标签:
Map
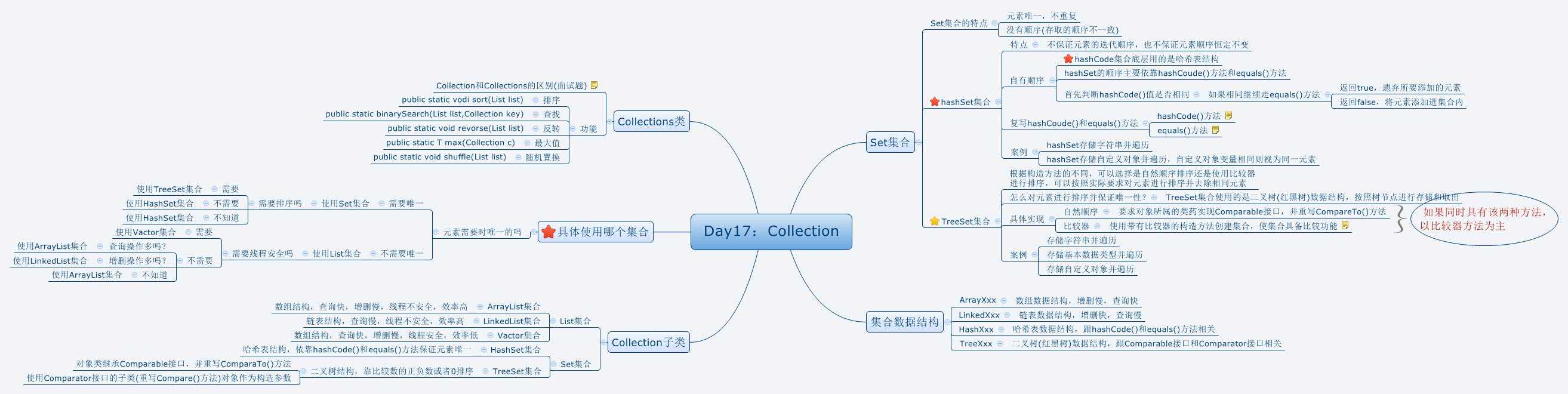
Map:是(键值对)双列形式集合,键必须唯一,不能重复,值是可以重复的;是夫妻对的集合
Collection:是单列值的集合,List集合值可重复,Set值不可重复,是光棍集合。
Map功能:
A:增加功能
V put(K key,V value):当key在集合中不存在时,添加元素;当key在集合存在时候,替换元素。
B:删除功能
void clear():清除所有键值对数据。
V remove(Object key):根据指定的键删除键值对。
C:判断功能
boolean containsKey(Object key):判断指定的键是否在集合中存在
boolean containsValue(Object vlaue):判断指定的值是否在集合中存在
boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
D:获取功能
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():键值对对象的集合。
Object get(Object key):根据键获取值
Set<K> keySet():所有键的集合
Collection<V> values():所有值的集合
E:长度功能
int size()
Map遍历:
一、第一种方式:【丈夫找妻子】
A:获取所有的键;
B:根据键,获取对应的值。
二、第二种方式:【通过结婚证找丈夫、妻子】
A:获取关系集合,Set<集合关系> entrySet()
B:迭代器,增强for循环,获取关系集合;
C:获取键、值 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
TreeMap存储自定义对象并遍历【重点】-----集合的整理
HashMap与Hashtable的区别:
A:Hashtable线程安全,效率低;不允许null键和值
B:HashMap线程不安全,效率高;允许null键和值
统计字符串中每一个字符出现的次数:
A:获取字符串中每一个字符:字符串转字符数组
B:定义Map集合:
Map<Character,Integer>
C:用每一个字符map中匹配
Map的嵌套
获取字符串中每一个字符出现的次数:
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.util.Set; 4 import java.util.TreeMap; 5 6 /** 7 * 有一个字符串: "cbxzbvavdvgd" 要求获取字符串中 每一个字母出现次数:"a(1)b(2)c(1)d(2)g(1)v(3)x(1)z(1)" 8 * 9 */ 10 public class CountDemo { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 字符串变字符数组 13 String s = "cbxzbvavdvgd"; 14 char[] charArr = s.toCharArray(); 15 16 // 创建TreeMap 17 TreeMap<Character, Integer> tm = new TreeMap<Character, Integer>(); 18 19 // 遍历数组,将元素压入TreeMap 20 for (int i = 0; i < charArr.length; i++) { 21 if (tm.get(charArr[i]) == null) { 22 tm.put(charArr[i], 1); 23 } else { 24 tm.put(charArr[i], (tm.get(charArr[i]) + 1)); 25 } 26 } 27 // 遍历数组,进行输出 28 System.out.println(tm); 29 Set<Character> set = tm.keySet(); 30 for(Character ch:set){ 31 Integer in = tm.get(ch); 32 System.out.println(ch+"**"+in); 33 } 34 } 35 }
Map的遍历
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.util.Map; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 import java.util.TreeMap; 6 7 /** 8 * 9 * 创建一个TreeMap,存储5对元素,,字符串做为键,Student做为值.然后遍历集合. 10 完成需求并思考,如果使用TreeMap集合存储学生对象,并且去除其中的重复元素,该怎么做 11 调换key和value值 12 * 13 */ 14 public class TreeMapDemo2 { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 17 TreeMap<Student,String> tm = new TreeMap<Student,String>(); 18 19 Student s1 = new Student("张无忌",21); 20 Student s2 = new Student("石敢当",22); 21 Student s3 = new Student("萧峰",23); 22 Student s4 = new Student("李连杰",24); 23 Student s5 = new Student("甄子丹",25); 24 25 tm.put(s1,"1"); 26 tm.put(s2,"2"); 27 tm.put(s3,"3"); 28 tm.put(s4,"4"); 29 tm.put(s5,"5"); 30 tm.put(s5,"6");//键相同,值不同【值替换】 31 tm.put(s2,"1");//值相同,键不同 32 33 //第一种遍历 34 Set<Student> studentSet = tm.keySet(); 35 36 for(Student stu:studentSet){ 37 String str = tm.get(stu); 38 System.out.println(stu.getName()+"***"+stu.getAge()+"***"+str); 39 } 40 System.out.println("-------------------------------------"); 41 42 //第二种遍历 43 //Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 44 Set<Map.Entry<Student,String>> husbandSet = tm.entrySet(); 45 for(Map.Entry<Student,String> me:husbandSet){ 46 Student keyStudent = me.getKey(); 47 String valueStr= me.getValue(); 48 System.out.println(keyStudent.getName()+"***"+keyStudent.getAge()+"***"+valueStr);//默认复写toString()方法 49 } 50 51 } 52 }
