标签:
NetworkComms是一款来自英国的C#语言编写的通信框架
NetworkComms通信框架默认使用的是protobuf.net序列化器
NetworkComms 通信框架还内置了 BinaryFormaterSerializer 序列化器,此序列化器是对.net框架自带的 BinaryFormatter 的封装使用。
在networkcomms v2版本中的BinaryFormaterSerializer代码如下:

#if WINDOWS_PHONE #else using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary; using System.IO; #if ANDROID using PreserveAttribute = Android.Runtime.PreserveAttribute; #elif iOS using PreserveAttribute = MonoTouch.Foundation.PreserveAttribute; #endif namespace DPSBase { /// <summary> /// DataSerializer that uses .Net <see cref="System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary.BinaryFormatter"/> to perform <see cref="object"/> serialization /// </summary> [DataSerializerProcessor(2)] public class BinaryFormaterSerializer : DataSerializer { static DataSerializer instance; /// <summary> /// Instance singleton used to access serializer instance. Use instead <see cref="DPSManager.GetDataSerializer{T}"/> /// </summary> [Obsolete("Instance access via class obsolete, use DPSManager.GetSerializer<T>")] public static DataSerializer Instance { get { if (instance == null) instance = GetInstance<BinaryFormaterSerializer>(); return instance; } } #if ANDROID || iOS [Preserve] #endif private BinaryFormaterSerializer() { } #region ISerialize Members /// <inheritdoc /> protected override void SerialiseDataObjectInt(Stream ouputStream, object objectToSerialise, Dictionary<string, string> options) { BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter(); formatter.Serialize(ouputStream, objectToSerialise); ouputStream.Seek(0, 0); } /// <inheritdoc /> protected override object DeserialiseDataObjectInt(Stream inputStream, Type resultType, Dictionary<string, string> options) { BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter(); return formatter.Deserialize(inputStream); } #endregion } } #endif
在networkcomms v2版本中,通信框架内部使用了protobuf.net序列化器,比如ConnectionInfo类

[ProtoContract] public class ConnectionInfo : IEquatable<ConnectionInfo> { /// <summary> /// The type of this connection /// </summary> [ProtoMember(1)] public ConnectionType ConnectionType { get; internal set; } /// <summary> /// We store our unique peer identifier as a string so that it can be easily serialised. /// </summary> [ProtoMember(2)] string NetworkIdentifierStr; [ProtoMember(3)] string localEndPointIPStr; //Only set on serialise [ProtoMember(4)] int localEndPointPort; //Only set on serialise bool hashCodeCacheSet = false; int hashCodeCache; /// <summary> /// True if the <see cref="RemoteEndPoint"/> is connectable. /// </summary> [ProtoMember(5)] public bool IsConnectable { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// The DateTime corresponding to the creation time of this connection object /// </summary> public DateTime ConnectionCreationTime { get; protected set; } /// <summary> /// True if connection was originally established by remote /// </summary> public bool ServerSide { get; internal set; } /// <summary> /// The DateTime corresponding to the creation time of this connection object /// </summary> public DateTime ConnectionEstablishedTime { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// The <see cref="IPEndPoint"/> corresponding to the local end of this connection. /// </summary> public IPEndPoint LocalEndPoint { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// The <see cref="IPEndPoint"/> corresponding to the remote end of this connection. /// </summary> public IPEndPoint RemoteEndPoint { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Describes the current state of the connection /// </summary> public ConnectionState ConnectionState { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Returns the networkIdentifier of this peer as a ShortGuid. If the NetworkIdentifier has not yet been set returns ShortGuid.Empty. /// </summary> public ShortGuid NetworkIdentifier { get { if (NetworkIdentifierStr == null || NetworkIdentifierStr == "") return ShortGuid.Empty; else return new ShortGuid(NetworkIdentifierStr); } } DateTime lastTrafficTime; object internalLocker = new object(); /// <summary> /// The DateTime corresponding to the time data was sent or received /// </summary> public DateTime LastTrafficTime { get { lock (internalLocker) return lastTrafficTime; } protected set { lock (internalLocker) lastTrafficTime = value; } } /// <summary> /// Private constructor required for deserialisation. /// </summary> #if