标签:
android 使用 linux 内核,一般运行在 ARM 体系架构上,android 设备启动的过程,应用层之下基本等同于linux, 从应用层第一个程序init开始有所区别,下面开始介绍。
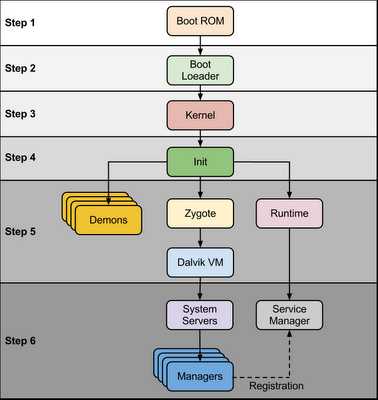
step1, boot rom 主要作用是加载 boot loader 进入内存并执行,boot rom 一般固化在芯片上,设备启动加电自检后从固定的地址开始执行
step2,boot loader 分2步执行,boot rom只加载了第一部分bootloader代码进入内存,这部分代码随即加载第二部分bootloader代码,第二部分是核心,它完成了必要的环境准备后,开始加载内核.
step3, android 内核启动过程与标准linux类似,完成内存子系统、保护模式、任务调度系统、驱动子系统、设备系统、文件系统等的初始化,最后运行第一个应用程序init. 与标准系统有所不同的是,android的内核增加了部分驱动及补丁,
What is the difference between the linux and android kernels?, here‘s a list of changes/addons that the Android Project made to the Linux kernel: Binder: It is an Android specific interprocess communication mechanism and remote method invocation system. ashmem: "Android Shared Memory". It is a new shared memory allocator, similar to POSIX SHM but with a different behavior and sporting a simpler file-based API. pmem: "Process memory allocator": It is used to manage large (1-16+ MB) physically contigous regions of memory shared between userspace and kernel drivers. logger: This is the kernel support for the logcat command. wakelocks: It is used for power management files. It holds the machine awake on a per-event basis until wakelock is released. oom handling: It kills processes as available memory becomes low. alarm manager: It lets user space tell the kernel when it would like to wake up. RAM_CONSOLE: Allows to save kernel printk messages to a buffer in RAM, so that after a kernel panic they can be viewed in the next kernel invocation. USB gadget driver for ADB yaffs2 flash filesystem
step4, init 进程,从这一步开始,android的启动跟其他linux发行版(如redhat,gentoo,ubuntu)就不一样了,init程序的实现、init.rc文件的格式,都是不一样的。init 进程主要功能是挂载磁盘分区,然后根据init.rc的配置解析并执行
Init is the very first process, we can say it is a root process, or the grandfather of all processes. The init process has two responsibilities. 1- Mounts directories like /sys , /dev or /proc 2- Runs init.rc script - The init process can be found at /init :: <android source>/system/core/init - Init.rc file can be found at :: <android source>/system/core/rootdir/ Android has specific format and rules for init.rc files. More information about this rules can be found in: What is inside the init.rc and what is it used for. At this stage, you can finally see the Android logo in your screen.
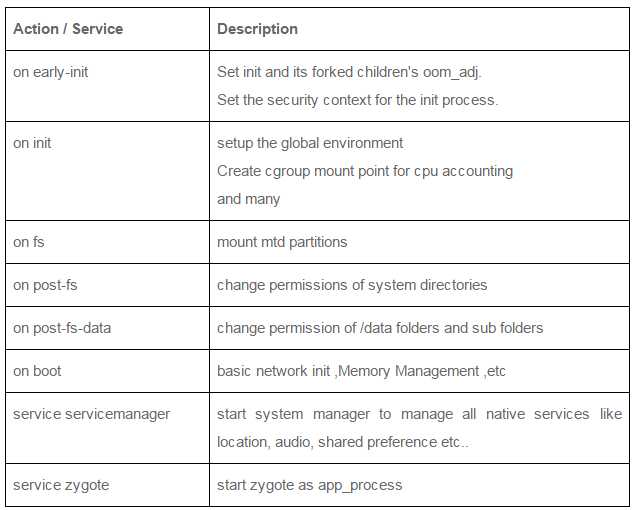
init.rc主要配置项如下:
/system/bin/logd/sbin/adbd/system/bin/usbd/system/bin/debuggerd/system/bin/rild/system/bin/runtime/system/bin/dbus-daemonsystem_server这些进程都是 init 进程 fork+execve 出来的子进程
After the above steps are completed, Zygote launches the system services. The Zygote forks a new process to launch the system services. Core services: Starting power manager Creating the Activity Manager Starting telephony registry Starting package manager Set activity manager service as system process Starting context manager Starting system contact providers Starting battery service Starting alarm manager Starting sensor service Starting window manager Starting Bluetooth service Starting mount service Other services: Starting status bar service Starting hardware service Starting NetStat service Starting connectivity service Starting Notification Manager Starting DeviceStorageMonitor service Starting Location Manager Starting Search Service Starting Clipboard Service Starting checkin service Starting Wallpaper service Starting Audio Service Starting HeadsetObserver Starting AdbSettingsObserver Now we have finally completed the booting process (system service are up and running in memory).
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jiayy/p/4301049.html