标签:c#
1. 顺序查找算法
=====================================================
算法思想简单描述:
最突出的查找类型就是从记录集的开始处顺次遍历每条记录,直到找到所要的记录或者是
到达数据集的末尾。这就是所谓的顺序查找。顺序查找(也被称为线性查找)是非常容易实现
的。从数组的起始处开始,把每个访问到的数组元素依次和所要查找的数值进行比较。如果找
到匹配的数据项,就结束查找操作。如果遍历到数组的末尾仍没有产生匹配,那么就说明此数
值不在数组内。
=====================================================
实例1:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SeqSearch
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] array = new int[] {2,3,4,5,1,3,22,33};
int foundItem = 2;
int result = SeqSearch(array, foundItem);
if (result != -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Find the item {0} on Array[{1}].", foundItem,result);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Can‘t find the item {0}", foundItem);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int SeqSearch(int [] array, int key)
{
for (int index = 0; index < array.Length;index++ )
{
if(array[index]==key)
return index;
}
return -1;
}
}
}2. 二分查找算法
=====================================================
算法思想简单描述:
折半搜索,也称二分查找算法、二分搜索,是一种在有序数组中查找某一特定元素的搜索算法。
A 搜素过程从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是要查找的元素,则搜素过程结束;
B 如果某一特定元素大于或者小于中间元素,则在数组大于或小于中间元素的那一半中查找,而且跟开始一样从中间元素开始比较。
C 如果在某一步骤数组为空,则代表找不到。这种搜索算法每一次比较都使搜索范围缩小一半。
时间复杂度折半搜索每次把搜索区域减少一半,时间复杂度为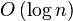 。
。
(n代表集合中元素的个数)空间复杂度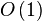
题目:在一个已经排序的数组中查找给定数值的索引,如果未找到,则返回-1.
=====================================================
实例2:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SeqSearch
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] y = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 };
int findItem = 13;
int rr = BinarySearch(y, 0, y.Length - 1, findItem);
Console.WriteLine("Find the item {0} on Array[{1}].",findItem, rr);
//Console.Write(rr); //12
Console.ReadLine();
}
/// <summary>
/// 二分查找
/// </summary>
/// <param name="arr"></param>
/// <param name="low">开始索引 0</param>
/// <param name="high">结束索引 </param>
/// <param name="key">要查找的对象</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int BinarySearch(int[] arr, int low, int high, int key)
{
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (low > high)
return -1;
else
{
if (arr[mid] == key)
return mid;
else if (arr[mid] > key)
return BinarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, key);
else
return BinarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, key);
}
}
}
}3.哈希查找算法
=====================================================
算法思想简单描述:
哈希查找,也称为散列查找(本文以哈希称呼)。
提起哈希,我的第一印象就是C#中的Hashtable类,它是由一组key/value的键值对组成的集合,它就是应用了散列技术。
那么,什么是哈希查找呢?在弄清楚什么是哈希查找之前,我们要弄清楚哈希技术,哈希技术是在记录的存储位置和记录的关键字之间建立一个确定的对应关系f,使得每个关键字key对应一个存储位置f(key)。查找时,根据这个确定的对应关系找到给定值的映射f(key),若查找集合中存在这个记录,则必定在f(key)的位置上。哈希技术既是一种存储方法,也是一种查找方法。
=====================================================
实例3:
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DataStructure
{
class Search
{
public static void Main()
{
//1.新建一个新哈希表.
Hashtable openWith = new Hashtable();
//2.给哈希表增加一些元素
openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe");
openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe");
//3.如果键已经在表中抛出错误
try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); }
catch { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = \"txt\" already exists."); }
//4.用键来访问元素
Console.WriteLine("For key = \"rtf\", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]);
//5.改变项目的值
openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe";
Console.WriteLine("For key = \"rtf\", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]);
//如果访问的项目不存在,则新建一个,并为他添加键值对
openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe";
//如果请求抛出例外,则键不会进入表中
try { Console.WriteLine("For key = \"tif\", value = {0}.", openWith["tif"]); }
catch { Console.WriteLine("Key = \"tif\" is not found."); }
//6.在插入以前通常用ContainsKey来测试键是不是已经在哈希表中
if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht"))
{
openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe");
Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = \"ht\": {0}", openWith["ht"]);
}
//7.用foreach来枚举元素
//当你用foreach语句来枚举表中元素时,返回键值对对象(DictionaryEntry)
Console.WriteLine();
foreach (DictionaryEntry de in openWith)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", de.Key, de.Value);
}
//8.单独得到“键”、“值”
//单独得到“值”
ICollection valueColl = openWith.Values;
Console.WriteLine();
foreach (string s in valueColl)
{ Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); }
