标签:
------- android培训、java培训、期待与您交流! ----------
由于字节流操作中文不是特别方便,所以,java就提供了转换流。
字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
编码表:计算机只能识别二进制数据,早期又来是电信号,为了方便应用计算机,让它可以识别各个国家的文字,就将各个国家的文字用数字来表示,并一一对应,形成一张表,就是编码表。
简单的说编码表就是由字符及其对应的数值组成的一张表。
常见的编码表:
ASCII:美国标准信息交换码,用1个字节的7位可以表示
ISO8859-1:拉丁码表,欧洲码表,用1个字节的8位表示
GBK2312:中国的中文编码表
GBK:中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号
GB18030:GBK的取代版本
BIG-5码 :通行于台湾、香港地区的一个繁体字编码方案,俗称“大五码”
Unicode:国际标准码,融合了多种文字,所有的文字都用2个字节表示,Java中使用的就是Unicode码表
UTF-8:最多用3个字节来表示一个字符(能用一个字节表示的就用一个字节,一个表示不了就用两个,最多用三个字节)
1.public String(byte[] bytes,String charsetName)throws UnsupportedEncodingException
通过使用指定的 charset 解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。
2.public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName)throws UnsupportedEncodingException
使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
字符串→字节数组 编码:把看得懂的变成看不懂的
字节数组→字符串 解码:把看不懂的变成看得懂的
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException 4 { 5 String s = "你好"; 6 //编码,使用GBK码表将此字符串编码为 byte序列 7 byte[] bys = s.getBytes("GBK"); 8 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys));//[-60, -29, -70, -61] 9 10 //解码,使用GBK码表解码指定的byte数组 11 String ss = new String(bys,"GBK"); 12 System.out.println(ss);//你好 13 } 14 }
Windows平台默认编码为GBK
OutputStreamWriter 字符输出流
1.public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out)
创建使用默认字符编码的 OutputStreamWriter。
2.public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName)throws UnsupportedEncodingException
创建使用指定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。
例:
//默认编码GBK OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStrea("D:\\aa.txt")); osw.write("中国"); osw.close();
21.05 转换流InputStreamReader的使用
InputStreamReader 字符输入流
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
创建一个使用默认字符集的 InputStreamReader。
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException
创建使用指定字符集的 InputStreamReader。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 创建对象,默认编码GBK 6 // InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw.txt")); 7 //指定编码GBK 8 // InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw.txt"), "GBK"); 9 //指定编码UTF-8 10 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw.txt"), "UTF-8"); 11 12 // 读取数据 13 // 一次读取一个字符 14 int ch = 0; 15 while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1) 16 { 17 System.out.print((char) ch); 18 } 19 20 // 释放资源 21 isr.close(); 22 } 23 }
21.06 字符流的5种写数据的方式
1.public void write(int c)throws IOException
写入单个字符。要写入的字符包含在给定整数值的 16 个低位中,16 高位被忽略。
2.public void write(char[] cbuf)throws IOException
写入字符数组。
3.public abstract void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len)throws IOException
写入字符数组的某一部分。
4.public void write(String str)throws IOException
写入字符串。
5.public void write(String str,int off,int len)throws IOException
写入字符串的某一部分。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 创建对象 6 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\osw2.txt")); 7 8 // 写数据 9 // 写一个字符 10 // osw.write(‘a‘); 11 // osw.write(97);//osw2.txt文件中的内容为aa 12 13 // 写一个字符数组 14 // char[] chs = {‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘}; 15 // osw.write(chs);//osw2.txt文件中的内容abcde 16 17 // 写一个字符数组的一部分 18 // osw.write(chs,1,3);//osw2.txt文件中的内容bcd 19 20 // 写一个字符串 21 // osw.write("helloworld");//osw2.txt文件中的内容helloworld 22 23 // public void write(String str,int off,int len):写一个字符串的一部分 24 osw.write("helloworld", 2, 3);//osw2.txt文件中的内容llo 25 26 // 刷新缓冲区,可以继续写数据 27 osw.flush(); 28 29 // 释放资源,关闭此流,但要先刷新它 30 osw.close(); 31 } 32 }
