标签:
Spring框架支持事务管理的核心是事务管理器抽象,对于不同的数据访问框架(如Hibernate)通过实现策略接口PlatformTransactionManager,从而能支持各种数据访问框架的事务管理
PlatformTransactionManager接口定义如下:
public interface PlatformTransactionManager { TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException; void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException; void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException; }
方法介绍
getTransaction()
返回一个已经激活的事务或创建一个新的事务(根据给定的TransactionDefinition类型参数定义的事务属性),返回的是TransactionStatus对象代表了当前事务的状态,其中该方法抛出TransactionException(未检查异常)表示事务由于某种原因失败。
commit()
用于提交TransactionStatus参数代表的事务,具体语义请参考Spring Javadoc;
rollback()
用于回滚TransactionStatus参数代表的事务,具体语义请参考Spring Javadoc。
TransactionDefinition接口定义如下:
public interface TransactionDefinition { int getPropagationBehavior(); int getIsolationLevel(); int getTimeout(); boolean isReadOnly(); String getName(); }
方法介绍
getPropagationBehavior()
返回定义的事务传播行为;
getIsolationLevel()
返回定义的事务隔离级别;
getTimeout()
返回定义的事务超时时间;
isReadOnly()
返回定义的事务是否是只读的;
getName()
返回定义的事务名字。
TransactionStatus接口定义如下:
public interface TransactionStatus extends SavepointManager { boolean isNewTransaction(); boolean hasSavepoint(); void setRollbackOnly(); boolean isRollbackOnly(); void flush(); boolean isCompleted(); }
方法介绍
isNewTransaction()
返回当前事务状态是否是新事务; hasSavepoint()
返回当前事务是否有保存点; setRollbackOnly()
设置当前事务应该回滚; isRollbackOnly(()
返回当前事务是否应该回滚; flush()
用于刷新底层会话中的修改到数据库,一般用于刷新如Hibernate/JPA的会话,可能对如JDBC类型的事务无任何影响; isCompleted()
当前事务否已经完成。
学习Spring的事务配置只要把思路理清,还是比较好掌握的
Spring配置文件中关于事务配置总是由三个组成部分,分别是DataSource、TransactionManager和代理机制这三部分,无论哪种配置方式,一般变化的只是代理机制这部分。
DataSource、TransactionManager这两部分只是会根据数据访问方式有所变化,比如使用Hibernate进行数据访问时,DataSource实际为SessionFactory,TransactionManager的实现为HibernateTransactionManager
具体如下图:

图解画出了Spring的一些内置事物管理器。Spring本身提供了许多内置事物管理器的实现,常用的有以下几种:
DataSourceTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.jdbc.datasource包中,数据源事务管理器,提供对单个javax.sql.DataSource事务管理,用于Spring JDBC抽象框架、iBATIS或MyBatis框架的事务管理;
JdoTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.orm.jdo包中,提供对单个javax.jdo.PersistenceManagerFactory事务管理,用于集成JDO框架时的事务管理;
JpaTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.orm.jpa包中,提供对单个javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory事务支持,用于集成JPA实现框架时的事务管理;
HibernateTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.orm.hibernate3包中,提供对单个org.hibernate.SessionFactory事务支持,用于集成Hibernate框架时的事务管理;该事务管理器只支持Hibernate3+版本,且Spring3.0+版本只支持Hibernate 3.2+版本;
JtaTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.transaction.jta包中,提供对分布式事务管理的支持,并将事务管理委托给Java EE应用服务器事务管理器;
OC4JjtaTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.transaction.jta包中,Spring提供的对OC4J10.1.3+应用服务器事务管理器的适配器,此适配器用于对应用服务器提供的高级事务的支持;
WebSphereUowTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.transaction.jta包中,Spring提供的对WebSphere 6.0+应用服务器事务管理器的适配器,此适配器用于对应用服务器提供的高级事务的支持;
WebLogicJtaTransactionManager
位于org.springframework.transaction.jta包中,Spring提供的对WebLogic 8.1+应用服务器事务管理器的适配器,此适配器用于对应用服务器提供的高级事务的支持。
Spring不仅提供这些事务管理器,还提供对如JMS事务管理的管理器等,Spring提供一致的事务抽象。

一、声明对本地事务的支持:
a)JDBC及iBATIS、MyBatis框架事务管理器
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean>
通过dataSource属性指定需要事务管理的单个javax.sql.DataSource对象。
b)Jdo事务管理器
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jdo.JdoTransactionManager"> <property name="persistenceManagerFactory" ref="persistenceManagerFactory"/> </bean>
通过persistenceManagerFactory属性指定需要事务管理的javax.jdo.PersistenceManagerFactory对象。
c)Jpa事务管理器
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager"> <property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"/> </bean>
通过entityManagerFactory属性指定需要事务管理的javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory对象。
还需要为entityManagerFactory对象指定jpaDialect属性,该属性所对应的对象指定了如何获取连接对象、开启事务、关闭事务等事务管理相关的行为。
<bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"> …… <property name="jpaDialect" ref="jpaDialect"/> </bean> <bean id="jpaDialect" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaDialect"/>