iOS || ANDROID public ConnectionInfo() { } #else private ConnectionInfo() { } #endif /// <summary> /// Create a new ConnectionInfo object pointing at the provided remote <see cref="IPEndPoint"/> /// </summary> /// <param name="remoteEndPoint">The end point corresponding with the remote target</param> public ConnectionInfo(IPEndPoint remoteEndPoint) { this.RemoteEndPoint = remoteEndPoint; this.ConnectionCreationTime = DateTime.Now; } /// <summary> /// Create a new ConnectionInfo object pointing at the provided remote ipAddress and port. Provided ipAddress and port are parsed in to <see cref="RemoteEndPoint"/>. /// </summary> /// <param name="remoteIPAddress">IP address of the remote target in string format, e.g. "192.168.0.1"</param> /// <param name="remotePort">The available port of the remote target. /// Valid ports are 1 through 65535. Port numbers less than 256 are reserved for well-known services (like HTTP on port 80) and port numbers less than 1024 generally require admin access</param> public ConnectionInfo(string remoteIPAddress, int remotePort) { IPAddress ipAddress; if (!IPAddress.TryParse(remoteIPAddress, out ipAddress)) throw new ArgumentException("Provided remoteIPAddress string was not succesfully parsed.", "remoteIPAddress"); this.RemoteEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, remotePort); this.ConnectionCreationTime = DateTime.Now; } /// <summary> /// Create a connectionInfo object which can be used to inform a remote peer of local connectivity /// </summary> /// <param name="connectionType">The type of connection</param> /// <param name="localNetworkIdentifier">The local network identifier</param> /// <param name="localEndPoint">The localEndPoint which should be referenced remotely</param> /// <param name="isConnectable">True if connectable on provided localEndPoint</param> public ConnectionInfo(ConnectionType connectionType, ShortGuid localNetworkIdentifier, IPEndPoint localEndPoint, bool isConnectable) { this.ConnectionType = connectionType; this.NetworkIdentifierStr = localNetworkIdentifier.ToString(); this.LocalEndPoint = localEndPoint; this.IsConnectable = isConnectable; } /// <summary> /// Create a connectionInfo object for a new connection. /// </summary> /// <param name="serverSide">True if this connection is being created serverSide</param> /// <param name="connectionType">The type of connection</param> /// <param name="remoteEndPoint">The remoteEndPoint of this connection</param> internal ConnectionInfo(bool serverSide, ConnectionType connectionType, IPEndPoint remoteEndPoint) { this.ServerSide = serverSide; this.ConnectionType = connectionType; this.RemoteEndPoint = remoteEndPoint; this.ConnectionCreationTime = DateTime.Now; } /// <summary> /// Create a connectionInfo object for a new connection. /// </summary> /// <param name="serverSide">True if this connection is being created serverSide</param> /// <param name="connectionType">The type of connection</param> /// <param name="remoteEndPoint">The remoteEndPoint of this connection</param> /// <param name="localEndPoint">The localEndpoint of this connection</param> internal ConnectionInfo(bool serverSide, ConnectionType connectionType, IPEndPoint remoteEndPoint, IPEndPoint localEndPoint) { this.ServerSide = serverSide; this.ConnectionType = connectionType; this.RemoteEndPoint = remoteEndPoint; this.LocalEndPoint = localEndPoint; this.ConnectionCreationTime = DateTime.Now; } [ProtoBeforeSerialization] private void OnSerialise() { lock (internalLocker) { localEndPointIPStr = LocalEndPoint.Address.ToString(); localEndPointPort = LocalEndPoint.Port; } } [ProtoAfterDeserialization] private void OnDeserialise() { IPAddress ipAddress; if (!IPAddress.TryParse(localEndPointIPStr, out ipAddress)) throw new ArgumentException("Failed to parse IPAddress from localEndPointIPStr", "localEndPointIPStr"); LocalEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, localEndPointPort); } /// <summary> /// Marks the connection as establishing /// </summary> internal void NoteStartConnectionEstablish() { lock(internalLocker) { if (ConnectionState == ConnectionState.Shutdown) throw new ConnectionSetupException("Unable to mark as establishing as connection has already shutdown."); if (ConnectionState == ConnectionState.Establishing) throw new ConnectionSetupException("Connection already marked as establishing"); else ConnectionState = ConnectionState.Establishing; } } /// <summary> /// Set this connectionInfo as established. /// </summary> internal void NoteCompleteConnectionEstablish() { lock (internalLocker) { if (ConnectionState == ConnectionState.Shutdown) throw new ConnectionSetupException("Unable to mark as established as connection has already shutdown."); if (!