标签:
MIT的算法导论公开课,很多年前就看到了,一直没有坚持去看,最近找暑假实习,面试基本都是算法,只好抽时间去狂刷leetcode,也借着这个机会希望把这个视频看完,把算法的基本功打扎实,这个公开课讲得还是挺不错的。
之前学习其他东西的时候,记了很多笔记,最后都丢了,想再翻看的时候已经找不到,于是想到把学习笔记放到博客上,这样方便以后自己查询。
公开课视频地址:http://open.163.com/special/opencourse/algorithms.html
第一节:课程简介及算法分析
第一集视频一半的时间都是给学生讲课程要求和作业情况的,剩下的才讲了点干货,以Insertion Sort和Merge Sort为切入点,讲解算法分析。
Insertion Sort:
Pseudocode
Insertion (A, n) // Sorts A[1, ... , n] for j ← 2 to n do key ← A[j] i ← j - 1 while i > 0 and A[i] > key do A[i+1] ← A[i] i ← i - 1 A[i+1] ← key
Example:
8 2 4 9 3 6
2 8 4 9 3 6
2 4 8 9 3 6
2 4 8 9 3 6
2 3 4 8 9 6
2 3 4 6 8 9
Running Time:
Kinds of analysis
Worst-case (usually)
T(n) = max time on any input of size n
Average-case (sometimes)
T(n) = expected time over all input of size n
(Need assumption of statistic distribution)
Best-case (bogus)
Cheat
What is insertion sort‘s worst time?
Depends on compater
——relative speed (on same machine)
——absolute speed (on different machine)
BIG IDEA! —— asymptotic analysis
Asymptotic notation
θ - notation Drop low-order terms and ignore leading constants
Ex. 3n3+90n2-5n+6046 = θ(n3)
As n → ∞, θ(n2) algorithm always beats a θ(n3) algorithm.
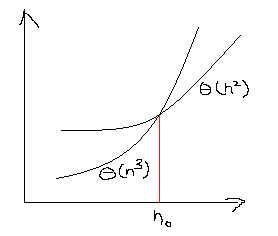 Sometimes, n0 may be too big so that a low-speed algorithm would be better.
Sometimes, n0 may be too big so that a low-speed algorithm would be better.
Insertion Sort Analysis
Worst-case: input reverse sorted
T(n) = ![]() =θ(n2)
=θ(n2)
Is insertion Sort fast?
Merge Sort Analysis
Merge sort A[1, ..., n] 1. If n = 1, done. -------------------------- T(n) 2. Recursively sort -------------------------- θ(1) A[1, ..., n/2] and A[n/2 + 1, ..., n] ----- 2T(n/2) 3. Merge 2 sorted list ----------------- θ(n)
Key subroutine: Merge
For example, two sorted list:
2 7 13 20
1 9 11 12
compare 2 and 1, choose 1 [1]
comapre 2 and 9, choose 2 [1, 2]
comapre 7 and 9, choose 7 [1, 2, 7]
comapre 13 and 9, choose 9 [1, 2, 7, 9]
comapre 13 and 11, choose 11 [1, 2, 7, 9, 11]
comapre 13 and 12, choose 12 [1, 2, 7, 9, 11, 12]
put 13 and 20 to the end [1, 2, 7, 9, 11, 12, 13, 20]
Time = θ(n) on n totoal elements
Recurrence
T(n) = θ(1), if n = 1 (usually omit it)
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + θ(n)
Recursive tree for T(n) = 2T(n/2) + cn
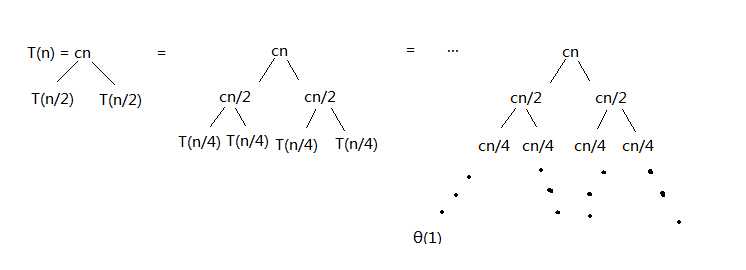
The height of this tree is lgn, the number of leavers is n, the subtotal of each depth is cn, So the total time is (cn)lgn+θ(n)
Omit the constant c and low-order θ(n), T(n) = θ(nlgn).
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/binarylu/p/4377024.html