d)Hibernate事务管理器
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/> </bean>
二、Spring对全局事务的支持:
a)Jta事务管理器
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.0.xsd"> <jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="jdbc/test"/> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager"> <property name="transactionManagerName" value=" java:comp/TransactionManager"/> </bean> </beans>
“dataSource”Bean表示从JNDI中获取的数据源,而txManager是JTA事务管理器,其中属性transactionManagerName指定了JTA事务管理器的JNDI名字,从而将事务管理委托给该事务管理器。
这只是最简单的配置方式,更复杂的形式请参考Spring Javadoc。
/** 篇章 */
根据代理机制的不同,总结了五种Spring事务的配置方式,配置文件如下:
首先看下UserDaoImpl
@Service public class UserDaoImpl{ @Autowired private JdbcTemplateDao jdbcTemplateDao; public void domain(){ jdbcTemplateDao.save(); int i = 2/0;//这里出错了,事务就会回滚,之前的save就无效了 jdbcTemplateDao.update(); jdbcTemplateDao.delete(); } } //main方法 String[] configLocations = new String[] {"applicationContext.xml"}; ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configLocations);
UserDaoImpl j = ctx.getBean(UserDaoImpl.class);
j.domain();
第一种方式:每个Bean都有一个代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" /> <property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" /> </bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> <!-- 配置DAO --> <bean id="userDaoTarget" class="com.bluesky.spring.dao.UserDaoImpl"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="userDao" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean"> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" /> <property name="target" ref="userDaoTarget" /> <property name="proxyInterfaces" value="com.bluesky.spring.dao.GeneratorDao" /> <!-- 配置事务属性 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
第二种方式:所有Bean共享一个代理基类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" /> <property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" /> </bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="transactionBase" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean" lazy-init="true" abstract="true"> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" /> <!-- 配置事务属性 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置DAO --> <bean id="userDaoTarget" class="com.bluesky.spring.dao.UserDaoImpl"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="userDao" parent="transactionBase" > <property name="target" ref="userDaoTarget" /> </bean> </beans>
第三种方式:使用拦截器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" /> <property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" /> </bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="transactionInterceptor" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" /> <!-- 配置事务属性 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator"> <property name="beanNames"> <list> <value>*Dao</value> </list> </property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>transactionInterceptor</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置DAO --> <bean id="userDao" class="com.bluesky.spring.dao.UserDaoImpl"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> </beans>
第四种方式:使用tx标签配置的拦截器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <context:annotation-config /> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bluesky" /> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" /> <property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" /> </bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="interceptorPointCuts" expression="execution(* com.bluesky.spring.dao.*.*(..))" /> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="interceptorPointCuts" /> </aop:config> </beans>
XML形式的事务配置<tx:method >的属性详解
| 属性 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
| propagation | Propagation枚举 | REQUIRED | 事务传播属性 |
| isolation | isolation枚举 | DEFAULT(所用数据库默认级别) | 事务隔离级别 |
| readOnly | boolean | false | 是否才用优化的只读事务 |