(ConnectionState == ConnectionState.Establishing)) throw new ConnectionSetupException("Connection should be marked as establishing before calling CompleteConnectionEstablish"); if (ConnectionState == ConnectionState.Established) throw new ConnectionSetupException("Connection already marked as establised."); ConnectionState = ConnectionState.Established; ConnectionEstablishedTime = DateTime.Now; if (NetworkIdentifier == ShortGuid.Empty) throw new ConnectionSetupException("Unable to set connection established until networkIdentifier has been set."); } } #region Modify 修改 private bool reconnectFlag = false; /// <summary> /// 是否为重连接模式 /// </summary> public bool ReconnectFlag { get { return reconnectFlag; } set { reconnectFlag = value; } } /// <summary> /// Note this connection as shutdown /// </summary> internal void NoteConnectionShutdown() { lock (internalLocker) ConnectionState = ConnectionState.Shutdown; //添加以下代码 连接信息类的初始状态为非重连模式 触发连接状态改变事件 if (reconnectFlag == false) { StateChanged.Raise(this, new StringEventArgs("连接出现异常")); } } //添加状态改变事件 public event EventHandler<StringEventArgs> StateChanged; #endregion /// <summary> /// Update the localEndPoint information for this connection /// </summary> /// <param name="localEndPoint"></param> internal void UpdateLocalEndPointInfo(IPEndPoint localEndPoint) { lock (internalLocker) { hashCodeCacheSet = false; this.LocalEndPoint = localEndPoint; } } /// <summary> /// During a connection handShake we might be provided with more update information regarding endPoints, connectability and identifiers /// </summary> /// <param name="handshakeInfo"><see cref="ConnectionInfo"/> provided by remoteEndPoint during connection handshake.</param> /// <param name="remoteEndPoint">The correct remoteEndPoint of this connection.</param> internal void UpdateInfoAfterRemoteHandshake(ConnectionInfo handshakeInfo, IPEndPoint remoteEndPoint) { lock (internalLocker) { NetworkIdentifierStr = handshakeInfo.NetworkIdentifier.ToString(); RemoteEndPoint = remoteEndPoint; LocalEndPoint.Address = handshakeInfo.LocalEndPoint.Address; IsConnectable = handshakeInfo.IsConnectable; } } /// <summary> /// Updates the last traffic time for this connection /// </summary> internal void UpdateLastTrafficTime() { lock (internalLocker) lastTrafficTime = DateTime.Now; } /// <summary> /// Replaces the current networkIdentifier with that provided /// </summary> /// <param name="networkIdentifier">The new networkIdentifier for this connectionInfo</param> public void ResetNetworkIdentifer(ShortGuid networkIdentifier) { NetworkIdentifierStr = networkIdentifier.ToString(); } /// <summary> /// A connectionInfo object may be used across multiple connection sessions, i.e. due to a possible timeout. /// This method resets the state of the connectionInfo object so that it may be reused. /// </summary> internal void ResetConnectionInfo() { lock (internalLocker) { ConnectionState = ConnectionState.Undefined; } } /// <summary> /// Compares this <see cref="ConnectionInfo"/> object with obj and returns true if obj is ConnectionInfo and both the <see cref="NetworkIdentifier"/> and <see cref="RemoteEndPoint"/> match. /// </summary> /// <param name="obj">The object to test of equality</param> /// <returns></returns> public override bool Equals(object obj) { lock (internalLocker) { var other = obj as ConnectionInfo; if (((object)other) == null) return false; else return this == other; } } /// <summary> /// Compares this <see cref="ConnectionInfo"/> object with other and returns true if both the <see cref="NetworkIdentifier"/> and <see cref="RemoteEndPoint"/> match. /// </summary> /// <param name="other"></param> /// <returns></returns> public bool Equals(ConnectionInfo other) { lock (internalLocker) return this == other; } /// <summary> /// Returns left.Equals(right) /// </summary> /// <param name="left">Left connectionInfo</param> /// <param name="right">Right connectionInfo</param> /// <returns>True if both are equal, otherwise false</returns> public static bool operator ==(ConnectionInfo left, ConnectionInfo right) { if (((object)left) == ((object)right)) return true; else if (((object)left) == null || ((object)right) == null) return false; else { if (left.RemoteEndPoint != null && right.RemoteEndPoint != null) return (left.NetworkIdentifier.ToString() == right.NetworkIdentifier.ToString() && left.RemoteEndPoint.Equals(right.RemoteEndPoint)); else return (left.NetworkIdentifier.ToString() == right.NetworkIdentifier.ToString()); } } /// <summary> /// Returns !left.Equals(right) /// </summary> /// <param name="left">Left connectionInfo</param> /// <param name="right">Right connectionInfo</param> /// <returns>True if both are different, otherwise false</returns> public static bool operator !=(ConnectionInfo left, ConnectionInfo right) { return !(left == right); } /// <summary> /// Returns NetworkIdentifier.GetHashCode() ^ RemoteEndPoint.GetHashCode(); /// </summary> /// <returns>The hashcode for this connection info</returns> public override int GetHashCode() { lock (internalLocker) { if (!hashCodeCacheSet) { if (RemoteEndPoint != null) hashCodeCache = NetworkIdentifier.GetHashCode() ^ RemoteEndPoint.GetHashCode(); else hashCodeCache = NetworkIdentifier.GetHashCode(); hashCodeCacheSet = true; } return hashCodeCache; } } /// <summary> /// Returns a string containing suitable information about this connection /// </summary> /// <returns>A string containing suitable information about this connection</returns> public override string ToString() { string returnString = "[" + ConnectionType.ToString() + "] "; if (ConnectionState == ConnectionState.Established) returnString += LocalEndPoint.Address + ":" + LocalEndPoint.Port.ToString() + " -> " + RemoteEndPoint.Address + ":" + RemoteEndPoint.Port.ToString() + " (" + NetworkIdentifier + ")"; else { if (RemoteEndPoint != null && LocalEndPoint != null) returnString += LocalEndPoint.Address + ":" + LocalEndPoint.Port.ToString() + " -> " + RemoteEndPoint.Address + ":" + RemoteEndPoint.Port.ToString(); else if (RemoteEndPoint != null) returnString += "Local -> " + RemoteEndPoint.Address + ":" + RemoteEndPoint.Port.ToString(); else if (LocalEndPoint != null) returnString += LocalEndPoint.Address + ":" + LocalEndPoint.Port.ToString() + " " + (IsConnectable ? "Connectable" : "NotConnectable"); } return returnString.Trim(); } }
在NetworkComms V3版本中,为了更好的兼容性和对解除对protobuf.net序列化器的依赖,已经在框架内部使用了显式的序列化,而不再使用Protobuf.net序列化器。
显式的序列化方式大致如下:
byte[] conTypeData = BitConverter.GetBytes((int)ConnectionType); data.Add(conTypeData); byte[] netIDData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(NetworkIdentifierStr); byte[] netIDLengthData = BitConverter.GetBytes(netIDData.Length); data.Add(netIDLengthData); data.Add(netIDData);
言归正传,看一下如何使用BinaryFormatter序列化器
第一步,定义3个工程文件
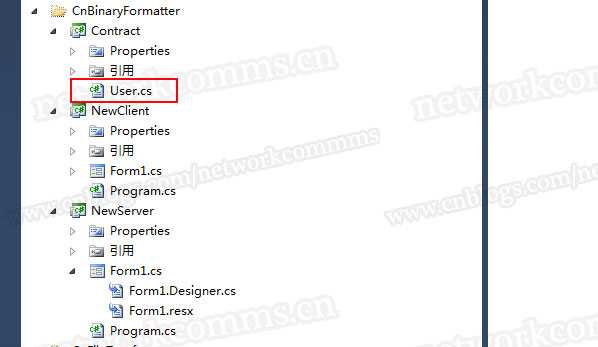
上图中的User类是契约类,用于传递数据
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace Contract { [Serializable] public class User { public string UserName { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } } }
第二步:服务器端
开始监听:
IPEndPoint thePoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(txtIP.Text), int.Parse(txtPort.Text)); TCPConnection.StartListening(thePoint, false); button1.Text = "监听中"; button1.Enabled = false;
定义序列化器:
SendReceiveOptions sro = new SendReceiveOptions(DPSManager.GetDataSerializer<BinaryFormaterSerializer>(), null, null);
注册消息类型的处理方法
NetworkComms.AppendGlobalIncomingPacketHandler<User>("ReqMessage", IncomingLoginRequest, sro);
具体的处理方法:
private void IncomingLoginRequest(PacketHeader header, Connection connection, User user) { string resMessage = user.UserName + "欢迎您"; connection.SendObject("ResMessage", resMessage); }
第三步:客户端
连接服务器:
//给连接信息对象赋值 connInfo = new ConnectionInfo(txtIP.Text, int.Parse(txtPort.Text)); //如果不成功,会弹出异常信息 newTcpConnection = TCPConnection.GetConnection(connInfo); button1.Enabled = false; button1.Text = "连接成功";
序列化器
SendReceiveOptions sro = new SendReceiveOptions(DPSManager.GetDataSerializer<BinaryFormaterSerializer>(), null, null);
提交数据并获取返回信息
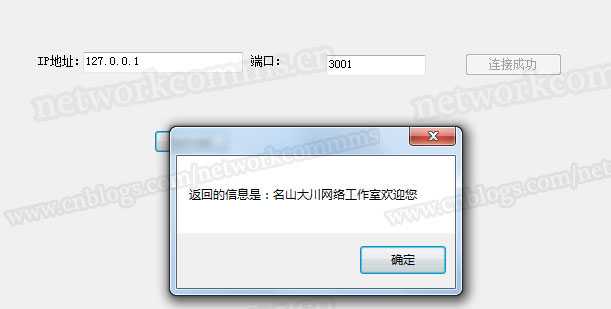
User theUser = new User(); theUser.UserName = "名山大川网络工作室"; string resMsg = newTcpConnection.SendReceiveObject<string>("ReqMessage", "ResMessage", 5000, theUser, sro, sro); MessageBox.Show("返回的信息是:" + resMsg);
本Demo源码 (含通信框架networkcomms2.31源码)
www.networkcomms.cn编辑
NetworkComms c#通信框架之使用BinaryFormatter序列化器进行网络通信
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/networkcomms/p/4342416.html