标签:
废话不多说,直接开始步骤!
1.创建一个Dynamic Web Project
2.在WEB-INF包下的lib文件夹中引入相关jar
commons-logging-1.1.1.jar jstl.jar spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-webmvc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar standard.jar
3.编写web.xml文件---该文件配置SpringMVC的主控制器DispatcherServlet,该主控负责拦截请求,并将请求分发给handler控制器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5"> <display-name>SpringMVC</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <!-- The front controller of this Spring Web application, responsible for handling all application requests --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- Map all requests to the DispatcherServlet for handling --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
4.编写springmvc-servlet.xml---该文件必须配置注解自动扫描包(否则注解无法使用),还必须配置视图解析器等等
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.jesse"></context:component-scan> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> </beans>
5.创建三个包,如以下图所实
说明:由于还没整合mybatis,所以先创建一些静态数据,只要方便操作就可以
以下是三个包中的代码:
package com.jesse.model; public class Employee { private Integer id; private String lastName; private String email; private Integer gender; private Department department; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public Integer getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Integer gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Department getDepartment() { return department; } public void setDepartment(Department department) { this.department = department; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + ", gender=" + gender + ", department=" + department + "]"; } public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender, Department department) { super(); this.id = id; this.lastName = lastName; this.email = email; this.gender = gender; this.department = department; } public Employee() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } }
package com.jesse.model; public class Department { private Integer id; private String departmentName; public Department() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Department(int i, String string) { this.id = i; this.departmentName = string; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getDepartmentName() { return departmentName; } public void setDepartmentName(String departmentName) { this.departmentName = departmentName; } @Override public String toString() { return "Department [id=" + id + ", departmentName=" + departmentName + "]"; } }
package com.jesse.dao; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.jesse.model.Department; import com.jesse.model.Employee; @Repository public class EmployeeDao { private static Map<Integer, Employee> employees = null; @Autowired private DepartmentDao departmentDao; static{ employees = new HashMap<Integer, Employee>(); employees.put(1001, new Employee(1001, "E-AA", "aa@163.com", 1, new Department(101, "D-AA"))); employees.put(1002, new Employee(1002, "E-BB", "bb@163.com", 1, new Department(102, "D-BB"))); employees.put(1003, new Employee(1003, "E-CC", "cc@163.com", 0, new Department(103, "D-CC"))); employees.put(1004, new Employee(1004, "E-DD", "dd@163.com", 0, new Department(104, "D-DD"))); employees.put(1005, new Employee(1005, "E-EE", "ee@163.com", 1, new Department(105, "D-EE"))); } private static Integer initId = 1006; public void save(Employee employee){ if(employee.getId() == null){ employee.setId(initId++); } employee.setDepartment(departmentDao.getDepartment(employee.getDepartment().getId())); employees.put(employee.getId(), employee); } public Collection<Employee> getAll(){ return employees.values(); } public Employee get(Integer id){ return employees.get(id); } public void delete(Integer id){ employees.remove(id); } public void update(Integer id,Employee employee){ Employee emp = employees.get(id); emp = employee; } }
package com.jesse.dao; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.jesse.model.Department; @Repository public class DepartmentDao { private static Map<Integer, Department> departments = null; static{ departments = new HashMap<Integer, Department>(); departments.put(101, new Department(101, "D-AA")); departments.put(102, new Department(102, "D-BB")); departments.put(103, new Department(103, "D-CC")); departments.put(104, new Department(104, "D-DD")); departments.put(105, new Department(105, "D-EE")); } public Collection<Department> getDepartments(){ return departments.values(); } public Department getDepartment(Integer id){ return departments.get(id); } }
6.首先先创建index.jsp,用于跳转显示所有数据(查询)
<a href="query">query</a>
以上代码在我们运行时显示query,只要我们点击,就会跳转到控制器中调用使用@RequestMapping("query")修饰的方法
@Controller public class EmployeeHandler { @Autowired private EmployeeDao employeeDao; /* @Autowired private DepartmentDao departmentDao; */ /** * 查询 */ @RequestMapping("query") public String query(Map<String,Object> map){ map.put("allEmployees", employeeDao.getAll()); return "list"; }
根据视图解析器的配置,当调用该方法后会跳转/WEB-INF/list.jsp页面,现在就来编写list.jsp页面,以让我们看到所有数据
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <table border="1" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0"> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>lastName</th> <th>email</th> <th>gender</th> <th>department</th> <th>Edit</th> <th>Delete</th> </tr> <c:forEach items="${requestScope.allEmployees}" var="emp"> <tr> <td>${emp.id}</td> <td>${emp.lastName}</td> <td>${emp.email}</td> <td>${emp.gender==0?‘Female‘:‘Male‘}</td> <td>${emp.department.departmentName}</td> <td><a href="edit/${emp.id}">Edit</a></td> <td><a href="delete/${emp.id}">Delete</a></td> </tr> </c:forEach> </table> <a href="readyData">Add Employee</a> </body> </html>
查询就写好了,让大家一起来看显示的结果,界面有点粗糙,但是是练习,所有漂亮美观与否无关紧要,把握时间才重要!
