标签:
最近在学Android,看到ListView的Adaptor优化这里遇到一点理解上的困难。
目前流行的优化方法是结合convertView和ViewHolder来优化View的创建和查找,如:
public class ViewHolderAdapter extends ArrayAdapter { static class ViewHolder { TextView text1; TextView text2; TextView longtext; } public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) { Log.d(TAG, "position=" + position); ViewHolder holder; if (convertView == null) { convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item, parent, false); holder = new ViewHolder(); holder.text1 = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.text1); holder.text2 = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.text2); holder.longtext = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.longtext); convertView.setTag(holder); } else { holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag(); } MyObj data = getItem(position); holder.text1.setText(data.text1); holder.text2.setText(data.text2); holder.longtext.setText(data.longText); return convertView; } }
convertView的获取涉及ListView的recycle问题,不是本文的重点。这里主要看ViewHolder的实现。ViewHolder的实现依赖于View提供的setTag与getTag两个方法,为了方便理解这两个方法与所维持对象的行为,这里举一个实例:
XML:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context="com.example.settagandgettag.MainActivity" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/textView1" android:layout_marginTop="120dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textView1" android:text="Button" /> </RelativeLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.example.settagandgettag; import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity { Button btn =null; TextView tv = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1); btn =(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1); btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { MyObject obj = new MyObject(); obj.str="str before change"; tv.setTag(obj); Log.v("#1", ((MyObject)tv.getTag()).str); obj.str="str after change"; Log.v("#2", ((MyObject)tv.getTag()).str); } }); } public class MyObject{ public String str = ""; } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true; } @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. int id = item.getItemId(); if (id == R.id.action_settings) { return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } }
说明:通过以上实例可以发现,setTag维持的是一个可变的对象(如果该对象有其他的引用,则可以在getTag之外进行修改),而不能想当然的以为其行为是将用来setTag的对象映射为一个静态的、不可变的数据(毕竟Android还提供了fingViewByTag方法,参照findViewByID,按常理,作为ID的关键值是不应该能被修改的,这里之前理解上有一点误解)
触发按钮点击后的log如下:
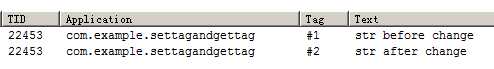
Android中View的setTag与getTag行为理解一例
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ownage/p/4286579.html