面试题:close()和flush()的区别
A:close()关闭流对象,但是先刷新一次缓冲区。关闭之后,流对象不可以继续再使用了。
B:flush()仅仅刷新缓冲区,刷新之后,流对象还可以继续使用。
1.public int read()throws IOException
读取单个字符。在字符可用、发生 I/O 错误或者已到达流的末尾前,此方法一直阻塞。
2.public int read(char[] cbuf)throws IOException
将字符读入数组。在某个输入可用、发生 I/O 错误或者已到达流的末尾前,此方法一直阻塞。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 InputStreamReader isr1 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\Demo.java")); 6 //一次读取一个字符 7 int ch = 0; 8 while((ch = isr1.read()) != -1) 9 { 10 System.out.print((char)ch); 11 } 12 13 14 InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\Demo.java")); 15 //一次读取一个字符数组 16 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 17 int len = 0; 18 while((len = isr2.read(chs)) != -1) 19 { 20 System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len)); 21 } 22 23 isr1.close(); 24 isr2.close(); 25 } 26 }
21.08 字符流复制文本文件案例(转换流一次读取一个字符)
数据源:a.txt -- 读取数据 -- 字符转换流 -- InputStreamReader
目的地:b.txt -- 写出数据 -- 字符转换流 -- OutputStreamWriter
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\Demo.java")); 6 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\bb.txt")); 7 //一次读取一个字符 8 int ch = 0; 9 while((ch = isr.read()) != -1) 10 { 11 osw.write(ch); 12 } 13 14 isr.close(); 15 osw.close(); 16 } 17 }
21.09 字符流复制文本文件案例(使用便捷类)
转换流的名字比较长,而我们常见的操作都是按照本地默认编码实现的,所以,为了简化我们的书写,转换流提供了对应的子类。
FileWriter以及FileReader
OutputStreamWriter = FileOutputStream + 编码表(GBK)
FileWriter = FileOutputStream + 编码表(GBK)
InputStreamReader = FileInputStream + 编码表(GBK)
FileReader = FileInputStream + 编码表(GBK)
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装数据源 6 FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\a.txt"); 7 // 封装目的地 8 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\b.txt"); 9 10 // 一次一个字符 11 // int ch = 0; 12 // while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) 13 //{ 14 // fw.write(ch); 15 //} 16 17 // 一次一个字符数组 18 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 19 int len = 0; 20 while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) 21 { 22 fw.write(chs, 0, len); 23 fw.flush(); 24 } 25 26 // 释放资源 27 fw.close(); 28 fr.close(); 29 } 30 }
21.10 字符缓冲输出流BufferedWriter的使用
将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。
可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者接受默认的大小。在大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
构造方法:
1.public BufferedWriter(Writer out)
创建一个使用默认大小输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
2.public BufferedWriter(Writer out,int sz)
创建一个使用给定大小输出缓冲区的新缓冲字符输出流。
例:
1 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\bw.txt")); 2 bw.write("hello"); 3 bw.write("world"); 4 bw.write("java"); 5 bw.flush(); 6 bw.close();
21.11 字符缓冲输入流BufferedReader的使用
从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而实现字符、数组和行的高效读取。
可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者可使用默认的大小。大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
构造方法:
1.public BufferedReader(Reader in)
创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
2.public BufferedReader(Reader in,int sz)
