标签:
前言
之前一直在讲AndroidUI的内容,但是还没有完结,之后会慢慢补充。今天讲讲其他的,关于数据持久化的内容。对于一个应用程序而言,不可避免的要能够对数据进行存储,Android程序也不例外。而在Android中,提供了几种实现数据持久化的方法。后面会分别介绍。
在Android中,可以使用几种方式实现数据持久化:
后面几天会分别介绍以上几种方式实现的数据持久化,对于SharedPreferences而言,之前写过一篇博客,但是自己不是很满意,之后有时间会再重新写一份关于SharedPreferences的博客,有兴趣的朋友可以先去看看,Android--使用SharedPreferences。今天先介绍Internal Storage以及External Storage。
Internal Storage
内部存储,在Android中,开发者可以直接使用设备的内部存储器中保存文件,默认情况下,以这种方式保存的和数据是只能被当前程序访问,在其他程序中是无法访问到的,而当用户卸载该程序的时候,这些文件也会随之被删除。
使用内部存储保存数据的方式,基本上也是先获得一个文件的输出流,然后以write()的方式把待写入的信息写入到这个输出流中,最后关闭流即可,这些都是Java中IO流的操作。具体步骤如下:
上面介绍的Context.openFileOutput()方法有两个重载函数,它们的签名分别是:
上面第二个重载函数中,mode为一个int类型的数据,这个一般使用Context对象中设置好的常量参数,有如下几个:
还有几个方法需要特别注意一下,这几个方法对于文件关系提供了更好的支持,配合上面介绍的方式,就可以对文件的数据进行常规的CRUD操作(增删改查),方法如下:
讲了这么多,下面通过一个简单的Demo来演示一下上面提到的内容。在这个Demo中,指定文件名和内容,既可创建文件,并且可以对其内容进行追加、修改、删除、查询等操作。

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="file name:" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etInternalFilename"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Content:" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etInternalContent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnInternalSave"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="save" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnInternalDelete"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="delete" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnInternalAppend"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="append" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnInternalQuery"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="query" />
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 以一个ListView的形式展示当前程序内部存储路径下的所有文件 -->
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lvInternalData"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
内部存储的操作类,对其实现CRUD操作:

package com.example.internal;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyInternalStorage {
//需要保存当前调用对象的Context
private Context context;
public MyInternalStorage(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
/**
* 保存内容到内部存储器中
* @param filename 文件名
* @param content 内容
*/
public void save(String filename, String content) throws IOException {
// FileOutputStream fos=context.openFileOutput(filename,
// Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
File file = new File(context.getFilesDir(), filename);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(content.getBytes());
fos.close();
}
/**
* 通过文件名获取内容
* @param filename 文件名
* @return 文件内容
*/
public String get(String filename) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = context.openFileInput(filename);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len = fis.read(data)) != -1) {
baos.write(data, 0, len);
}
return new String(baos.toByteArray());
}
/**
* 以追加的方式在文件的末尾添加内容
* @param filename 文件名
* @param content 追加的内容
*/
public void append(String filename, String content) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = context.openFileOutput(filename,
Context.MODE_APPEND);
fos.write(content.getBytes());
fos.close();
}
/**
* 删除文件
* @param filename 文件名
* @return 是否成功
*/
public boolean delete(String filename) {
return context.deleteFile(filename);
}
/**
* 获取内部存储路径下的所有文件名
* @return 文件名数组
*/
public String[] queryAllFile() {
return context.fileList();
}
}
Activity代码:

