标签:
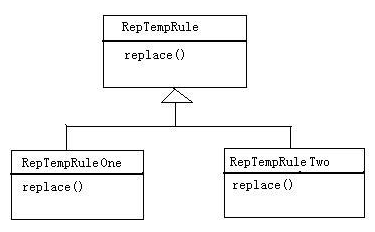
public abstract class RepTempRule{ protected String oldString=""; public void setOldString(String oldString){ this.oldString=oldString; } protected String newString=""; public String getNewString(){ return newString; } public abstract void replace() throws Exception; }
public class RepTempRuleOne extends RepTempRule{ public void replace() throws Exception{ //replaceFirst是jdk1.4新特性 newString=oldString.replaceFirst("aaa", "bbbb") System.out.println("this is replace one"); } }
public class RepTempRuleTwo extends RepTempRule{ public void replace() throws Exception{ newString=oldString.replaceFirst("aaa", "ccc") System.out.println("this is replace Two"); } }
第二步:我们要建立一个算法解决类,用来提供客户端可以自由选择算法。
public class RepTempRuleSolve { private RepTempRule strategy; public RepTempRuleSolve(RepTempRule rule){ this.strategy=rule; } public String getNewContext(Site site,String oldString) { return strategy.replace(site,oldString); } public void changeAlgorithm(RepTempRule newAlgorithm) { strategy = newAlgorithm; } }
调用如下:
public class test{ ...... public void testReplace(){ //使用第一套替代方案 RepTempRuleSolve solver=new RepTempRuleSolve(new RepTempRuleSimple()); solver.getNewContext(site,context); //使用第二套 solver=new RepTempRuleSolve(new RepTempRuleTwo()); solver.getNewContext(site,context); } ..... }
我们达到了在运行期间,可以自由切换算法的目的。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Coda/p/4310098.html