创建一个使用指定大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 创建字符缓冲输入流对象 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\bw.txt")); 7 8 // 方式1 9 // int ch = 0; 10 // while ((ch = br.read()) != -1) { 11 // System.out.print((char) ch); 12 // } 13 14 // 方式2 15 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 16 int len = 0; 17 while ((len = br.read(chs)) != -1) 18 { 19 System.out.print(new String(chs, 0, len)); 20 } 21 22 // 释放资源 23 br.close(); 24 } 25 }
21.12 字符缓冲流复制文本文件案例
数据源:a.txt -- 读取数据 -- 字符转换流 -- InputStreamReader -- FileReader -- BufferedReader
目的地:b.txt -- 写出数据 -- 字符转换流 -- OutputStreamWriter -- FileWriter -- BufferedWriter
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装数据源 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\a.txt")); 7 // 封装目的地 8 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\b.txt")); 9 10 // 一次读写一个字符数组 11 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 12 int len = 0; 13 while ((len = br.read(chs)) != -1) 14 { 15 bw.write(chs, 0, len); 16 bw.flush(); 17 } 18 19 // 释放资源 20 bw.close(); 21 br.close(); 22 } 23 }
21.13 字符缓冲流的特殊功能
字符缓冲流的特殊方法:
BufferedWriter:
public void newLine()throws IOException
写入一个行分隔符。行分隔符字符串由系统属性 line.separator 定义,并且不一定是单个新行 (‘\n‘) 符。
BufferedReader:
public String readLine()throws IOException
读取一个文本行。通过下列字符之一即可认为某行已终止:换行 (‘\n‘)、回车 (‘\r‘) 或回车后直接跟着换行。包含该行内容的字符串,不包含任何行终止符,如果已到达流末尾,则返回 null
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // write(); 6 read(); 7 } 8 private static void read() throws IOException 9 { 10 // 创建字符缓冲输入流对象 11 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\bw.txt")); 12 String line = null; 13 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) 14 { 15 System.out.println(line); 16 } 17 //释放资源 18 br.close(); 19 } 20 21 private static void write() throws IOException 22 { 23 // 创建字符缓冲输出流对象 24 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\bw.txt")); 25 for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++) 26 { 27 bw.write("hello" + x); 28 bw.newLine(); 29 bw.flush(); 30 } 31 bw.close(); 32 } 33 }
21.14 IO流小结图解
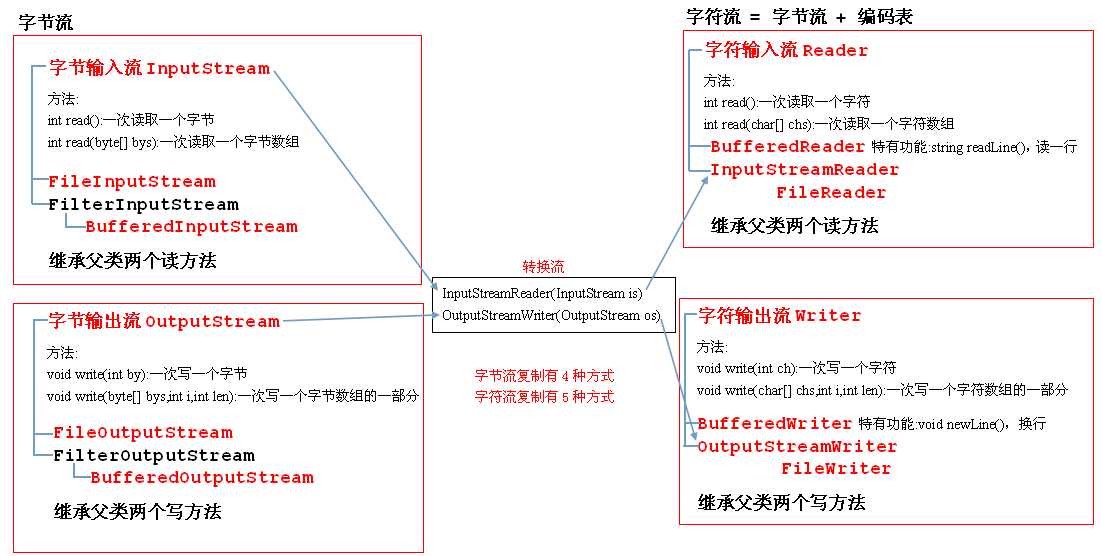
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 String srcString = "c:\\a.txt"; 6 String destString = "d:\\b.txt"; 7 // method1(srcString, destString); 8 // method2(srcString, destString); 9 // method3(srcString, destString); 10 // method4(srcString, destString); 11 method5(srcString, destString); 12 } 13 // 字符缓冲流一次读写一个字符串 14 private static void method5(String src, String dest)throws IOException 15 { 16 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); 17 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); 18 19 String line = null; 20 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) 21 { 22 bw.write(line); 23 bw.newLine(); 24 bw.flush(); 25 } 26 27 bw.close(); 28 br.close(); 29 } 30 31 // 字符缓冲流一次读写一个字符数组 32 private static void method4(String src, String dest)throws IOException 33 { 34 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); 35 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); 36 37 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 38 int len = 0; 39 while ((len = br.read(chs)) != -1) 40 { 41 bw.write(chs, 0, len); 42 } 43 44 bw.close(); 45 br.close(); 46 } 47 48 // 字符缓冲流一次读写一个字符 49 private static void method3(String src, String dest)throws IOException 50 { 51 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); 52 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); 