标签:
开始本篇总结之前,首先聊一聊上一篇中存在的一点小问题,上上篇总结数据库创建表时,存在一个问题,name、year、form好像属于关键字,不能做为表的属性,所以大家注意一下,在创建表时保证表的属性不存在冲突,故而上一篇中关于sql语句的地方大家需要修改一下表的属性名。
下面开始本篇关于JSP与MYSQL的交互连接,为了方便总结,我将以创建一个学生信息管理系统为目标,本篇就以登录功能的实现为主体进行总结。
1、创建管理员表:
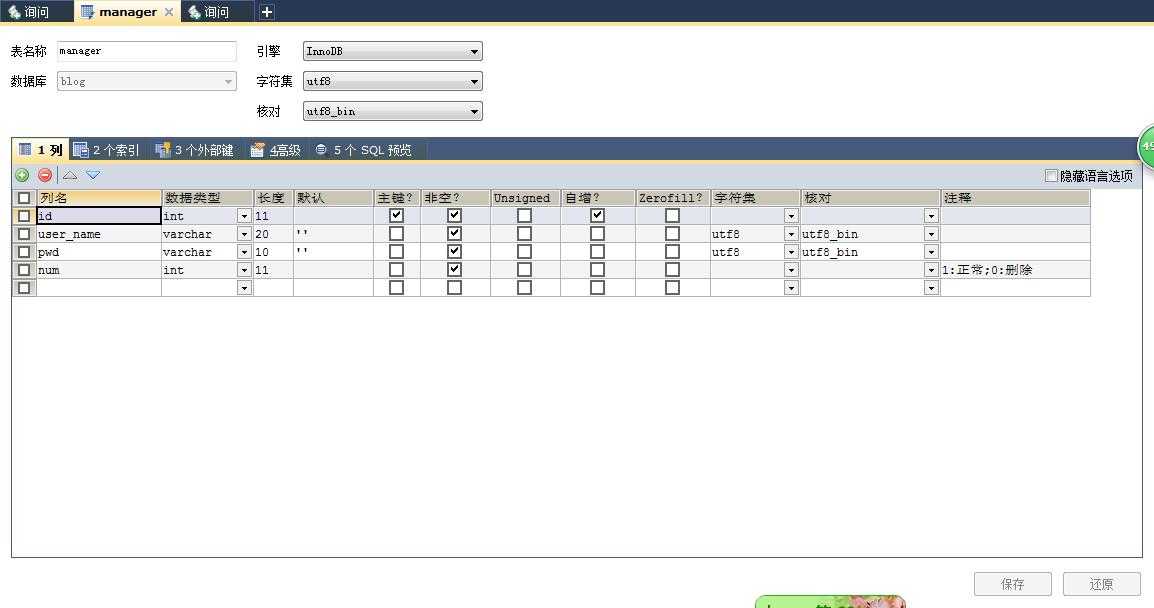
2、创建一个管理员类:
public class Manager { private int id; private String name ; private String password; private int key; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public int getKey() { return key; } public void setKey(int key) { this.key = key; } }
3、添加用户名、密码判断方法:
public class ManagerMaImp { //登录验证 public boolean getByName(String name, String password){ System.out.println(name+" "+password); boolean flag = false; Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; conn = DBO.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from manager where user_name=‘"+name+"‘ and pwd=‘"+password+"‘ and num="+1; try { st = conn.createStatement(); rs = st.executeQuery(sql); if(rs.next()){ flag = true; } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return flag; } }
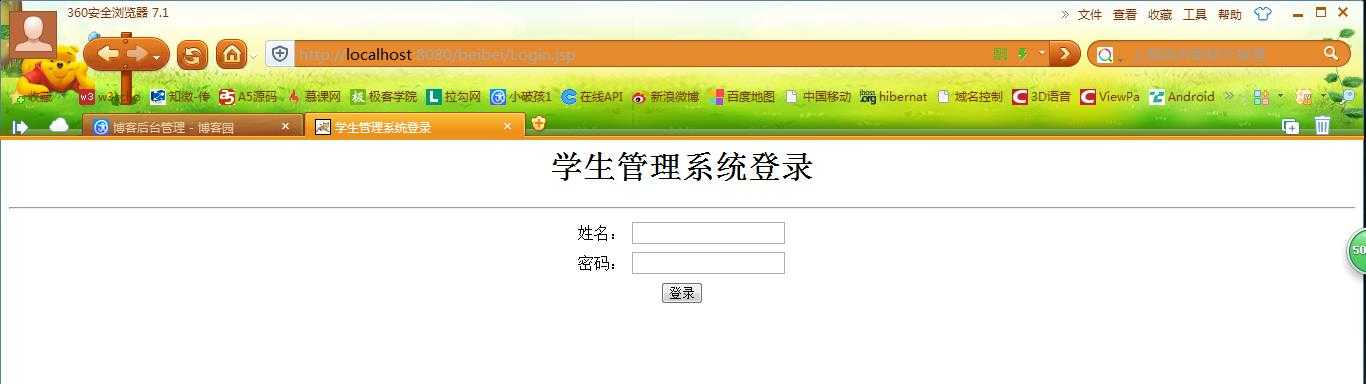
4、设计登录JSP页面:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>学生管理系统登录</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> </head> <body> <center> <h1>学生管理系统登录</h1> <hr/> <form action="login" method="post" > <table> <tr> <td>姓名:</td><td><input type="text" name="name" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>密码:</td><td><input type="password" name="pwd" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit" value="登录"/></td> </tr> </table> </form> </center> </body> </html>
效果图:
5、用于身份判断的select:
public class login extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(request, response); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); String name = request.getParameter("name"); String password = request.getParameter("pwd"); ManagerMaImp mmi = new ManagerMaImp(); boolean flag = mmi.getByName(name, password); if(flag){ StudentMaImp smi = new StudentMaImp(); List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>(); list = smi.getAll(); request.setAttribute("list", list); request.getRequestDispatcher("All.jsp").forward(request, response); }else{ response.sendRedirect("Login.jsp"); } } }
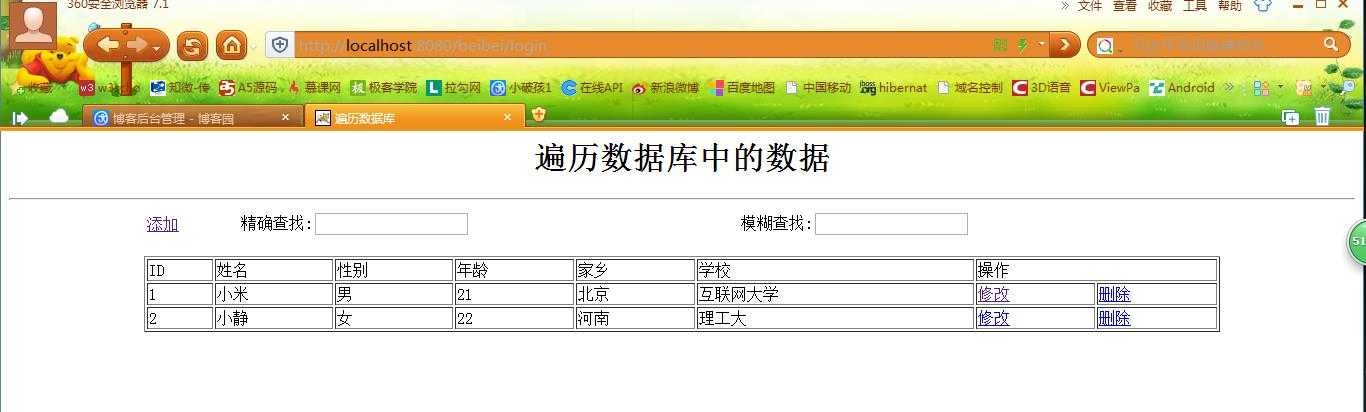
6、主界面(All.jsp):
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@page import="com.mysql.jsp.student.Student"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>遍历数据库</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> </head> <body> <% List<Student> list = (List<Student>)request.getAttribute("list"); %> <center> <h1>遍历数据库中的数据</h1> <hr/> <form action="get" method="post"> <table width="80%"> <tr> <td><a href="Add.jsp">添加</a></td><td> </td><td>精确查找:<input type="text" name="queding"/></td><td> </td><td>模糊查找:<input type="text" name="mohu"/></td> </tr> </table> </form> <table border="1" width="80%"> <TR> <TD>ID</TD><td>姓名</td><td>性别</td><td>年龄</td><td>家乡</td><td>学校</td><td colspan="2">操作</td> </TR> <% if(list.size()!=0){ for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){ Student student = list.get(i); %> <tr><TD><%=student.getId() %></TD><td><%=student.getName() %></td><td><%if(student.getSex()==1){ %>男<%}else{ %>女<%} %></td><td><%=student.getYear() %></td><td><%=student.getFrom() %></td><td><%=student.getSchool() %></td><td><a href="getId?id=<%=student.getId() %>">修改</a></td><td><a href="del?id=<%=student.getId() %>">删除</a></td></tr> <% } } %> </table> </center> </body> </html>
效果图:
本篇总结:本篇提到了select,JSP就是通过select与后台数据库进行交互的,我们上一篇总结的增删改查方法,将会在接下来的几篇一一为大家实现具体的使用。在主界面JSP代码中,你一定看到了很多:<%%>,我们可以在<%添加JAVA代码%>。
下一篇将系统为大家总结增、删、改的具体操作。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/AndroidJotting/p/4345106.html