ICollection keyColl = openWith.Keys;
Console.WriteLine();
foreach (string s in keyColl)
{ Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); }
//9.用Remove移除键值对
Console.WriteLine("\nRemove(\"doc\")"); openWith.Remove("doc");
if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Key \"doc\" is not found.");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}4.索引查找算法
=====================================================
算法思想简单描述:
索引查找又称为分块查找,是一种介于顺序查找和二分查找之间的一种查找方法,分块查找的基本思想是:首先查找索引表,可用二分查找或顺序查找,然后在确定的块中进行顺序查找。
分块查找的时间复杂度为O(√n)。
在实现索引查找算法前需要弄清楚以下三个术语。
1,主表。即要查找的对象。
2,索引项。一般我们会将主表分成几个子表,每个子表建立一个索引,这个索引就叫索引项。
3,索引表。即索引项的集合。
同时,索引项包括以下三点。
1,index,即索引指向主表的关键字。
2,start,即index在主表中的位置。
3,length,即子表的区间长度。
=====================================================
实例4:
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DataStructure
{
/// <summary>
/// 索引项实体
/// </summary>
public class IndexItem
{
public int Index { get; set; }
public int Start { get; set; }
public int Length { get; set; }
}
public class Program
{
/// <summary>
/// 主表
/// </summary>
static int[] studentList = new int[] {
101,102,103,104,105,0,0,0,0,0,
201,202,203,204,0,0,0,0,0,0,
301,302,303,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
};
/// <summary>
/// 索引表
/// </summary>
static IndexItem[] IndexItemList = new IndexItem[] {
new IndexItem{ Index=1,Start=0,Length=5},
new IndexItem{ Index=2,Start=10,Length=4},
new IndexItem{ Index=3,Start=20,Length=3}
};
/// <summary>
/// 索引查找算法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">给定值</param>
/// <returns>给定值在表中的位置</returns>
public static int IndexSearch(int key)
{
IndexItem item = null;
// 建立索引规则
var index = key / 100;
//遍历索引表,找到对应的索引项
for (int i = 0; i < IndexItemList.Count(); i++)
{
//找到索引项
if (IndexItemList[i].Index == index)
{
item = new IndexItem() { Start = IndexItemList[i].Start, Length = IndexItemList[i].Length };
break;
}
}
//索引表中不存在该索引项
if (item == null)
return -1;
//在主表顺序查找
for (int i = item.Start; i < item.Start + item.Length; i++)
{
if (studentList[i] == key)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("********************IndexSearch(C#)********************\n");
Console.WriteLine("Old array data:{0}",String.Join(" ",studentList));
int value = 201;
Console.WriteLine("\nThe item 205 is on array[{0}] ",IndexSearch(value));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}5.二叉查找算法
=====================================================
算法思想简单描述:
构造一棵二叉排序树的目的,其实并不是为了排序,而是为了提高查找和插入删除的效率。
那么什么是二叉排序树呢?二叉排序树具有以下几个特点。
1,若根节点有左子树,则左子树的所有节点都比根节点小。
2,若根节点有右子树,则右子树的所有节点都比根节点大。
3,根节点的左,右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
下面是二叉排序树的图示,通过图可以加深对二叉排序树的理解。
下面是二叉排序树常见的操作及思路。
1,插入节点
思路:比如我们要插入数字20到这棵二叉排序树中。那么步骤如下:
1) 首先将20与根节点进行比较,发现比根节点小,所以继续与根节点的左子树30比较。
2) 发现20比30也要小,所以继续与30的左子树10进行比较。
3) 发现20比10要大,所以就将20插入到10的右子树中。
此时二叉排序树效果如图:
2,查找节点
比如我们要查找节点10,那么思路如下:
1) 还是一样,首先将10与根节点50进行比较大小,发现比根节点要小,所以继续与根节点的左子树30进行比较。
2) 发现10比左子树30要小,所以继续与30的左子树10进行比较。
3) 发现两值相等,即查找成功,返回10的位置。
过程与插入相同,这里就不贴图了。
3,删除节点
删除节点的情况相对复杂,主要分以下三种情形:
1) 删除的是叶节点(即没有孩子节点的)。比如20,删除它不会破坏原来树的结构,最简单。如图所示。
2) 删除的是单孩子节点。比如90,删除它后需要将它的孩子节点与自己的父节点相连。情形比第一种复杂一些。
3) 删除的是有左右孩子的节点。比如根节点50,这里有一个问题就是删除它后将谁做为根节点的问题?利用二叉树的中序遍历,就是右节点的左子树的最左孩子。
分析完了,有了思路之后,下面就开始写代码来实现这些功能了。
=====================================================
实例5:
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DataStructure
{
/// <summary>
/// Description:二叉排序树的常见操作
/// Author:McgradyLu
/// Time:8/24/2013 4:12:18 PM
/// </summary>
public class BSTreeBLL
{
/// <summary>
/// 创建二叉排序树
/// </summary>
/// <param name="list"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static BSTree Create(List<int> list)
{
//创建根节点
BSTree bsTree = new BSTree()
{
Data = list[0],
Left = null,
Right = null
};
//将list中的节点一个一个地插入到二叉排序树中
for (int i = 1; i < list.Count; i++) //注意这里从1开始,因为0位置上元素已经给了根节点
{
bool isExcute = false;
Insert(bsTree, list[i], ref isExcute);
}
return bsTree;
}
/// <summary>
/// 插入节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bsTree">二叉排序树</param>
/// <param name="key">待插入值</param>
/// <param name="isExcute">是否执行了if语句(节点是否插入)</param>
public static void Insert(BSTree bsTree, int key, ref bool isExcute)
{
if (bsTree == null) return;
//如果小于根节点,遍历左子树,否则遍历右子树(找到当前要插入节点的父节点)
if (key < bsTree.Data) Insert(bsTree.Left, key, ref isExcute);
else Insert(bsTree.Right, key, ref isExcute);
if (!isExcute)
{
//创建当前节点
BSTree current = new BSTree()
{
Data = key,
Left = null,
Right = null
};