53 54 int ch = 0; 55 while ((ch = br.read()) != -1) 56 { 57 bw.write(ch); 58 } 59 60 bw.close(); 61 br.close(); 62 } 63 64 // 基本字符流一次读写一个字符数组 65 private static void method2(String src, String dest)throws IOException 66 { 67 FileReader fr = new FileReader(src); 68 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(dest); 69 70 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 71 int len = 0; 72 while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) 73 { 74 fw.write(chs, 0, len); 75 } 76 77 fw.close(); 78 fr.close(); 79 } 80 81 // 基本字符流一次读写一个字符 82 private static void method1(String src, String dest)throws IOException 83 { 84 FileReader fr = new FileReader(src); 85 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(dest); 86 87 int ch = 0; 88 while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) 89 { 90 fw.write(ch); 91 } 92 93 fw.close(); 94 fr.close(); 95 } 96 }
21.16 复制图片的4种方式案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 使用字符串作为路径 6 // String srcString = "c:\\a.jpg"; 7 // String destString = "d:\\b.jpg"; 8 // 使用File对象做为参数 9 File srcFile = new File("c:\\a.jpg"); 10 File destFile = new File("d:\\b.jpg"); 11 12 // method1(srcFile, destFile); 13 // method2(srcFile, destFile); 14 // method3(srcFile, destFile); 15 method4(srcFile, destFile); 16 } 17 // 字节缓冲流一次读写一个字节数组 18 private static void method4(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException 19 { 20 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); 21 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile)); 22 23 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 24 int len = 0; 25 while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) 26 { 27 bos.write(bys, 0, len); 28 } 29 30 bos.close(); 31 bis.close(); 32 } 33 34 // 字节缓冲流一次读写一个字节 35 private static void method3(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException 36 { 37 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); 38 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile)); 39 40 int by = 0; 41 while ((by = bis.read()) != -1) 42 { 43 bos.write(by); 44 } 45 46 bos.close(); 47 bis.close(); 48 } 49 50 // 基本字节流一次读写一个字节数组 51 private static void method2(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException 52 { 53 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); 54 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); 55 56 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 57 int len = 0; 58 while ((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) 59 { 60 fos.write(bys, 0, len); 61 } 62 63 fos.close(); 64 fis.close(); 65 } 66 67 // 基本字节流一次读写一个字节 68 private static void method1(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException 69 { 70 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); 71 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); 72 73 int by = 0; 74 while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) 75 { 76 fos.write(by); 77 } 78 fos.close(); 79 fis.close(); 80 } 81 }
21.17 把集合中的数据存储到文本文件案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装数据源(创建集合对象) 6 ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>(); 7 array.add("hello"); 8 array.add("world"); 9 array.add("java"); 10 11 // 封装目的地 12 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\a.txt")); 13 14 // 遍历集合 15 for (String s : array) 16 { 17 // 写数据 18 bw.write(s); 19 bw.newLine(); 20 bw.flush(); 21 } 22 23 // 释放资源 24 bw.close(); 25 } 26 }