Map嵌套
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 import java.util.TreeSet; 6 7 8 9 /** 10 * 11 * 需求 12 * 用HashMap的key来存预热班和就业班 13 * 用value的位置来存ArrayList集合, 14 * ArrayList集合中再来存Student对象.Student对象中再来存数据. 15 * 第一步:实现简单的HashMap嵌套 16 * czbk 17 * yr 18 * 01 zhangsan 19 * 02 lisi 20 * jy 21 * 01 wangwu 22 * 02 zhaoliu 23 * 第二步:实现修改 24 */ 25 public class MapCollectionDemo2 { 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 /* 28 //创建对象 29 HashMap<String,HashMap<String,String>> czbk = new HashMap<String,HashMap<String,String>>(); 30 //创建元素对象 31 HashMap<String,String> yr = new HashMap<String,String>(); 32 yr.put("01","zhangsan"); 33 yr.put("02","lisi"); 34 35 HashMap<String,String> jy = new HashMap<String,String>(); 36 jy.put("01","wangwu"); 37 jy.put("02","zhaoliu"); 38 39 //添加元素 40 czbk.put("yr", yr); 41 czbk.put("jy", jy); 42 43 //遍历 44 Set<String> czbkKeys = czbk.keySet(); 45 for(String czbkKey :czbkKeys){ 46 HashMap<String,String> czbkvalue = czbk.get(czbkKey); 47 System.out.println(czbkKey); 48 Set<String> bjKeys = czbkvalue.keySet(); 49 for(String bjKey:bjKeys){ 50 String bjValue = czbkvalue.get(bjKey); 51 System.out.println("\t"+bjKey+"\t"+bjValue); 52 } 53 } 54 */ 55 56 //优化后效果 57 //创建对象 58 HashMap<String,TreeSet<Student>> czbk = new HashMap<String,TreeSet<Student>>(); 59 //创建元素对象 60 61 TreeSet<Student> yr = new TreeSet<Student>(); 62 yr.add(new Student("01","zhangsan")); 63 yr.add(new Student("02","lisi")); 64 65 TreeSet<Student> jy = new TreeSet<Student>(); 66 jy.add(new Student("01","wangwu")); 67 jy.add(new Student("02","zhaoliu")); 68 69 //添加元素 70 czbk.put("yr", yr); 71 czbk.put("jy", jy); 72 73 //遍历 74 Set<String> czbkKeys = czbk.keySet(); 75 for(String czbkKey:czbkKeys){ 76 System.out.println(czbkKey); 77 TreeSet<Student> ts = czbk.get(czbkKey); 78 for(Student stu:ts){ 79 System.out.println("\t"+stu.getName()+"***"+stu.getId()); 80 } 81 } 82 83 } 84 }
其中使用Student类:
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 /** 3 * 标准学生类 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ 8 //姓名 9 private String name; 10 //学号 11 private String id; 12 public Student() { 13 super(); 14 } 15 public Student(String name, String id) { 16 super(); 17 this.name = name; 18 this.id = id; 19 } 20 public String getName() { 21 return name; 22 } 23 public void setName(String name) { 24 this.name = name; 25 } 26 public String getId() { 27 return id; 28 } 29 public void setId(String id) { 30 this.id = id; 31 } 32 @Override 33 public int compareTo(Student s) { 34 int num = this.getId().compareTo(s.getId()); 35 int num1 = (num==0)?(this.getName().compareTo(s.getName())):num; 36 return num1; 37 } 38 39 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhidianhcuan/p/4393679.html