标签:
首先,我们回顾一下在MapReduce中,排序和分组在哪里被执行:
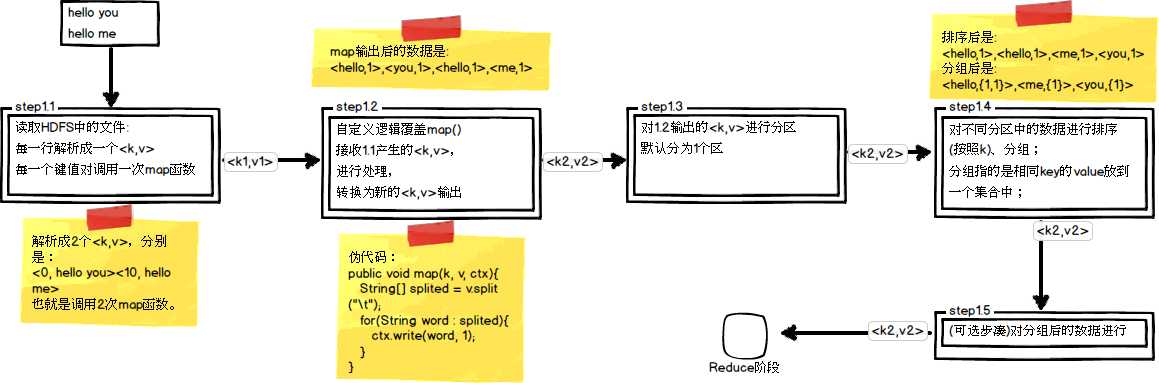
从上图中可以清楚地看出,在Step1.4也就是第四步中,需要对不同分区中的数据进行排序和分组,默认情况下,是按照key进行排序和分组。
在一些特定的数据文件中,不一定都是类似于WordCount单次统计这种规范的数据,比如下面这类数据,它虽然只有两列,但是却有一定的实践意义。
3 3 3 2 3 1 2 2 2 1 1 1
(1)如果按照第一列升序排列,当第一列相同时,第二列升序排列,结果如下所示
1 1 2 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 3 3
(2)如果当第一列相同时,求出第二列的最小值,结果如下所示
3 1 2 1 1 1
接着,我们会针对这个数据文件,进行排序和分组的实践尝试,以求达到结果所示的效果。
在Hadoop默认的排序算法中,只会针对key值进行排序,我们最初的代码如下(这里只展示了map和reduce函数):
public class MySortJob extends Configured implements Tool { public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, LongWritable> { protected void map( LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { String[] spilted = value.toString().split("\t"); long firstNum = Long.parseLong(spilted[0]); long secondNum = Long.parseLong(spilted[1]); context.write(new LongWritable(firstNum), new LongWritable( secondNum)); }; } public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable> { protected void reduce( LongWritable key, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> values, Reducer<LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { for (LongWritable value : values) { context.write(key, value); } }; } }
这里我们将第一列作为了key,第二列作为了value。
可以查看一下运行后的结果,如下所示:
1 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 3 2 3 1
从运行结果来看,并没有达到我们最初的目的,于是,我们需要抛弃默认的排序规则,因此我们要自定义排序。
(1)封装一个自定义类型作为key的新类型:将第一列与第二列都作为key
private static class MyNewKey implements WritableComparable<MyNewKey> { long firstNum; long secondNum; public MyNewKey() { } public MyNewKey(long first, long second) { firstNum = first; secondNum = second; } @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeLong(firstNum); out.writeLong(secondNum); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { firstNum = in.readLong(); secondNum = in.readLong(); } /* * 当key进行排序时会调用以下这个compreTo方法 */ @Override public int compareTo(MyNewKey anotherKey) { long min = firstNum - anotherKey.firstNum; if (min != 0) { // 说明第一列不相等,则返回两数之间小的数 return (int) min; } else { return (int) (secondNum - anotherKey.secondNum); } } }
PS:这里为什么需要封装一个新类型呢?因为原来只有key参与排序,现在将第一个数和第二个数都参与排序,作为一个新的key。
(2)改写最初的MapReduce方法函数代码:(只展示了map和reduce函数,还需要修改map和reduce输出的类型设置)
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, MyNewKey, LongWritable> { protected void map( LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, MyNewKey, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { String[] spilted = value.toString().split("\t"); long firstNum = Long.parseLong(spilted[0]); long secondNum = Long.parseLong(spilted[1]); // 使用新的类型作为key参与排序 MyNewKey newKey = new MyNewKey(firstNum, secondNum); context.write(newKey, new LongWritable(secondNum)); }; } public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<MyNewKey, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable> { protected void reduce( MyNewKey key, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> values, Reducer<MyNewKey, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { context.write(new LongWritable(key.firstNum), new LongWritable( key.secondNum)); }; }
从上面的代码中我们可以发现,新类型MyNewKey实现了一个叫做WritableComparable的接口,该接口中有一个compareTo()方法,当对key进行比较时会调用该方法,而我们将其改为了我们自己定义的比较规则,从而实现我们想要的效果。
其实,这个WritableComparable还实现了两个接口,我们看看其定义:
public interface WritableComparable<T> extends Writable, Comparable<T> { }
Writable接口是为了实现序列化,而Comparable则是为了实现比较。
(3)现在看看运行结果:
1 1 2 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 3 3
运行结果与预期的已经一致,自定义排序生效!