21.18 随机获取文本文件中的姓名案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 把文本文件中的数据存储到集合中 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\a.txt")); 7 ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 String line = null; 9 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) 10 { 11 array.add(line); 12 } 13 br.close(); 14 15 // 随机产生一个索引 16 Random r = new Random(); 17 int index = r.nextInt(array.size()); 18 19 // 根据该索引获取一个值 20 String name = array.get(index); 21 System.out.println("该幸运者是:" + name); 22 } 23 }
21.19 复制单级文件夹案例
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装目录 6 File srcFolder = new File("e:\\demo"); 7 // 封装目的地 8 File destFolder = new File("e:\\test"); 9 // 如果目的地文件夹不存在,就创建 10 if (!destFolder.exists()) 11 { 12 destFolder.mkdir(); 13 } 14 15 // 获取该目录下的所有文本的File数组 16 File[] fileArray = srcFolder.listFiles(); 17 18 // 遍历该File数组,得到每一个File对象 19 for (File file : fileArray) 20 { 21 // System.out.println(file); 22 // 数据源:e:\\demo\\e.mp3 23 // 目的地:e:\\test\\e.mp3 24 String name = file.getName(); // e.mp3 25 File newFile = new File(destFolder, name); // e:\\test\\e.mp3 26 27 copyFile(file, newFile); 28 } 29 } 30 private static void copyFile(File file, File newFile) throws IOException 31 { 32 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); 33 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile)); 34 35 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 36 int len = 0; 37 while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) 38 { 39 bos.write(bys, 0, len); 40 } 41 bos.close(); 42 bis.close(); 43 } 44 }
21.20 复制指定目录下指定后缀名的文件并修改名称案例
需求:复制指定目录下的指定文件,并修改后缀名。
指定的文件是:.java文件
指定的后缀名是:.jad
指定的目录是:jad
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装目录 6 File srcFolder = new File("e:\\java"); 7 // 封装目的地 8 File destFolder = new File("e:\\jad"); 9 // 如果目的地目录不存在,就创建 10 if (!destFolder.exists()) 11 { 12 destFolder.mkdir(); 13 } 14 15 // 获取该目录下的java文件的File数组 16 File[] fileArray = srcFolder.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() 17 { 18 @Override 19 public boolean accept(File dir, String name) 20 { 21 return new File(dir, name).isFile() && name.endsWith(".java"); 22 } 23 }); 24 25 // 遍历该File数组,得到每一个File对象 26 for (File file : fileArray) 27 { 28 // System.out.println(file); 29 // 数据源:e:\java\DataTypeDemo.java 30 // 目的地:e:\\jad\DataTypeDemo.java 31 String name = file.getName(); 32 File newFile = new File(destFolder, name); 33 copyFile(file, newFile); 34 } 35 36 // 在目的地目录下改名 37 File[] destFileArray = destFolder.listFiles(); 38 for (File destFile : destFileArray) 39 { 40 // System.out.println(destFile); 41 // e:\jad\DataTypeDemo.java 42 // e:\\jad\\DataTypeDemo.jad 43 String name =destFile.getName(); //DataTypeDemo.java 44 String newName = name.replace(".java", ".jad");//DataTypeDemo.jad 45 46 File newFile = new File(destFolder,newName); 47 destFile.renameTo(newFile); 48 } 49 } 50 private static void copyFile(File file, File newFile) throws IOException 51 { 52 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); 53 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile)); 54 55 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 56 int len = 0; 57 while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) 58 { 59 bos.write(bys, 0, len); 60 } 61 62 bos.close(); 63 bis.close(); 64 } 65 }