| timeout | int | -1 | 超时(秒) |
| rollbackFor | Class[] | {} | 需要回滚的异常类 |
| rollbackForClassName | String[] | {} | 需要回滚的异常类名 |
| noRollbackFor | Class[] | {} | 不需要回滚的异常类 |
| noRollbackForClassName | String[] | {} | 不需要回滚的异常类名 |
readOnly
事务属性中的readOnly标志表示对应的事务应该被最优化为只读事务。如果值为true就会告诉Spring我这个方法里面没有insert或者update,你只需要提供只读的数据库Connection就行了,这种执行效率会比read-write的Connection高,所以这是一个最优化提示。在一些情况下,一些事务策略能够起到显著的最优化效果,例如在使用Object/Relational映射工具(如:Hibernate或TopLink)时避免dirty checking(试图“刷新”)。
timeout
在属性中还有定义“timeout”值的选项,指定事务超时为几秒。一般不会使用这个属性。在JTA中,这将被简单地传递到J2EE服务器的事务协调程序,并据此得到相应的解释。
第五种方式:全注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <context:annotation-config /> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bluesky" /> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" /> <property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration" /> </bean> <!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> </beans>
此时在DAO上需加上@Transactional注解,如下
package com.bluesky.spring.dao; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.bluesky.spring.domain.User; @Transactional @Component("userDao") public class UserDaoImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements UserDao { public List<User> listUsers() { return this.getSession().createQuery("from User").list(); } }
/** 篇章 */
spring事物主要在spring* AOP类库中
事物配置介绍:
首先在/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml添加以下内容:(这里使用集成hibernate测试)
<!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory"> <ref bean="mySessionFactory"/> </property> </bean>
注:这是作为公共使用的事务管理器Bean。这个会是事先配置好的,不需各个模块各自去配。
下面就开始配置各个模块所必须的部分,在各自的applicationContext-XXX-beans.xml配置的对于事务管理的详细信息。
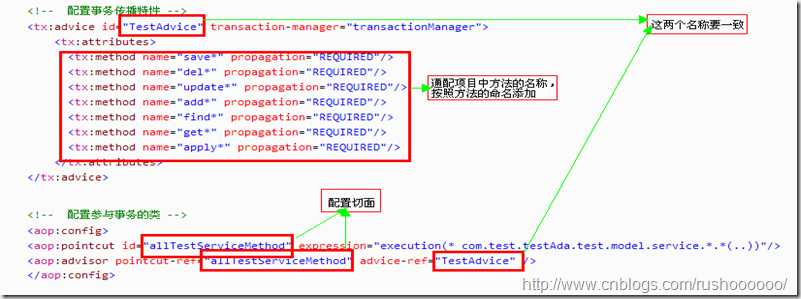
首先就是配置事务的传播特性,如下:
<!-- 配置事务传播特性 --> <tx:advice id="TestAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="del*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="get*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="apply*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置参与事务的类 --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="allTestServiceMethod" expression="execution(* com.test.testAda.test.model.service.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor pointcut-ref="allTestServiceMethod" advice-ref="TestAdvice" /> </aop:config>
需要注意的地方:
(1) advice(建议)的命名:由于每个模块都会有自己的Advice,所以在命名上需要作出规范,初步的构想就是模块名+Advice(只是一种命名规范)。 (2) tx:attribute标签所配置的是作为事务的方法的命名类型。 如<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> 其中*为通配符,即代表以save为开头的所有方法,即表示符合此命名规则的方法作为一个事务。 propagation="REQUIRED"代表支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择。 (3) aop:pointcut标签配置参与事务的类,由于是在Service中进行数据库业务操作,配的应该是包含那些作为事务的方法的Service类。 首先应该特别注意的是id的命名,同样由于每个模块都有自己事务切面,所以我觉得初步的命名规则因为 all+模块名+ServiceMethod。而且每个模块之间不同之处还在于以下一句: expression="execution(* com.test.testAda.test.model.service.*.*(..))" 其中第一个*代表返回值,第二*代表service下子包,第三个*代表方法名,“(..)”代表方法参数。 (4) aop:advisor标签就是把上面我们所配置的事务管理两部分属性整合起来作为整个事务管理。
图解:
spring事物类型详解
<prop key="load*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop>
<prop key="store*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
Spring中常用事务类型:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED--支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择。
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS--支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY--支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW--新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED--以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。
PROPAGATION_NEVER--以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
PROPAGATION_NESTED--如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则进行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。
对PROPAGATION_NESTED嵌套事务类型的补充
假设一个事物中嵌套了一个事物,有嵌套的事物为一级事物,嵌套在里面的暂称为二级事物;
1.当二级事物被rollback后,一级事物会不会被rollback?
答案是不回,二级事物的rollback只针对自己的操作。(但是最终一级事物还是回回滚,想看下一问题)
2.什么时候一级事务会commit,什么时候会被rollback呢?
