *base; /* libevent handle this thread uses libevent事件*/ struct event notify_event; /* listen event for notify pipe 注册事件*/ int notify_receive_fd; /* receiving end of notify pipe 管道中接收端*/ int notify_send_fd; /* sending end of notify pipe 管道中发送端*/ struct thread_stats stats; /* Stats generated by this thread 线程状态*/ struct conn_queue *new_conn_queue; /* queue of new connections to handle 消息队列*/ cache_t *suffix_cache; /* suffix cache */ uint8_t item_lock_type; /* use fine-grained or global item lock */ } LIBEVENT_THREAD;
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { int fds[2]; /* 创建管道 */ if (pipe(fds)) { perror("Can‘t create notify pipe"); exit(1); } /* 设置线程管道的读写入口 */ threads[i].notify_receive_fd = fds[0]; threads[i].notify_send_fd = fds[1]; /* 设置线程属性 */ setup_thread(&threads[i]); /* Reserve three fds for the libevent base, and two for the pipe */ stats.reserved_fds += 5; }
/* * Set up a thread‘s information. */ static void setup_thread(LIBEVENT_THREAD *me) { me->base = event_init(); //初始化线程事件 if (! me->base) { fprintf(stderr, "Can‘t allocate event base\n"); exit(1); } /* 初始化监听事件 */ /* Listen for notifications from other threads */ event_set(&me->notify_event, me->notify_receive_fd, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, thread_libevent_process, me); /* 把事件绑定到线程事件 */ event_base_set(me->base, &me->notify_event); /* 注册事件到监听状态 */ if (event_add(&me->notify_event, 0) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Can‘t monitor libevent notify pipe\n"); exit(1); } ... }
/* * Processes an incoming "handle a new connection" item. This is called when * input arrives on the libevent wakeup pipe. */ static void thread_libevent_process(int fd, short which, void *arg) { ... /* 从管道读取消息 */ if (read(fd, buf, 1) != 1) if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Can‘t read from libevent pipe\n"); item = cq_pop(me->new_conn_queue); //读取连接 ... }
/* Create threads after we‘ve done all the libevent setup. */ for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { create_worker(worker_libevent, &threads[i]); }
`create_woker`函数创建工作者线程,
/* * Creates a worker thread. */ static void create_worker(void *(*func)(void *), void *arg) { pthread_t thread; pthread_attr_t attr; int ret; pthread_attr_init(&attr); if ((ret = pthread_create(&thread, &attr, func, arg)) != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Can‘t create thread: %s\n", strerror(ret)); exit(1); } }
`worker_libevent`函数进入线程循环监听状态,
/* * Worker thread: main event loop */ static void *worker_libevent(void *arg) { LIBEVENT_THREAD *me = arg; /* Any per-thread setup can happen here; thread_init() will block until * all threads have finished initializing. */ /* set an indexable thread-specific memory item for the lock type. * this could be unnecessary if we pass the conn *c struct through * all item_lock calls... */ me->item_lock_type = ITEM_LOCK_GRANULAR; pthread_setspecific(item_lock_type_key, &me->item_lock_type); register_thread_initialized(); event_base_loop(me->base, 0); return NULL; }
static struct event_base* mian_base; /* initialize main thread libevent instance */ main_base = event_init();
在`memcache.c`的主函数中,使用`libevent`的事件初始化函数来初始化`main_base`。
这里只介绍tcp连接,其中使用`server_sockets`来调用`server_socket`来初始化连接。
if (settings.port && server_sockets(settings.port, tcp_transport, portnumber_file)) { vperror("failed to listzhefen on TCP port %d", settings.port); exit(EX_OSERR); }
static int server_sockets(int port, enum network_transport transport, FILE *portnumber_file) { if (settings.inter == NULL) { return server_socket(settings.inter, port, transport, portnumber_file); } ... }
而在`server_socket`中完成了socket的初始化、绑定等操作。

/** * Create a socket and bind it to a specific port number * @param interface the interface to bind to * @param port the port number to bind to * @param transport the transport protocol (TCP / UDP) * @param portnumber_file A filepointer to write the port numbers to * when they are successfully added to the list of ports we * listen on. */ static int server_socket(const char *interface, int port, enum network_transport transport, FILE *portnumber_file) { int sfd; struct linger ling = {0, 0}; struct addrinfo *ai; struct addrinfo *next; struct addrinfo hints = { .ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE, .ai_family = AF_UNSPEC }; char port_buf[NI_MAXSERV]; int error; int success = 0; int flags =1; hints.ai_socktype = IS_UDP(transport) ? SOCK_DGRAM : SOCK_STREAM; if (port == -1) { port = 0; } snprintf(port_buf, sizeof(port_buf), "%d", port); error= getaddrinfo(interface, port_buf, &hints, &ai); if (error != 0) { if (error != EAI_SYSTEM) fprintf(stderr, "getaddrinfo(): %s\n", gai_strerror(error)); else perror("getaddrinfo()"); return 1; } for (next= ai; next; next= next->ai_next) { conn *listen_conn_add; if ((sfd = new_socket(next)) == -1) { /* getaddrinfo can return "junk" addresses, * we make sure at least one works before erroring. */ if (errno == EMFILE) { /* ...unless we‘re out of fds */ perror("server_socket"); exit(EX_OSERR); } continue; } #ifdef IPV6_V6ONLY if (next->ai_family == AF_INET6) { error = setsockopt(sfd, IPPROTO_IPV6, IPV6_V6ONLY, (char *) &flags, sizeof(flags)); if (error != 0) { perror("setsockopt"); close(sfd); continue; } } #endif setsockopt(sfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, (void *)&flags, sizeof(flags)); if (IS_UDP(transport)) { maximize_sndbuf(sfd); } else { error = setsockopt(sfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_KEEPALIVE, (void *)&flags, sizeof(flags)); if (error != 0) perror("setsockopt"); error = setsockopt(sfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_LINGER, (void *)&ling, sizeof(ling)); if (error != 0) perror("setsockopt"); error = setsockopt(sfd, IPPROTO_TCP, TCP_NODELAY, (void *)&flags, sizeof(flags)); if (error != 0) perror("setsockopt"); } if (bind(sfd, next->ai_addr, next->ai_addrlen) == -1) { if (errno != EADDRINUSE) { perror("bind()"); close(sfd); freeaddrinfo(ai); return 1; } close(sfd); continue; } else { success++; if (!IS_UDP(transport) && listen(sfd, settings.backlog) == -1) { perror("listen()"); close(sfd); freeaddrinfo(ai); return 1; } if (portnumber_file != NULL && (next->ai_addr->sa_family == AF_INET || next->ai_addr->sa_family == AF_INET6)) { union { struct sockaddr_in in; struct sockaddr_in6 in6; } my_sockaddr; socklen_t len = sizeof(my_sockaddr); if (getsockname(sfd, (struct sockaddr*)&my_sockaddr, &len)==0) { if (next->ai_addr->sa_family == AF_INET) { fprintf(portnumber_file, "%s INET: %u\n", IS_UDP(transport) ? "UDP" : "TCP", ntohs(my_sockaddr.in.sin_port)); } else { fprintf(portnumber_file, "%s INET6: %u\n", IS_UDP(transport) ? "UDP" : "TCP", ntohs(my_sockaddr.in6.sin6_port)); } } } } if (IS_UDP(transport)) { int c; for (c = 0; c < settings.num_threads_per_udp; c++) { /* Allocate one UDP file descriptor per worker thread; * this allows "stats conns" to separately list multiple * parallel UDP requests in progress. * * The dispatch code round-robins new connection requests * among threads, so this is guaranteed to assign one * FD to each thread. */ int per_thread_fd = c ? dup(sfd) : sfd; dispatch_conn_new(per_thread_fd, conn_read, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, UDP_READ_BUFFER_SIZE, transport); } } else { if (!(listen_conn_add = conn_new(sfd, conn_listening, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 1, transport, main_base))) { fprintf(stderr, "failed to create listening connection\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } listen_conn_add->next = listen_conn; listen_conn = listen_conn_add; } } freeaddrinfo(ai); /* Return zero iff we detected no errors in starting up connections */ return success == 0; }
在主线程中通过`conn_new`函数来建立主线程和工作者线程之间的关系。
/* 设置线程事件 */ event_set(&c->event, sfd, event_flags, event_handler, (void *)c); event_base_set(base, &c->event); c->ev_flags = event_flags; /* 注册事件到监听 */ if (event_add(&c->event, 0) == -1) { perror("event_add"); return NULL; }
上面中设置了事件的回调函数`event_handler`,而在`event_handler`中,主要调用了`driver_machine`函数。
driver_machine看名字就知道,想发动机一样的函数,那么该函数主要是处理各种事件以及相应的处理方法。
这里只简要介绍一个函数调用`dispatch_conn_new`。
void dispatch_conn_new(int sfd, enum conn_states init_state, int event_flags, int read_buffer_size, enum network_transport transport) { CQ_ITEM *item = cqi_new(); char buf[1]; if (item == NULL) { close(sfd); /* given that malloc failed this may also fail, but let‘s try */ fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory for connection object\n"); return ; } int tid = (last_thread + 1) % settings.num_threads; LIBEVENT_THREAD *thread = threads + tid; //循环获取工作者线程 last_thread = tid; item->sfd = sfd; item->init_state = init_state; item->event_flags = event_flags; item->read_buffer_size = read_buffer_size; item->transport = transport; cq_push(thread->new_conn_queue, item); //连接加入懂啊队列 MEMCACHED_CONN_DISPATCH(sfd, thread->thread_id); buf[0] = ‘c‘; if (write(thread->notify_send_fd, buf, 1) != 1) {//向管道写入消息 perror("Writing to thread notify pipe"); } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/coder2012/p/4281577.html