在Hadoop中的默认分组规则中,也是基于Key进行的,会将相同key的value放到一个集合中去。这里以上面的例子继续看看分组,因为我们自定义了一个新的key,它是以两列数据作为key的,因此这6行数据中每个key都不相同,也就是说会产生6组,它们是:1 1,2 1,2 2,3 1,3 2,3 3。而实际上只可以分为3组,分别是1,2,3。
现在首先改写一下reduce函数代码,目的是求出第一列相同时第二列的最小值,看看它会有怎么样的分组:
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<MyNewKey, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable> { protected void reduce( MyNewKey key, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> values, Reducer<MyNewKey, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { long min = Long.MAX_VALUE; for (LongWritable number : values) { long temp = number.get(); if (temp < min) { min = temp; } } context.write(new LongWritable(key.firstNum), new LongWritable(min)); }; }
其运行结果为:
1 1 2 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 3 3
但是我们预期的结果为:
#当第一列相同时,求出第二列的最小值 3 3 3 2 3 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 ------------------- #预期结果应该是 3 1 2 1 1 1
为了针对新的key类型作分组,我们也需要自定义一下分组规则:
(1)编写一个新的分组比较类型用于我们的分组:
private static class MyGroupingComparator implements RawComparator<MyNewKey> { /* * 基本分组规则:按第一列firstNum进行分组 */ @Override public int compare(MyNewKey key1, MyNewKey key2) { return (int) (key1.firstNum - key2.firstNum); } /* * @param b1 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组 * * @param s1 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组的起始位置 * * @param l1 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组的偏移量 * * @param b2 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组 * * @param s2 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组的起始位置 * * @param l2 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组的偏移量 */ @Override public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) { return WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, s1, 8, b2, s2, 8); } }
从代码中我们可以知道,我们自定义了一个分组比较器MyGroupingComparator,该类实现了RawComparator接口,而RawComparator接口又实现了Comparator接口,下面看看这两个接口的定义:
首先是RawComparator接口的定义:
public interface RawComparator<T> extends Comparator<T> { public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2); }
其次是Comparator接口的定义:
public interface Comparator<T> { int compare(T o1, T o2); boolean equals(Object obj); }
在MyGroupingComparator中分别对这两个接口中的定义进行了实现,RawComparator中的compare()方法是基于字节的比较,Comparator中的compare()方法是基于对象的比较。
在基于字节的比较方法中,有六个参数,一下子眼花了:
Params:
* @param arg0 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组
* @param arg1 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组的起始位置
* @param arg2 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组的偏移量
*
* @param arg3 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组
* @param arg4 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组的起始位置
* @param arg5 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组的偏移量
由于在MyNewKey中有两个long类型,每个long类型又占8个字节。这里因为比较的是第一列数字,所以读取的偏移量为8字节。
(2)添加对分组规则的设置:
// 设置自定义分组规则 job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyGroupingComparator.class);
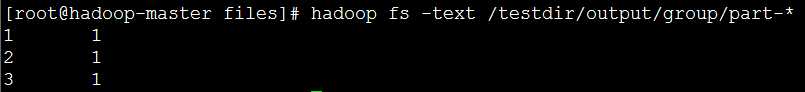
(3)现在看看运行结果:
(1)吴超,《深入浅出Hadoop》:http://www.superwu.cn/
(2)Suddenly,《Hadoop日记Day18-MapReduce排序和分组》:http://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4009751.html
Hadoop学习笔记—11.MapReduce中的排序和分组
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/4299085.html