标签:
C#扩展方法
当我们想为一个现有的类型添加一个方法的时候,有两种方式:一是直接在现有类型中添加方法;但是很多情况下现有类型都是不允许修改的,那么可以使用第二种方式,基于现有类型创建一个子类,然后在子类中添加想要的方法。
当C# 2.0中出现了静态类之后,对于上面的问题,我们也可以创建静态工具类来实现想要添加的方法。这样做可以避免创建子类,但是在使用时代码就没有那么直观了。
其实,上面的方法都不是很好的解决办法。在C# 3.0中出现了扩展方法,通过扩展方法我们可以直接在一个现有的类型上"添加"方法。当使用扩展方法的时候,可以像调用实例方法一样的方式来调用扩展方法。
扩展方法的创建和使用还是相对比较简单的。
相比普通方法,扩展方法有它自己的特征,下面就来看看怎么声明一个扩展方法:
根据上面的要求,我们给int类型添加了一个扩展方法,用来判断一个int值是不是偶数:
namespace ExtentionMethodTest { public static class ExtentionMethods { public static bool IsEven(this int num) { return num % 2 == 0; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int num = 10; //直接调用扩展方法 Console.WriteLine("Is {0} a even number? {1}", num, num.IsEven()); num = 11; //直接调用扩展方法 Console.WriteLine("Is {0} a even number? {1}", num, num.IsEven()); //通过静态类调用静态方法 Console.WriteLine("Is {0} a even number? {1}", num, ExtentionMethods.IsEven(num)); Console.Read(); } } }
虽然这个例子非常简单,但却演示了扩展方法的使用。
通过上面的例子可以看到,当调用扩展方法的时候,可以像调用实例方法一样。这就是我们使用扩展方法的原因之一,我们可以给一个已有类型"添加"一个方法。
既然扩展方法是一个静态类的方法,我们当然也可以通过静态类来调用这个方法。
通过IL可以看到,其实扩展方法也是编译器为我们做了一些转换,将扩展方法转化成静态类的静态方法调用
IL_001f: nop IL_0020: ldc.i4.s 11 IL_0022: stloc.0 IL_0023: ldstr "Is {0} a even number? {1}" IL_0028: ldloc.0 IL_0029: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_002e: ldloc.0 //直接调用扩展方法 IL_002f: call bool ExtentionMethodTest.ExtentionMethods::IsEven(int32) IL_0034: box [mscorlib]System.Boolean IL_0039: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string, object, object) IL_003e: nop IL_003f: ldstr "Is {0} a even number? {1}" IL_0044: ldloc.0 IL_0045: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_004a: ldloc.0 //通过静态类调用静态方法 IL_004b: call bool ExtentionMethodTest.ExtentionMethods::IsEven(int32) IL_0050: box [mscorlib]System.Boolean IL_0055: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string, object, object) IL_005a: nop IL_005b: call int32 [mscorlib]System.Console::Read() IL_0060: pop IL_0061: ret
有了扩展方法,当调用扩展方法的时候,我们就像是调用一个实例方法。但是,我们应该从两个角度看这个问题:
知道怎样调用扩展方法是我们前面部分介绍的,但是知道怎样不调用扩展方法同样重要。下面就看看编译器怎样决定要使用的扩展方法。
编译器处理扩展方法的过程:当编译器看到一个表达式好像是调用一个实例方法的时候,编译器就会查找所有的实例方法,如果没有找到一个兼容的实例方法,编译器就会去查找一个合适的扩展方法;编译器会检查导入的所有命名空间和当前命名空间中的所有扩展方法,并匹配变量类型到扩展类型存在一个隐式转换的扩展方法。
当编译器查找扩展方法的时候,它会检查System.Runtime.CompilerServices.ExtensionAttribute属性来判断一个方法是否是扩展方法
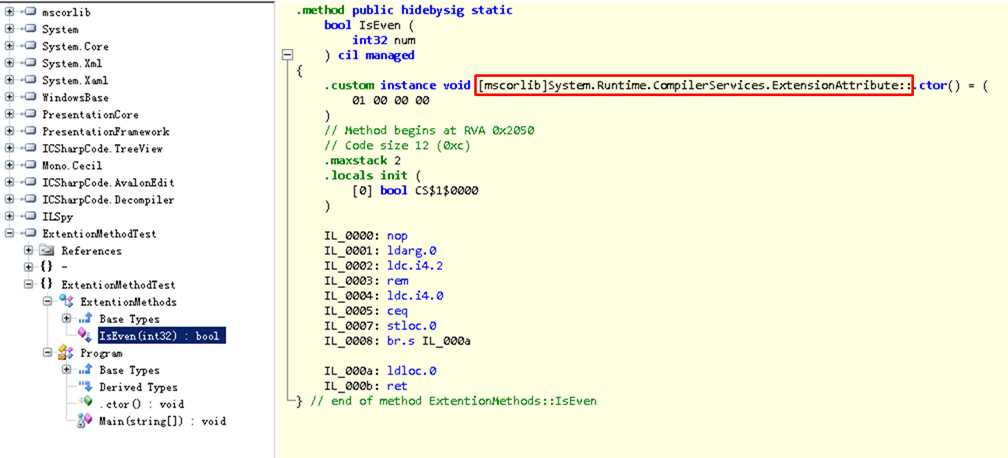