21.21 复制多级文件夹案例
需求:复制多极文件夹
数据源:E:\JavaSE\day21\code\demos
目的地:E:\\
分析:
A:封装数据源File
B:封装目的地File
C:判断该File是文件夹还是文件
a:是文件夹
就在目的地目录下创建该文件夹
获取该File对象下的所有文件或者文件夹File对象
遍历得到每一个File对象
回到C
b:是文件就复制(字节流)
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 // 封装数据源File 6 File srcFile = new File("E:\\JavaSE\\day21\\code\\demos"); 7 // 封装目的地File 8 File destFile = new File("E:\\"); 9 10 // 复制文件夹的功能 11 copyFolder(srcFile, destFile); 12 } 13 private static void copyFolder(File srcFile, File destFile)throws IOException { 14 // 判断该File是文件夹还是文件 15 if (srcFile.isDirectory()) 16 { 17 // 文件夹 18 File newFolder = new File(destFile, srcFile.getName()); 19 newFolder.mkdir(); 20 21 // 获取该File对象下的所有文件或者文件夹File对象 22 File[] fileArray = srcFile.listFiles(); 23 for (File file : fileArray) 24 { 25 copyFolder(file, newFolder); 26 } 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 // 文件 31 File newFile = new File(destFile, srcFile.getName()); 32 copyFile(srcFile, newFile); 33 } 34 } 35 36 private static void copyFile(File srcFile, File newFile) throws IOException 37 { 38 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); 39 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile)); 40 41 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 42 int len = 0; 43 while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) 44 { 45 bos.write(bys, 0, len); 46 } 47 bos.close(); 48 bis.close(); 49 } 50 }
21.22 键盘录入学生信息按照总分排序并写入文本文件案例
Student类同day17 17.16
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() 6 { 7 @Override 8 public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) 9 { 10 //按总分比较 11 int num1 = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum(); 12 //总分相同按语文成绩比较 13 int num2 = num1==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num1; 14 //语文成绩相同按数学成绩比较 15 int num3 = num2==0?s1.getMath() - s2.getMath():num2; 16 //数学成绩相同按英语成绩比较 17 int num4 = num3==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num3; 18 //英语成绩相同按姓名比较 19 int num5 = num4==0?s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()):num4; 20 return num5; 21 } 22 }); 23 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) 24 { 25 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 26 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的姓名"); 27 String name = sc.nextLine(); 28 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的语文成绩"); 29 String chinese = sc.nextLine(); 30 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的数学成绩"); 31 String math = sc.nextLine(); 32 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的英语成绩"); 33 String english = sc.nextLine(); 34 35 Student s = new Student(name, Integer.parseInt(chinese), Integer.parseInt(math), Integer.parseInt(english)); 36 ts.add(s); 37 } 38 // 遍历集合,把数据写到文本文件 39 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\students.txt")); 40 bw.write("学生信息如下:"); 41 bw.newLine(); 42 bw.flush(); 43 bw.write("姓名\t语文\t数学\t英语\t总分"); 44 bw.newLine(); 45 bw.flush(); 46 for (Student s : ts) 47 { 48 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 49 sb.append(s.getName()).append("\t").append(s.getChinese()) 50 .append("\t").append(s.getMath()).append("\t") 51 .append(s.getEnglish()).append("\t").append(s.getSum()); 52 bw.write(sb.toString()); 53 bw.newLine(); 54 bw.flush(); 55 } 56 // 释放资源 57 bw.close(); 58 System.out.println("学生信息存储完毕"); 59 } 60 }
