标签:
实现类图
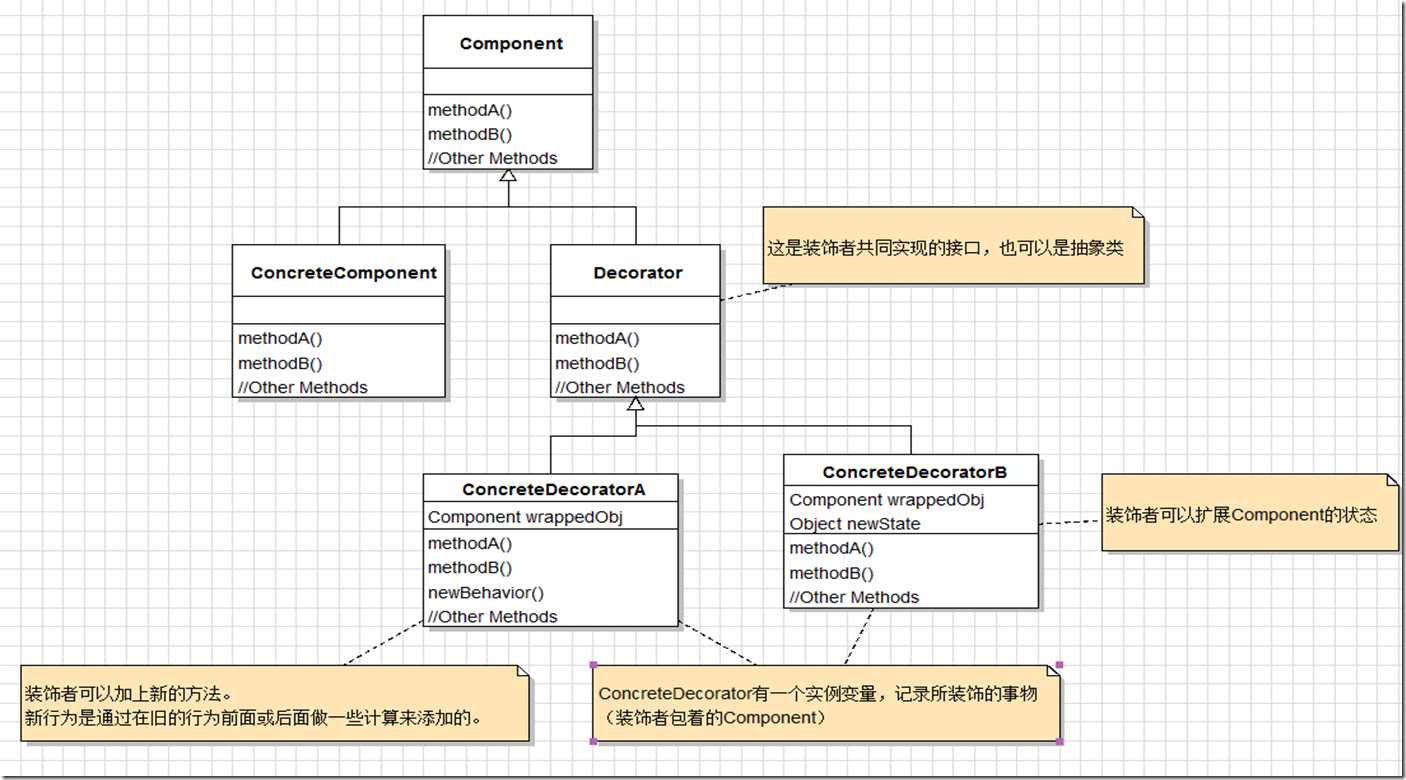
A 装饰者和被装饰对象有相同的超类型。(注意这是利用继承达到”类型匹配“,而不是利用继承获得”行为“,行为来自装饰者和基础组件,或者与其他装饰者之间的组合关系)
B 可以用一个或多个装饰者包装一个对象。
C 因为装饰者和被装饰者具有相同的类型,所以任何需要原始对象的场合,可以用装饰过的对象代替。
D 装饰者可以在所委托被装饰者的行为之前与/或之后,加上自己的行为,以达到特定的目的。
E 对象可以在任何时候被装饰,所以可以在运行时动态地、不限量地用你喜欢的装饰者来装饰对象interface Widget { void draw(); } // 1. "lowest common denominator"
class TextField implements Widget { // 3. "Core" class with "isa" rel
private int width, height;
public TextField( int w, int h ) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
public void draw() {
System.out.println( "TextField: " + width + ", " + height );
} }
// 2. Second level base class
abstract class Decorator implements Widget { // with "isa" relationship
private Widget wid; // 4. "hasa" relationship
public Decorator( Widget w ) { wid = w; }
public void draw() { wid.draw(); } // 5. Delegation
}
class BorderDecorator extends Decorator { // 6. Optional embellishment
public BorderDecorator( Widget w ) {
super( w );
}
public void draw() {
super.draw(); // 7. Delegate to base class
System.out.println( " BorderDecorator" ); // and add extra stuff
} }
class ScrollDecorator extends Decorator { // 6. Optional embellishment
public ScrollDecorator( Widget w ) {
super( w );
}
public void draw() {
super.draw(); // 7. Delegate to base class
System.out.println( " ScrollDecorator" ); // and add extra stuff
} }
//装饰者可以在所委托被装饰者的行为之前或者之后,加上自己的行为,以达到特定的目的
public class DecoratorDemo {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
// 8. Client has the responsibility to compose desired configurations
Widget aWidget = new BorderDecorator(
new BorderDecorator(
new ScrollDecorator(
new TextField( 80, 24 ))));
aWidget.draw();
} }对比python装饰模式实现的一个类似程序
def bread(func):
def wrapper():
print "</''''''\>"
func()
print "<\______/>"
return wrapper
def ingredients(func):
def wrapper():
print "#tomatoes#"
func()
print "~salad~"
return wrapper
@bread
@ingredients
def sandwich(food="--ham--"):
print food
if (__name__=="__main__"):
sandwich()
JAVA I/O类 就是利用装饰者模式来实现诸多的读取方式,InputStream是装饰者中的抽象组件。FilterInputStream是一个抽象装饰者,LIneNumberInputStream是一个具体装饰者,加上了计算行数的能力,BufferInputStream是一个加上缓冲输入功能和readline()方法的具体装饰者
下面一个例子是编写自己的Java I./O装饰器,把输入流内所有的大写字符转换成小写
import java.io.*;
class LowerCaseInputStream extends FilterInputStream{
public LowerCaseInputStream (InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
//必须实现两个read方法 一个针对字节 一个针对字节数组
public int read() throws IOException {
int c = super.read();
return (c == -1 ? c : Character.toLowerCase((char) (c)));
}
public int read(byte[] b,int offset,int len) throws IOException {
int result = super.read(b, offset, len);
for(int i =offset; i < offset + result ; i++){
b[i] = (byte)Character.toLowerCase((char)b[i]);
}
return result;
}
}
public class InputTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int c;
try{
InputStream in = new LowerCaseInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("test.txt") ) );
while((c = in.read() ) >= 0) {
System.out.print((char)c);
}
in.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u010786109/article/details/45844929