//插入到父节点中
if (key < bsTree.Data) bsTree.Left = current;
else bsTree.Right = current;
isExcute = true;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 中序遍历
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bsTree"></param>
public static void LDR(BSTree bsTree)
{
if (bsTree != null)
{
//遍历左子树
LDR(bsTree.Left);
//输出节点数据
Console.Write(bsTree.Data + " ");
//遍历右子树
LDR(bsTree.Right);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 查找节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bsTree">待查找的二叉排序树</param>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns>true表示查找成功,false表示查找失败</returns>
public static bool Search(BSTree bsTree, int key)
{
//遍历完没有找到,查找失败
if (bsTree == null) return false;
//要查找的元素为当前节点,查找成功
if (key == bsTree.Data) return true;
//继续去当前节点的左子树中查找,否则去当前节点的右子树中查找
if (key < bsTree.Data) return Search(bsTree.Left, key);
else return Search(bsTree.Right, key);
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bsTree"></param>
/// <param name="key"></param>
public static void Delete(ref BSTree bsTree, int key)
{
//空树
if (bsTree == null) return;
//判断是否是要删除的节点
if (key == bsTree.Data)
{
//第一种情况:叶子节点(没有孩子节点)
if (bsTree.Left == null && bsTree.Right == null)
{
bsTree = null;
return;
}
//第二种情况:仅有左子树
if (bsTree.Left != null && bsTree.Right == null)
{
bsTree = bsTree.Left;
return;
}
//第三种情况:仅有右子树
if (bsTree.Left == null && bsTree.Right != null)
{
bsTree = bsTree.Right;
return;
}
//第四种情况:有左,右子树
if (bsTree.Left != null && bsTree.Right != null)
{
//利用中序遍历找到右节点的左子树的最左孩子
var node = bsTree.Right;
while (node.Left != null)
{
node = node.Left;
}
node.Left = bsTree.Left;
if (node.Right == null)
{
Delete(ref bsTree, node.Data);
node.Right = bsTree.Right;
}
bsTree = node;
}
}
//遍历找到要删除的节点
if (key < bsTree.Data)
{
Delete(ref bsTree.Left, key);
}
else
{
Delete(ref bsTree.Right, key);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 封装二叉排序树结构
/// </summary>
public class BSTree
{
public int Data;
public BSTree Left;
public BSTree Right;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int> { 50, 30, 70, 10, 40, 90, 80 };
Console.WriteLine("***************Create binary tree***************");
BSTree bsTree = BSTreeBLL.Create(list);
Console.Write("in order traversal the old data:\n");
BSTreeBLL.LDR(bsTree);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************query node********************");
Console.WriteLine("query whether item 40 exist on the tree:{0}", BSTreeBLL.Search(bsTree, 40));
Console.WriteLine("\n********************insert node********************");
Console.WriteLine("insert item 20 into the tree");
bool isExcute = false;
BSTreeBLL.Insert(bsTree, 20, ref isExcute);
Console.Write("after LDR:\n");
BSTreeBLL.LDR(bsTree);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************Delete the node1********************");
Console.WriteLine("delete childnode 20,\n after LDR:\n");
BSTreeBLL.Delete(ref bsTree, 20);
BSTreeBLL.LDR(bsTree);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************Delete the node2********************");
Console.WriteLine("delete childnode 90,\n after LDR:\n");
BSTreeBLL.Delete(ref bsTree, 90);
BSTreeBLL.LDR(bsTree);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************Delete the node3********************");
Console.WriteLine("delete childnode 50,\n after LDR:\n");
BSTreeBLL.Delete(ref bsTree, 50);
BSTreeBLL.LDR(bsTree);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}参考:
顺序查找:
http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/p/3266065.html
http://blog.csdn.net/wust__wangfan/article/details/19563433
二分查找:
http://59949.htmlfyxspgpw.blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25498312-id-3440295.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/zengxiangzhan/p/3305908.html
哈希表操作和用法总结:
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoping8411/article/details/7706376
http://www.360doc.com/content/09/0808/16/163747_4759168.shtml
http://blog.163.com/qiu_zhizhong/blog/static/5472313020096633853622/
http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/archive/2013/09/01/3294871.html
索引查找:
http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/p/3271609.html
二叉排序树查找,二叉查找:
http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/p/3280624.html
本文出自 “Ricky's Blog” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://57388.blog.51cto.com/47388/1657930
2. C#数据结构与算法 -- 查找算法(顺序查找,哈希查找,二分查找(折半),索引,二叉)
标签:c#
原文地址:http://57388.blog.51cto.com/47388/1657930