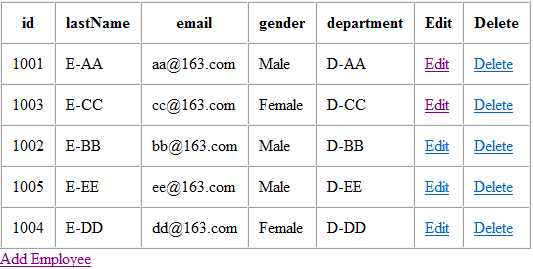
7.添加数据
在上图中,只要一点击Add Employee,就会跳转到添加页面,我们要做成以下图例的样子:
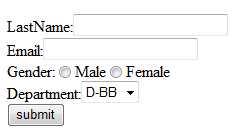
从上图看出,Department是下拉框,这意味着值必须从DepartmentDao取,所以我们得通过handler来取值
@RequestMapping("readyData")
public String readyData(Map<String,Object> map){
map.put("department", departmentDao.getDepartments());
map.put("employee", new Employee());
//map.put("actionType", "add");
return "addPage";
}
创建一个addPage.jsp的页面
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <%@page import="java.util.Map"%> <%@page import="java.util.HashMap"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> </head> <body> <form:form action="add" method="post" modelAttribute="employee"> <form:hidden path="id"/> LastName:<form:input path="lastName"/><br> Email:<form:input path="email"/><br> <% Map<String,String> gender = new HashMap(); gender.put("0", "Female"); gender.put("1","Male"); request.setAttribute("gender",gender); %> Gender:<form:radiobuttons path="gender" items="${gender}"/><br> Department:<form:select path="department.id" items="${department}" itemValue="id" itemLabel="departmentName"> </form:select><br> <input type="submit" value="submit"> </form:form> </body> </html>
也许大家注意到了,为什么方法中要存放一个空的Employee对象--->map.put("employee", new Employee()); 而addPage.jsp表单标签中也使用了该属性modelAttribute="employee",原因在于回显数据的功能,它认为我们肯定在更新数据时都要回显数据,所以必须有一个对象和表单内的属性一一对应,一个没对应都会异常,由于我们是添加数据,而不是回显数据,所有传入一个空的对象即可,当submit后,就会去寻找以下方法:
@RequestMapping("add")
public String addEmployee(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/query";
}
添加成功就重定向到查询结果集页面
8.删除数据
删除数据只要在方法中传入要删除数据的id,即可删除
在结果集点击Delete后,直接调用以下方法:
@RequestMapping(value="delete/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
employeeDao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/query";
}
同样的是删除成功后重定向到查询结果集页面
9.更新数据,也是整个增删改成最繁琐的,涉及到回显数据,以及@ModelAttribute的使用等等
在结果集点击Edit,跳转到修改数据页面,该页面之前是添加数据的页面,不同得是之前传的employee对象new出来的一个空对象,而现在传的employee是已查询出来的一个对象
回显数据:
@RequestMapping("edit/{id}")
public String updateEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
Map<String,Object> map){
map.put("employee", employeeDao.get(id));
map.put("actionType", "update");
map.put("department", departmentDao.getDepartments());
return "addPage";
}
说明:map中key值为employee的对象,是通过@PathVariable("id")获得的,就相当于根据id来获取结果集中的某一条记录,然后将该记录放入map中,并且这条记录必须和刚才的添加页面的modelAttribute="employee"的值是对应的,也就是表单标签具备回显功能,只要这两个值对应,自动把那条记录传入进来,结果为:
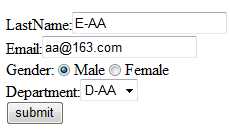
但是一个问题来了,更新页面其实是使用的之前的添加页面,而action值为add,这时需要进行修改,否则提交的都是add方法
在add方法和updateEmployee方法都放上一个actionType作为判断依据:
map.put("actionType", "update");
map.put("actionType","add");
然后再提交页面进行判断:
<form:form action="${requestScope.actionType==‘add‘?‘add‘:‘update‘}" method="post" modelAttribute="employee"> <form:hidden path="id"/> LastName:<form:input path="lastName"/><br> Email:<form:input path="email"/><br> <% Map<String,String> gender = new HashMap(); gender.put("0", "Female"); gender.put("1","Male"); request.setAttribute("gender",gender); %> Gender:<form:radiobuttons path="gender" items="${gender}"/><br> Department:<form:select path="department.id" items="${department}" itemValue="id" itemLabel="departmentName"> </form:select><br> <input type="submit" value="submit"> </form:form>
如果传入进来的actionType是update,调用控制器方法更新:
@RequestMapping("update")
public String update(@RequestParam(value="id") Integer id,Employee employee){
employeeDao.update(id, employee);
return "redirect:/query";
}
必须要注意的是:
必须使用@ModelAttribute编写一个方法,在update调用前查询出数据,然后将要更新的值直接更新,不更新的值保持之前查询数来的值,比如:
Employee[name=spring age=10 salary=2000]这时如果只更新salary的值,我们想要的结果如下:
Employee[name=spring age=10 salary=3000]
@ModelAttribute public void solvePro(@RequestParam(value="id",required=false)Integer id, Map<String,Object> map){ if (id != null) { map.put("employee", employeeDao.get(id)); } }
缺少以上方法,那更新结果就变成:
Employee[name=null age=null salary=3000]
整个增删改成的过程就是这样,可能表述的不是很清楚,欢迎提出您的困惑!
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Json1208/p/4332539.html