21.23 自定义类模拟BufferedReader的readLine()功能案例
用Reader模拟BufferedReader的readLine()功能
readLine():一次读取一行,根据换行符判断是否结束,只返回内容,不返回换行符
1 public class MyBufferedReader 2 { 3 private Reader r; 4 5 public MyBufferedReader(Reader r) 6 { 7 this.r = r; 8 } 9 10 //思考:写一个方法,返回值是一个字符串。 11 public String readLine() throws IOException 12 { 13 /* 14 * 要返回一个字符串,看看r对象的两个读取方法,一次读取一个字符或者一次读取一个字符数组 15 * 很容易想到字符数组比较好,但是不能确定这个数组的长度是多长 16 * 所以,只能选择一次读取一个字符。 17 * 但是呢,这种方式的时候,我们再读取下一个字符的时候,上一个字符就丢失了 18 * 所以,应该定义一个临时存储空间把读取过的字符给存储起来。 19 * 这个用谁比较和是呢?数组,集合,字符串缓冲区三个可供选择。 20 * 经过简单的分析,最终选择使用字符串缓冲区对象。并且使用的是StringBuilder 21 */ 22 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 23 24 // 做这个读取最麻烦的是判断结束,但是在结束之前应该是一直读取,直到-1 25 26 /* 27 hello 28 world 29 java 30 31 104101108108111 32 119111114108100 33 1069711897 34 \r 13 \n 10 35 */ 36 37 int ch = 0; 38 while ((ch = r.read()) != -1) 39 { //104,101,108,108,111 40 if (ch == ‘\r‘) 41 { 42 continue; 43 } 44 45 if (ch == ‘\n‘) 46 { 47 return sb.toString(); //hello 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 sb.append((char)ch); //hello 52 } 53 } 54 55 // 为了防止数据丢失,判断sb的长度不能大于0 56 if (sb.length() > 0) 57 { 58 return sb.toString(); 59 } 60 return null; 61 } 62 63 64 //关闭方法 65 public void close() throws IOException 66 { 67 this.r.close(); 68 } 69 } 70
21.24 LineNumberReader的使用案例
例:
1 public class Practice 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 4 { 5 LineNumberReader lnr = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader("D:\\students.txt")); 6 String line = null; 7 lnr.setLineNumber(9);//设置行号 8 while((line = lnr.readLine()) != null) 9 { 10 //获取行号 11 System.out.println(lnr.getLineNumber()+":"+line); 12 } 13 } 14 }
运行结果:
10:学生信息如下: 11:姓名 语文 数学 英语 总分 12:gdf 45 76 54 175 13:ftg 47 45 68 160 14:dcf 25 64 57 146 15:wdsa 23 45 76 144 16:ef 56 34 16 106
21.25 自定义类模拟LineNumberReader的获取行号功能案例
1 //方式1: 2 public class MyLineNumberReader 3 { 4 private Reader r; 5 private int lineNumber = 0; 6 7 public MyLineNumberReader(Reader r) 8 { 9 this.r = r; 10 } 11 12 public int getLineNumber() 13 { 14 // lineNumber++; 15 return lineNumber; 16 } 17 18 public void setLineNumber(int lineNumber) 19 { 20 this.lineNumber = lineNumber; 21 } 22 23 public String readLine() throws IOException 24 { 25 lineNumber++; 26 27 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 28 29 int ch = 0; 30 while ((ch = r.read()) != -1) 31 { 32 if (ch == ‘\r‘) 33 { 34 continue; 35 } 36 37 if (ch == ‘\n‘) 38 { 39 return sb.toString(); 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 sb.append((char) ch); 44 } 45 } 46 47 if (sb.length() > 0) 48 { 49 return sb.toString(); 50 } 51 52 return null; 53 } 54 55 public void close() throws IOException 56 { 57 this.r.close(); 58 } 59 } 60 61 //方式2:继承21.29的BufferedReader类 62 public class MyLineNumberReader extends MyBufferedReader 63 { 64 private Reader r; 65 66 private int lineNumber = 0; 67 68 public MyLineNumberReader(Reader r) 69 { 70 super(r); 71 } 72 73 public int getLineNumber() 74 { 75 return lineNumber; 76 } 77 78 public void setLineNumber(int lineNumber) 79 { 80 this.lineNumber = lineNumber; 81 } 82 83 @Override 84 public String readLine() throws IOException 85 { 86 lineNumber++; 87 return super.readLine(); 88 } 89 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhy7201/p/4537464.html