标签:
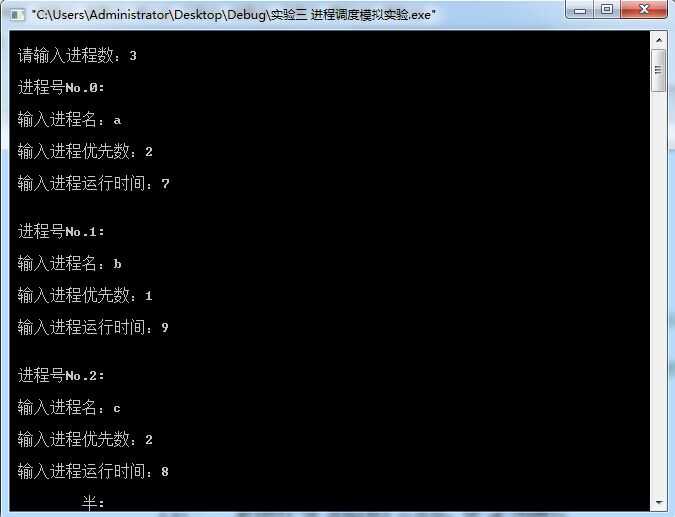
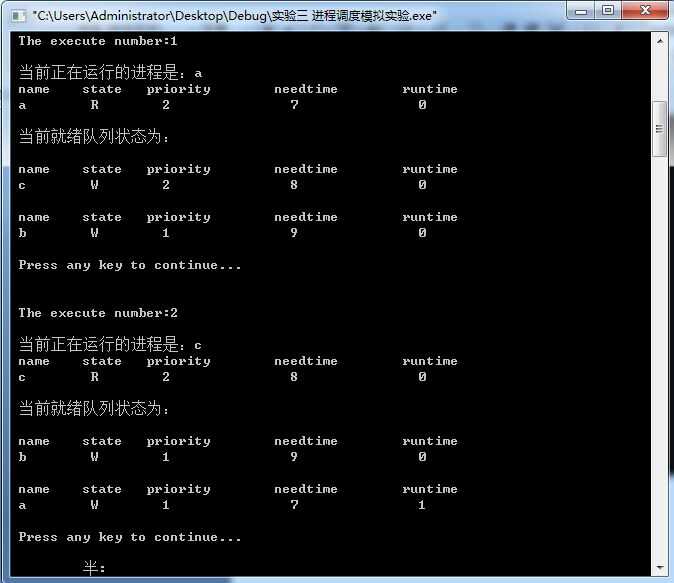
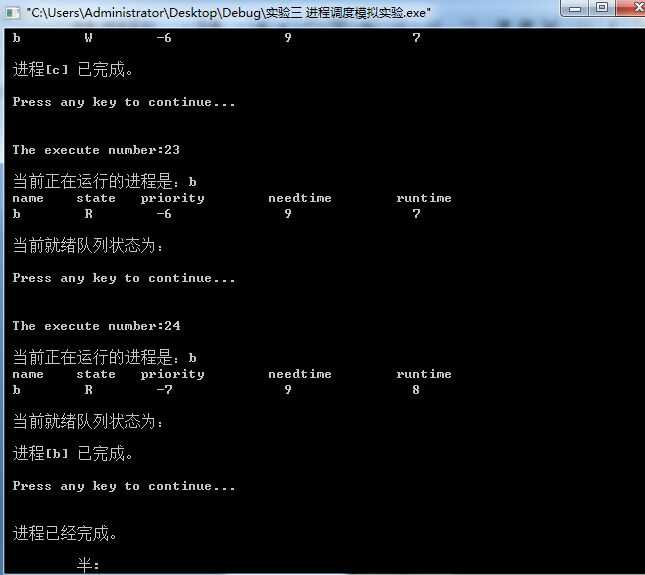
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define getpch(type)(type*)malloc(sizeof(type)) #define NULL 0 struct pcb{ //定义进程控制块PCB char name[10]; //进程名 char state; //状态 int priority; //优先级 int needtime; //运行所需时间 int rtime; //到达时间 struct pcb* link; }*ready=NULL,*p; typedef struct pcb PCB; sort() //建立对进程进行优先级排列顺序 { PCB *first,*second; int insert=0; if((ready==NULL)||((p->priority)>(ready->priority))) //优先级最大者,插入队首 { p->link=ready; ready=p; } else //进程比较优先级,插入适当的位置中 { first=ready; second=first->link; while(second!=NULL) { if((p->priority)>(second->priority)) //若插入进程比当前进程优先数大,插入到当前进程前面 { p->link=second; first->link=p; second=NULL; insert=1; } else //插入进程优先数最低,则插入到队尾 { first=first->link; second=second->link; } } if(insert==0) first->link=p; } } input() //建立进程控制块函数 { int i,num; printf("\n 请输入进程数:"); scanf("%d",&num); for(i=0;i<num;i++) { printf("\n 进程号No.%d:\n",i); p=getpch(PCB); printf("\n 输入进程名:"); scanf("%s",p->name); printf("\n 输入进程优先数:"); scanf("%d",&p->priority); printf("\n 输入进程运行时间:"); scanf("%d",&p->needtime); printf("\n"); p->rtime=0; p->state=‘W‘; p->link=NULL; sort(); //调用sort函数 } } int space() { int l=0; PCB *pr=ready; while(pr!=NULL) { l++; pr=pr->link; } return(l); } disp(PCB *pr) //建立进程显示函数,用于显示当前进程 { printf("\n name\t state\t priority\t needtime\t runtime \n"); printf(" %s\t",pr->name); printf(" %c\t",pr->state); printf(" %d\t\t",pr->priority); printf(" %d\t\t",pr->needtime); printf(" %d\t",pr->rtime); printf("\n"); } check() //建立进程查看函数 { PCB *pr; printf("\n 当前正在运行的进程是:%s",p->name); //显示当前运行进程 disp(p); pr=ready; printf("\n 当前就绪队列状态为:\n"); //显示就绪队列状态 while(pr!=NULL) { disp(pr); pr=pr->link; } } destroy() //建立进程撤销函数(进程运行结束,撤销进程) { printf("\n 进程[%s] 已完成。\n",p->name); free(p); } running() //建立进程就绪函数(进程运行时间到,置就绪状态) { (p->rtime)++; if(p->rtime==p->needtime) destroy(); //调用destroy函数 else { (p->priority)--; p->state=‘W‘; sort(); // 调用sort函数 } } main() //主函数 { int len,h=0; char ch; input(); len=space(); while((len!=0)&&(ready!=NULL)) { ch=getchar(); h++; printf("\n The execute number:%d \n",h); p=ready; ready=p->link; p->link=NULL; p->state=‘R‘; check(); running(); printf("\n Press any key to continue..."); ch=getchar(); } printf("\n\n 进程已经完成。\n"); ch=getchar(); }
总结:此次试验与上一次所做的实验有相似之处,故而实现起来相对来说比上一次实验简单一些。此次试验用到了指针、调度算法等等,加强了对它们的应用。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/summer--liumengyun/p/4520784.html