标签:
前一段时间,学习数据结构的各种算法,概念不难理解,只是被C++的指针给弄的犯糊涂,于是用java,web,javascript,分别去实现数据结构的各种算法。
二叉树的遍历,本分享只是以二叉树中的先序遍历为例进行说明,中序遍历和后序遍历,以此类推!
二叉树递归与非递归遍历的区别,虽然递归遍历,跟容易读懂,代码量少,运算快,但是却容易出现溢出的问题,所以所以非递归遍历,在处理千万级的运算量时会先的很有用处。
二叉树的先序遍历:先访问根节点,再访问先后访问左右节点。如图:
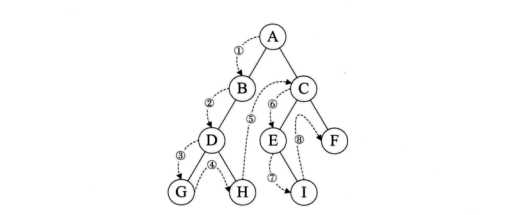
二叉树的递归遍历之java:
package rest;
//构造节点,生成一颗树
class Node
{
Node(String Letter){ //构造函数
value=Letter;
}
public Node left; //左节点
public Node right; //右节点
public String value;
}
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//以下是构建上图中的二叉树,从根节点起一层一层的构建
Node root = new Node("A");
Node first = new Node("B");
Node second = new Node("C");
Node third = new Node("D");
Node foth = new Node("E");
Node fifth = new Node("F");
Node sixth = new Node("G");
Node seventh = new Node("H");
Node eghit = new Node("I");
Node nineth = new Node("G");
//以下是建立二叉树之间的关系
root.left=first;
root.right=second;
first.left=third;
second.left=foth;
second.right=fifth;
third.right=seventh;
third.left=nineth;
foth.right=eghit;
// Node root.left.left = new Node("D");
Recursive(root);
}
//以下是二叉树递归遍历的主题代码算法函数
public static void Recursive(Node node){
if(node.value==""){
System.out.println("这是一颗空树!"); //测试根节点是否为空,并且为程序的出口
}else{
System.out.print(node.value);
}
if(node.left!=null){
Recursive(node.left); //递归左子树的节点
}
if(node.right!=null){
Recursive(node.right); //递归右子树的节点
}
}
}
打印查来的结果为:
run:
ABDGHCEIF成功构建 (总时间: 0 秒)
二叉树非递归遍历,不用栈使O(1)之java:
1 package rest;
2
3 //构造节点,生成一颗树
4 class Nod
5 {
6 Nod(String Letter){ //构造函数
7 value=Letter;
8 }
9 public Nod per; //为了实现不用栈,使O(1),记录他的父节点
10 public Nod left; //左节点
11 public Nod right; //右节点
12 public String value;
13 public int flag=0; //访问标志位
14 }
15 public class Cycles
16 {
17 public static void main(String[] args)
18 {
19 //以下是构建上图中的二叉树,从根节点起一层一层的构建
20 Nod root = new Nod("A");
21 Nod first = new Nod("B");
22 Nod second = new Nod("C");
23 Nod third = new Nod("D");
24 Nod foth = new Nod("E");
25 Nod fifth = new Nod("F");
26 Nod sixth = new Nod("G");
27 Nod seventh = new Nod("H");
28 Nod eghit = new Nod("I");
29 Nod set =new Nod("sdfsa");
30 //以下是建立二叉树之间的关系
31 root.left=first;
32 root.right=second;
33 first.per = root;
34 first.left=third;
35
36
37 second.per=root;
38 second.left=foth;
39 second.right=fifth;
40
41 third.per=first;
42 third.right=seventh;
43 third.left=sixth;
44
45 foth.per=second;
46 foth.right=eghit;
47 fifth.per=second;
48
49 sixth.per=third;
50 seventh.per=third;
51 eghit.per=foth;
52
53 if(root==null){
54 System.out.println("这是一颗空树");
55 }
56
57 Nod index=root;
58 while(index!=null){
59 if(index.flag==0){
60 System.out.print(index.value);
61
62 index.flag=1;
63 }
64 if(index.left!=null&&index.left.flag==0){
65 index=index.left;
66 }else{
67 if(index.right!=null&&index.right.flag==0){
68 index=index.right;
69 }else{
70 index = index.per; //回溯自己的父节点
71 }
72
73 }
74 }
75
76
77
78 }
79 }
run:
ABDGHCEIF成功构建 (总时间: 0 秒)
总结:我在调试这个的时候出现的几点问题:
我在回溯父节点的那段代码时,一开始尝试的是通过回溯父节点,然后再指向自己的子节点,判断是否为空,来测试代码是否运行到该行下,但是却行不通.
