标签:
本篇将为大家总结JAVA中的线程机制,谈到线程,大家一定会问线程和进程有什么区别?刚接触进程时我也有这样的疑问,今天就为大家简单介绍一下进程和线程。进程(Process)是计算机中的程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位,是操作系统结构的基础;线程是程序内部的顺序控制流。它们的区别:
每个进程都有独立的代码和数据空间,进程间的切换会有较多的开销;线程可以看做轻量级的进程,同以进程共享代码块和数据空间,每个进程有独立的运行栈和程序计数器(PC),线程间切换开销小。
JAVA的线程是通过java.lang.Thread类来实现的,VM启动时会有一个由主方法(public static void main(){})所定义的线程。可以通过创建Thread的实例来创建新的线程。每个线程都是通过某个特定的Thread对象所对应的方法run()来完成其操作的,方法run()称为线程体。通过调用Thread的start()的方法来启动线程。
1、线程的创建与启动:
public class Th { /** * @param 线程的创建与启动 */ public static void main(String[] args) { //第一种线程创建方式 Runnable run = new myRunnable(); Thread th1 = new Thread(run); //第二种线程创建方式 myThread th2 = new myThread(); //线程启动 th1.start(); th2.start(); for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ System.out.println("主线程"); } } } class myRunnable implements Runnable{ public void run() { for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ System.out.println("线程一"); } } } class myThread extends Thread{ public void run() { for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ System.out.println("线程二"); } } }
2、线程的基本控制:
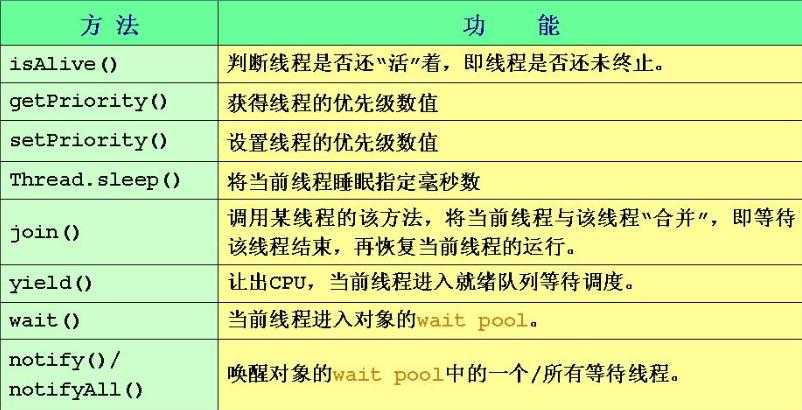
3、sleep、join、yield:
sleep(int time):休眠,当前线程休眠time毫秒
join():线程合并
yield:让出CPU,给其它线程执行的机会
实例代码:
public class SJY { /** * @param sleep、join、yield的使用 */ public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable run = new myRun(); Thread th1 = new Thread(run); myTh th2 = new myTh(); for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ if(i!=25){ System.out.println("主线程"); }else{ th1.yield();//让出CPU } } th1.start(); th2.start(); try { th1.join();//线程合并 th1.sleep(1000*3);//休眠3秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class myRun implements Runnable{ public void run() { for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ System.out.println("线程一"); } } } class myTh extends Thread{ public void run() { for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ System.out.println("线程二"); } } }
4、线程优先级:
JAVA提供了一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器根据线程的优先级决定应调那个线程来执行。线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1~10,一个线程的缺省优先级为5。Thread.MIN_PRIORITY=1;Thread.MAX_PRIORITY=10;Thread.NORM_PRIORITY=5。
使用下述方式获得线程的优先级和设置线程的优先级:int getPriority():获得线程的优先级,void setPriority(int newPriority):设置线程的优先级
临时有点事外出,半个小时后为大家总结线程同步和锁的机制。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/AndroidJotting/p/4338408.html