标签:
二 、选择器
内嵌、外部样式表的一般语法:
选择器
{
样式=值;
样式=值;
样式=值;
......
}
以下面html为例,了解区分一下各种样式的选择器
<head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <title>无标题文档</title> <link href="file:///E|/网页/Untitled-2.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" /> </head> <body> <input name="txt" id="a1" type="text" /><br/> <span>你好</span> <br/> <div> <input name="txt" id="a2" type="text" /><br/> <input name="txt" id="a3" type="text" value="******"/><br/> <span> <input name="txt" id="a4" type="text" value="******"/><br/> </span> </div> <p>你好</p> </body>
1、标签选择器 ------用标签名做选择器
input{...} div{...} span{...} td{...} 都可以做标签选择器,标签选择器控制的是一类,范围大。
例:
@charset "utf-8"; /* CSS Document */ input { border:5px; color:#3F6; border-bottom:3px solid red; }
显示结果:
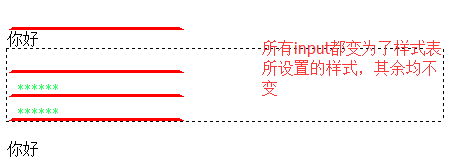
2、类别选择器 ------在HTML元素中使用class对元素进行分类,然后使用这个class的值作为选择器。
class选择器都是以"."开头。.class的名{...} 类别选择器相对于标签选择器来说,控制的更准确。
例:选择器 .uu
@charset "utf-8"; /* CSS Document */ .uu { border:5px; color:#3F6; border-bottom:3px solid red; }
HTML表的调用为:
<head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <title>无标题文档</title> <link href="file:///E|/网页/Untitled-2.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" /> </head> <body> <input name="txt" type="text" id="a1" /><br/> <span class="uu">你好</span> <br/> <div> <input name="txt" type="text" id="a2" class="uu" /><br/> <input name="txt" type="text" id="a3" value="******"/><br/> <span> <input name="txt" type="text" id="a4" class="uu" value="******"/><br/> </span> </div> <p>你好</p> </body>
显示结果:

3、ID选择器 ------针对HTML中相对应ID的元素起作用,以"#"开头。
#ID的名{...}
例:选择器#a3
@charset "utf-8"; /* CSS Document */ #a3 { border:5px; color:#3F6; border-bottom:3px solid red; }
显示结果:

4、复合选择器
(1)、用","隔开 -------表示并列关系,同时起作用。
input,#dd,.yellow,.uu { color:gray; line-height:28px; }
(2)、用"空格"隔开,------表示后代关系。
.uu { color:gray; line-height:28px; }
div .uu <!--div空格uu--> { background-color:blue; } <input name="txt" type="text" class="uu"/> <div> <!--相当于父代--> <input name="txt" type="text" /> <!--子代--> <input name="txt" type="text" class="uu" value="******"/> <!--子代--> <span> <!--子代--> <input name="txt" type="text" class="uu" value="******"/> <!--孙子代--> </span> </div>
不管是子代,还是孙子代,都是后代,只要在div的后代中有uu的就变化。
显示结果:

(3)class二次筛选。
标签选择器后面紧跟着 .class选择器{...}
input.uu
{
border:5px double red;
}
例:
.uu { color:gray; line-height:28px; } div.uu { background-color:red; } <body> <input name="txt" type="text" class="uu"/><br/> <div> <input name="txt" type="text" /><br/> <input name="txt" type="text" class="uu" value="******"/><br/> <span> <input name="txt" type="text" class="uu" value="******"/> </span> </div> </body>
显示结果:

div.uu的意思是:div存在的同时.uu也存在,属于二次筛选。
*对比:(div空格 .uu)与div.uu的不同。
div空格.uu的意思是:div的后代中(不管是子代还是孙子代中)出现.uu,出现的项就会随样式表变化。
div.uu的意思是:div存在的同时.uu也存在时,才会随样式表变化,属于二次筛选。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dawasai/p/4301242.html