代码如下:
if(index.right==null){
System.out.print("代码可运行至此");
}else{
System.out.print("代码无法判断右节点");
}
但是结果却是,什么都没有显示,尼玛真的什么都没有显示。。。。我就无语了,好在不影响代码实现。
2.但是我在测试System.out.print(index.right.value);居然可以!居然可以!这一点还不太明白。
二叉树非递归遍历,使用栈之java:
既然要用到栈,那就要说明一下栈是什么???栈无非就是先进后出的数据结构,我们可以引进import java.util.Stack;但是也可以自己写。
栈主要的操作有
1.public Stack() 创建一个空堆栈类
2.public boolean empty() 带布尔返回值的函数,测试堆栈是否为空;
3.public pop() 弹出堆栈顶部的对象,并作为此函数的值返回该对象,输出 ,出栈操作
4.public push() 压栈操作
5.public peek() 查看堆栈顶部的对象,但不从堆栈中移除它。 起标记作用
6.public boolean full() 满栈
1 package rest;
2
3 /**
4 *
5 * @author 曹想-
6 */
7 class Stack
8 {
9 private Nod2 StackArr[] ;
10 private int top;
11 public Stack(){
12 this.top=-1; //之所以是以-1开始是因为数组是以0为开始
13 this.StackArr = new Nod2[50]; //限定长度为50
14 }
15 public void push(Nod2 index){
16 StackArr[++top]=index;
17 }
18 public Nod2 pop(){
19 return StackArr[top--]; //出栈操作
20 }
21 public boolean isempty(){ //判断是否为空
22 return this.top==-1;
23 }
24
25 }
26
27 class Nod2
28 {
29 Nod2(String Letter){ //构造函数
30 value=Letter;
31 }
32 public Nod2 left; //左节点
33 public Nod2 right; //右节点
34 public String value;
35 }
36
37 public class Test2{
38 public static void main(String arg[]){
39 //以下是构建上图中的二叉树,从根节点起一层一层的构建
40 Nod2 root = new Nod2("A");
41 Nod2 first = new Nod2("B");
42 Nod2 second = new Nod2("C");
43 Nod2 third = new Nod2("D");
44 Nod2 foth = new Nod2("E");
45 Nod2 fifth = new Nod2("F");
46 Nod2 sixth = new Nod2("G");
47 Nod2 seventh = new Nod2("H");
48 Nod2 eghit = new Nod2("I");
49 Nod2 set =new Nod2("sdfsa");
50 //以下是建立二叉树之间的关系
51 root.left=first;
52 root.right=second;
53
54 first.left=third;
55
56
57 second.left=foth;
58 second.right=fifth;
59
60 third.right=seventh;
61 third.left=sixth;
62
63
64 foth.right=eghit;
65
66
67
68 //以下是利用栈的实现
69 Stack st = new Stack();
70 if(root==null){
71 System.out.println("这是一颗空树");
72 }
73
74 Nod2 index = root;
75 while (index != null || !st.isempty()) { //如果index为空说明节点遍历完了,栈为空说明已经完成遍历
76 while (index != null) { //先遍历左子树,并打印节点,将节入栈
77 System.out.print(index.value);
78 st.push(index);
79 index = index.left;
80 }
81 if (!st.isempty()) { //将节点出栈,遍历右节点
82 index = st.pop();
83 index = index.right;
84 }
85 }
86 }
87 }
非递归栈的另一种算法:
Stack st = new Stack();
if(root==null){
System.out.println("这是一颗空树");
}
Nod2 index = root;
int n=9; //这里的n是节点的个数,由一开始输入节点的个数决定
while(n--!=0){
System.out.println(index.value); //输出遍历节点值
st.push(index); //将节点值入栈
if(index.left!=null){
index = index.left; //遍历左节点
}else{
while(!st.isempty()){ //栈不为空,则循环
Nod2 Tem = st.pop().right; //右节点不为空则设置右节点为index遍历
if(Tem!=null){
index =Tem;
break;
}
}
}
}
QQ:1689986723
欢迎批评指正!
数据结构二叉树的递归与非递归遍历之 实现可编译(1)java
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuqiandoudou/p/4503361.html