主要看二级里面出现的情况,当所有的二级事务被commit了并且一级事务没有失败的操作,那整个事务就算是一个成功的事务,这种情况整个事务会被commit。
当任意一个二级事务没有被commit那整个事务就是失败的,整个事务会被roolback。
Spring中的四种声明式事务的配置
以下两个bean的配置是下面要用到的。
<!-- 定义事务管理器(声明式的事务) --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory"> <ref local="sessionFactory" /> </property> </bean> <!-- *******业务逻辑层(是对各个DAO层的正面封装)主要用到<<门面模式>>****** --> <bean id="fundService" class="com.jack.fund.service.serviceimpl.FundService"> <property name="operdao"> <ref bean="operatorDAO" /> </property> <property name="producedao"> <ref bean="fundProduceDAO" /> </property> <property name="customerdao"> <ref bean="customerDAO" /> </property> <property name="accountdao"> <ref bean="accountDAO" /> </property> <property name="fundaccountdao"> <ref bean="fundAccountDAO" /> </property> <property name="fundtransdao"> <ref bean="fundTransDAO" /> </property> </bean>
可能还有其他很多模块。<bean id="fundService"/>可能只是其中的模块。
第一种:配置声明式事务的方法如下。也是我们最常用的方法了,它适用于你的库表比较少的情况下。
<bean id="fundServiceDAOProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean"> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <property name="transactionManager"> <ref bean="transactionManager" /> </property> <!-- 此属性指定目标类本省是否是代理的对象,如果目标类没有实现任何类,就设为true代表自己 --> <property name="proxyTargetClass"> <value>false</value> </property> <property name="proxyInterfaces"> <value>com.jack.fund.service.IFundService</value> </property> <!-- 目标bean --> <property name="target"> <ref bean="fundService" /> </property> <!-- 配置事务属性 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="delete*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="add*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="update*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="save*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="find*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop> </props> </property> </bean>
以下可能还有其他的xxxServiceDAOProxy.大家可以看出针对每一个功能模块配置一个业务代理服务。如果模块多大话,就显得代码有点多了,发现他们只是稍微一点不一样。这时我们就应该想到继承的思想。用第二种方法。
第二种:配置声明式事务的方法如下。这种情况适合相对比较多的模块时使用。
<!-- 利用继承的思想简化配置,要把abstract="true" --> <bean id="transactionBase" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean" lazy-init="true" abstract="true"> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <property name="transactionManager"> <ref bean="transactionManager" /> </property> <!-- 配置事务属性 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="delete*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="add*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="update*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="save*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="find*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop> </props> </property> </bean>
而具体的模块可以简单的这样配置。只要指明它的parent(父类)就可以了。父类一般把abstract="true",因为在容器加载的时候不需要初始化,等到用的时候再有它的子类调用的时候,再去初始化。
<bean id="fundServiceDAOProxy" parent="transactionBase" > <property name="target"> <ref bean="fundService" /> </property> </bean>
这样配置的话,如果有多个像fundService这样模块时,可以少些很多重复的代码。
第三种:配置声明式事务的方法如下。主要利用BeanNameAutoProxyCreator自动创建事务代理
<bean id="transactionInterceptor" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor"> <property name="transactionManager"> <ref bean="transactionManager" /> </property> <!-- 配置事务属性 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="delete*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="add*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="update*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="save*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> <prop key="find*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator"> <property name="beanNames"> <list> <value>fundService</value> </list> </property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>transactionInterceptor</value> </list> </property> </bean>
这种方法主要利用了拦截器的原理。
前三种方法一般都必需指定具体的模块bean.如果模块过多话,比如一个大型的网站一般有几十个模块。我们就得考虑用第四种的配置方式了。自动创建事务代理的方式了。
第四种:配置声明式事务的方法如下。
<bean id="transactionInterceptor" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor"> <property name="transactionManager"> <ref bean="transactionManager" /> </property> <!-- 自动代理 --> <bean id="autoproxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator"> <!-- 可以是Service或DAO层(最好是针对业务层*Service) --> <property name="beanNames"> <list> <value>*Service</value> </list> </property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>transactionInterceptor</value> </list> </property> </bean>
自动代理还有一种用法就是结合正规表达式和advice使用。
<bean id="transactionInterceptor" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor"> <property name="transactionManager"> <ref bean="transactionManager" /> </property> </bean> <bean id="autoProxyCreator" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator" /> <bean id="regexpMethodPointcutAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="advice"> <ref bean="transactionInterceptor" /> </property> <property name="pattern"> <value>.*</value> </property> </bean>
这个方法可以针对具体的模块进行拦截并进行事务处理。
在你的实际项目中,你可以根据你的情况选用不同的方法。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hwaggLee/p/4439360.html