package com.internalstorageactivity;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class InternalStorageActivity extends Activity {
private EditText etFilename, etContent;
private Button btnSave, btnQuery, btnDelete, btnAppend;
private ListView lvData;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
lvData = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lvInternalData);
lvData.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener(){
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
System.out.println("1");
ListView lv = (ListView) parent;
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = (ArrayAdapter<String>) lv
.getAdapter();
String filename = adapter.getItem(position);
etFilename.setText(filename);
MyInternalStorage myInternal = new MyInternalStorage(
InternalStorageActivity.this);
try {
String content = myInternal.get(filename);
etContent.setText(content);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
etFilename = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.etInternalFilename);
etContent = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.etInternalContent);
btnSave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnInternalSave);
btnSave.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
String filename = null;
String content = null;
public void onClick(View v) {
filename = etFilename.getText().toString();
content = etContent.getText().toString();
MyInternalStorage myInternal = new MyInternalStorage(
InternalStorageActivity.this);
try {
myInternal.save(filename, content);
Toast.makeText(InternalStorageActivity.this, "保存文件成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(InternalStorageActivity.this, "保存文件失败",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
btnAppend = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnInternalAppend);
btnAppend.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
String filename = null;
String content = null;
public void onClick(View v) {
filename = etFilename.getText().toString();
content = etContent.getText().toString();
MyInternalStorage myInternal = new MyInternalStorage(
InternalStorageActivity.this);
try {
myInternal.append(filename, content);
Toast.makeText(InternalStorageActivity.this, "保存内容追加成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(InternalStorageActivity.this, "文件内容追加失败",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
btnQuery = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnInternalQuery);
btnQuery.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
MyInternalStorage myInternal = new MyInternalStorage(
InternalStorageActivity.this);
String[] files = myInternal.queryAllFile();
ArrayAdapter<String> fileArray = new ArrayAdapter<String>(
InternalStorageActivity.this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, files);
lvData.setAdapter(fileArray);
Toast.makeText(InternalStorageActivity.this, "查询文件列表",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
btnDelete = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnInternalDelete);
btnDelete.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
String filename = etFilename.getText().toString();
;
MyInternalStorage myInternal = new MyInternalStorage(
InternalStorageActivity.this);
myInternal.delete(filename);
Toast.makeText(InternalStorageActivity.this, "删除文件成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
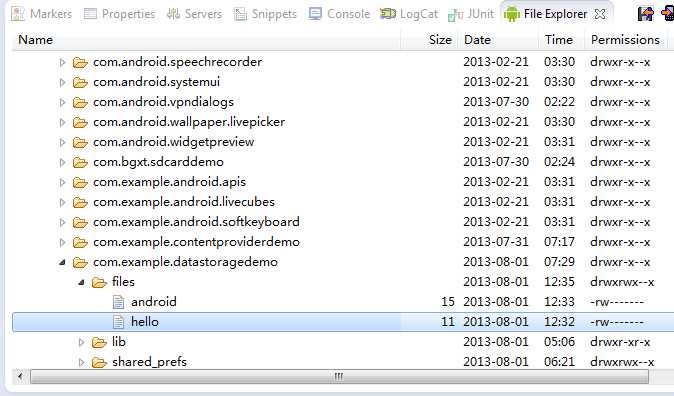
使用内部存储的方式进行数据持久化,文件的地址将保存在/data/data/<package_name>/files/路径下,上面创建了三个文件,最后删掉了一个,如果是使用的模拟器,可以直接在File Explorer中查看:
缓存(cache)
既然提到了内部存储,这里再简单的说说关于缓存文件(cache files)。cache files的操作与操作内部存储中的文件方式基本一致,只是获取文件的路径有说不同。如果需要使用缓存的方式进行数据持久话,那么需要使用Context.getCacheDir()方法获取文件保存的路径。
对于缓存文件而言,当设备内部内存存储空间不足的时候,Android会有自动删除的机制删除这些缓存文件,用来恢复可用空间,所以对于缓存文件而言,内容一般最好控制在1MB之下,并且也不要存放重要的数据,因为很可能下次去取数据的时候,已经被Android系统自动清理了。
External Storage
使用外部存储实现数据持久化,这里的外部存储一般就是指的是sdcard。使用sdcard存储的数据,不限制只有本应用访问,任何可以有访问Sdcard权限的应用均可以访问,而Sdcard相对于设备的内部存储空间而言,会大很多,所以一般比较大的数据,均会存放在外部存储中。
使用SdCard存储数据的方式与内部存储的方式基本一致,但是有三点需要注意的:
因为访问Sdcard的方式和访问内部存储的方式差不多,这里就展示一个Save的方法,用于保存文件,其他CRUD操作,这里就不再一一给出了。

public void saveToSdcard(String filename, String content) throws IOException {
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(Environment
.getExternalStorageState())) {
Log.i("main", "本设备有存储卡!");
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),
filename);
FileOutputStream fos = null;
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(content.getBytes());
fos.close();
}
}
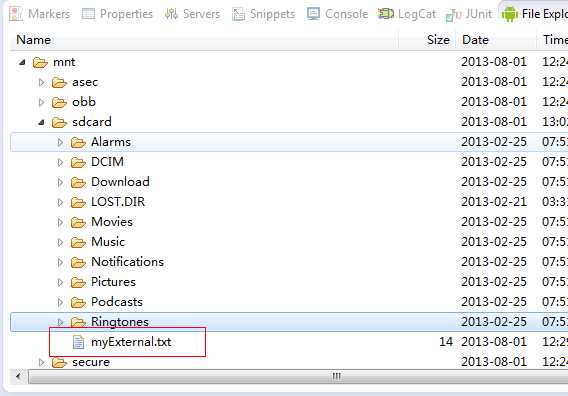
而如果使用SdCard存储文件的话,存放的路径在Sdcard的根目录下,如果使用模拟器运行程序的话,创建的文件在/mnt/sdcard/目录下:
补充:对于现在市面上很多Android设备,自带了一个大的存储空间,一般是8GB或16GB,并且又支持了Sdcard扩展,对于这样的设备,使用Enviroment.getExternalStorageDirectory()方法只能获取到设备自带的存储空间,对于另外扩展的Sdcard而言,需要修改路径。
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/weixing/p/3243115.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/summers/p/4320650.html