标签:
国际化:internationalization即I18N。
举例:
本科高校的网站,一般的都有中文和英文两种页面风格。因此将这种根据不同用户群体显示不同的页面风格的方式称之为页面的国际化。
翻译 VS 国际化
翻译:Chrome
国际化:主要做的是页面的显示信息的国际化,至于文件等其他的资源是无法进行国际化。
1 国际化的原理
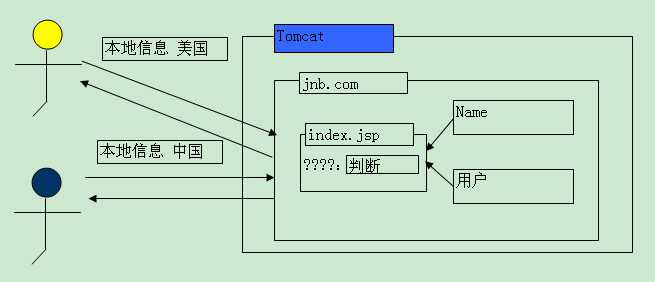
Locale通过静态属性获取区域对象。
全部使用properties配置文件进行实现。但是文件名需要按照指定的规则进行书写。
规范: 基本名_语言名.properties
基本名是随意的,语言名是固定可以参考浏览器的语言。
ResourceBundle 的静态方法static ResourceBundle getBundle(String baseName,
Locale locale)
绑定资源的原理:获取资源基本名和区域语言名锁定资源名。
String getString(String key)
一 体验
1. 编写两个如下的资源文件
greet_zh.properties
hello=\u4F60\u597D
greet_en.properties
hello=Hello
2. 实现一个如下的java类
public static void main(String[] args) { // 获取本地区域信息 Locale locale = Locale.US; // 绑定资源 ResourceBundle bundler = ResourceBundle.getBundle("cn.itcast.ps.greet", locale); System.out.println(bundler.getString("hello")); }
总结:
如果没有可视化编辑器那么直接使用native2ascii.exe进行中文的转码。
1 日期国际化
DateFormat该类主要提供的是以不同的区域显示不同的日期格式。
根据区域信息格式化和解析日期数据。
static DateFormat getDateInstance(int style, Locale aLocale) à 获取日期实例
static DateFormat getTimeInstance(int style, Locale aLocale) à 获取时间实例
static DateFormat getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle, int timeStyle, Locale aLocale)à 获取日期和时间
Date parse(String source) à 解析日期
String format(Object obj) à 格式化日期
举例:
获取日期和时间
Long 2013年1月21日 下午04时16分41秒 January 21, 2013 4:17:27 PM CST FULL 2013年1月21日 星期一 下午04时18分19秒 CST Monday, January 21, 2013 4:18:37 PM CST MEDIUM 2013-1-21 16:19:33 Jan 21, 2013 4:19:45 PM SHORT 13-1-21 下午4:20 1/21/13 4:20 PM
练习:将以下的字符号串解析为日期对象。
String date = “2013年1月21日 下午4:20”;解析为日期对象。
Long Short
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //I18NDate(); String date = "2013年1月21日 下午4:20"; Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG, DateFormat.SHORT, locale); Date new_date = format.parse(date); System.out.println(new_date); }
数字国际化
NumberFormat
static NumberFormat getInstance(Locale inLocale) ? 国际化普通数字 static NumberFormat getCurrencyInstance(Locale inLocale) ? 国际化货币 static NumberFormat getPercentInstance(Locale inLocale) ? 国际化百分比
国际化
String format(Object obj)
Number parse(String source)
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 获取国际化普通数字的对象 Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getInstance(locale); String str = format.format(123456.789); System.out.println(str); locale = Locale.CHINA; format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale); str = format.format(123456.789); System.out.println(str); locale = Locale.CHINA; format = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance(locale); str = format.format(0.789); System.out.println(str); }
练习:将String str = "¥123.7";解析为数字。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //I18NNumber(); String str = "¥123.7"; Locale locale = Locale.CHINA; NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale); Number num = format.parse(str); System.out.println(num.doubleValue()*3); }
动态文本国际化
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ String str = "On {0}, a hurricance destroyed {1} houses and caused {2} of damage."; String date = "Jul 3, 1998 12:30 PM"; DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, DateFormat.SHORT, Locale.US); Date new_date = format.parse(date); Double money = new Double(1E7); NumberFormat numfor = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.CHINA); String new_str = numfor.format(money); Object[] os = new Object[]{new_date,new Integer(77),new_str} MessageFormat msg_for = new MessageFormat(str,Locale.CHINA); String for_str = msg_for.format(os); System.out.println(for_str); }
以上的动态文本国际化每次需要将所有需要国际化的数据单独的进行国际化好之后逐一的进行填充。因此比较繁琐,可以使用以下的模式字符串。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ String pattern = "At {0, time, short} on {0, date}, a hurricance destroyed " + "{1} houses and caused {2, number, currency} of damage."; String datetimeString = "Jul 3, 1998 12:30 PM"; DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, DateFormat.SHORT, Locale.US); Date new_date = format.parse(datetimeString); Object[] os = new Object[]{new_date,new Integer(77),new Double(1E7)}; MessageFormat msg_for = new MessageFormat(pattern,Locale.US); String for_str = msg_for.format(os); System.out.println(for_str); }
<body>
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="in" %>
<in:setLocale value="${pageContext.request.locale}"/>
<in:setBundle basename="cn.itcast.login.greet" var="bund" scope="page"/>
<form action="">
<table align="center" border="1">
<tr>
<td><in:message bundle="${pageScope.bund}" key="name"/></td>
<td><input type="text" name="uname"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><in:message bundle="${pageScope.bund}" key="psw"/></td>
<td><input type="text" name="uname"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<input type="submit" value=‘<in:message bundle="${pageScope.bund}" key="submit"/>‘>
<input type="reset" value=‘<in:message bundle="${pageScope.bund}" key="reset"/>‘>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
后期在Struts2.x中需要使用struts的国际化标签。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhenghongxin/p/4436625.html