看到了编译器怎么处理扩展方法了,那么就需要了解一下使用扩展方法时要注意的地方了。
扩展方法使用的注意点:
下面看一个例子,通过这个例子来更好的理解编译器处理扩展方法时的一些注意点:
namespace ExtentionMethodTest { using AnotherNameSpace; public static class ExtentionMethods { public static void printInfo(this Student stu) { Console.WriteLine("printInfo(Student) from ExtentionMethodTest"); Console.WriteLine("{0} is {1} years old", stu.Name, stu.Age); } public static void printInfo(this object stu) { Console.WriteLine("printInfo(object) from ExtentionMethodTest"); Console.WriteLine("{0} is {1} years old", ((Student)stu).Name, ((Student)stu).Age); } } public class Student { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } //实例方法 //public void printInfo() //{ // Console.WriteLine("{0} is {1} years old", this.Name, this.Age); //} } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Student wilber = new Student { Name = "Wilber", Age = 28 }; //当实例方法printInfo存在的时候,所有的扩展方法都不可见 //此时调用的是实例方法 //wilber.printInfo(); //当注释掉实例方法后,下面代码会调用最近的命名空间的printInfo方法 //同时下面语句会选择“更好的转换”规则的扩展方法 //printInfo(Student) from ExtentionMethodTest //Wilber is 28 years old wilber.printInfo(); //当把wilber转换成object类型后,会调用printInfo(this object stu) //printInfo(object) from ExtentionMethodTest //Wilber is 28 years old object will = wilber; will.printInfo(); Console.Read(); } } } namespace AnotherNameSpace { using ExtentionMethodTest; public static class ExtentionClass { public static void printInfo(this Student stu) { Console.WriteLine("printInfo(Student) from AnotherNameSpace"); Console.WriteLine("{0} is {1} years old", stu.Name, stu.Age); } } }
当我们在空引用上调用实例方法是会引发NullReferenceException异常的。
但是,我们可以在空引用上调用扩展方法。
看下面的例子,我们可以判断一个对象是不是空引用。
namespace ExtentionMethodTest { public static class NullUitl { public static bool IsNull(this object o) { return o == null; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { object x = null; Console.WriteLine(x.IsNull()); x = new object(); Console.WriteLine(x.IsNull()); Console.Read(); } } }
通过上面的例子可以看到,即使引用为空,"x.IsNull()"仍然能够正常执行。
根据我们前面介绍的扩展方法的工作原理,其实上面的调用会被编译器转换为静态方法的调用"NullUitl.IsNull(x)"(可以查看IL代码验证),这也就解释了为什么空引用上可以调用扩展方法。
本文介绍了扩展方法的使用以及工作原理,其实扩展方法的本质就是通过静态类调用静态方法,只不过是编译器帮我们完成了这个转换。
然后还介绍了编译器是如何发现扩展方法的,以及使用扩展方法时要注意的地方。了解了编译器怎么查找扩展方法,对编写和调试扩展方法都是有帮助的。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wilber2013/p/4307282.html