标签:style class blog code http tar
简述:
0、ext2格式。
1、包括权限管理,精确到角色。
2、数据块采用连续分配(离散分配大家来弄吧)。
3、为实现间接索引,相信实现了目录,简介索引也不是问题吧。。
4、删除目录不支持递归删除。自己写去吧。
5、整体结构:
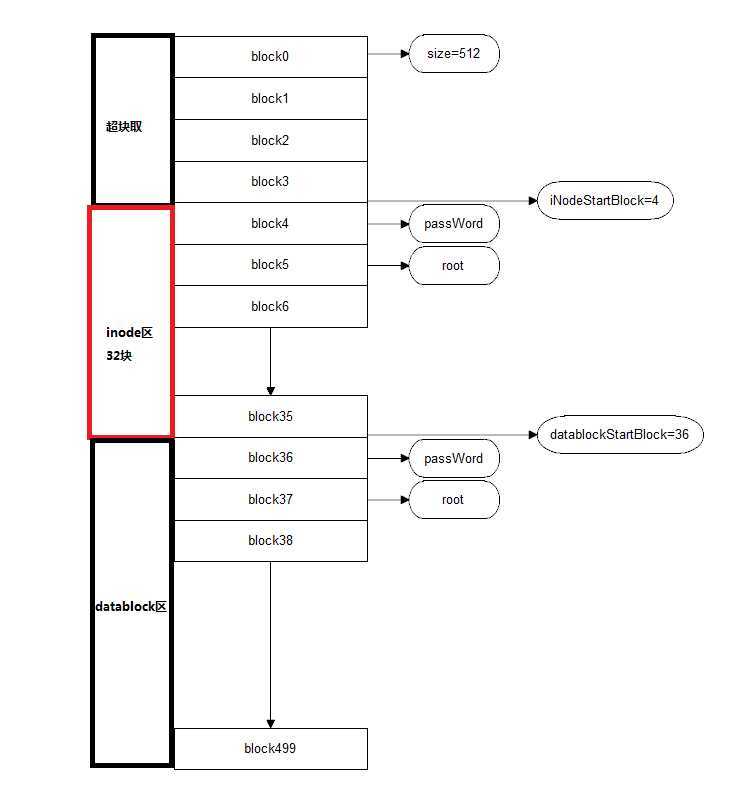
6、主要数据结构:

//超级块 struct SuperBlock { int s_block_count;//block总个数 int s_block_size;//block块的大小 int s_inode_count;//inode总个数 int s_datablock_count;//datablock总个数 int s_free_inode_count;//空闲的inode个数 int s_free_datablock_count;//空闲的数据block个数 int s_inode_bitmap[INODE_COUNT];//inode节点位图 1使用 0未用 int s_datablock_bitmap[DATABLOCK_COUNT];//数据块block位图 1使用 0未用 }; //磁盘索引节点INode struct INode { int i_key;//标识 int i_type;//文件类型:正规文件、目录文件 int i_size;//针对文件,文件长度;针对目录,目录项个数 int i_group_id;//针对文件/目录,关联文件所属组别id 0管理员组 1用户组 2非法 char i_create_time[30];//针对文件/目录 char i_modify_time[30];//针对文件/目录 int i_datablock_count;//针对文件,使用datablock数目;目录只能用一个 int i_datablock[BLOCK_POINTER_NUMBER_IN_INODE];//一组datablock指针,前十个1级指针,第十一个2级指针,第十二个3级指针 }; //用户密码 struct PassWord { int p_group_id;//权限仅验证到“组别级”,且假设:管理员组对所有文件/目录有增删改查权限;用户组对本组创建文件/目录有增删改查权限,对管理员组创建的文件/目录只有查(读)权限。 char p_userName[USER_NAME_SIZE]; char p_passWord[USER_PASSWORD_SIZE]; }; //目录项结构 struct DirFil { char df_name[FILE_NAME_SIZE];//目录/文件名 int df_inode_key;//目录/文件对应的inode编号 };
7、定义与全局变量:

# define GROUP_ADMIN 0//管理员组 # define GROUP_USER 1//普通用户组 # define GROUP_UNDEFINE 2//未定义,非法用户组 # define TYPE_FILE 0//普通文件 # define TYPE_DIRE 1//目录 # define TYPE_PASS 2//用户账号文件 # define BLOCK_SIZE 512//磁盘分块的大小 # define BLOCK_COUNT 500//磁盘分块的总数目,【包括超块、inode区的32块】 //区分DATA_BLOCK(存放数据的区域)与BLOCK(整个的磁盘区域)的区别 # define DATABLOCK_SIZE 512//每个DATABLOCK的大小 # define DATABLOCK_COUNT BLOCK_COUNT-36//数据BLOCK的块数,0-3超块,4-35共32块inode区 # define INODE_SIZE sizeof(struct INode)//每个inode的大小 # define INODE_COUNT 32//inode区的inode块数 # define BLOCK_POINTER_NUMBER_IN_INODE 12//inode节点中,指向数据块的指针个数,前十个1级,第十一个2级 # define INODE_START_BLOCK 4//inode区的开始BLOCK,从0计数 # define DATABLOCK_START_BLOCK 36//数据区的开始BLOCK,从0计数 # define USER_NAME_SIZE 15//单个用户名的长度 # define USER_PASSWORD_SIZE 15//单个密码的长度 # define PASSWORD_SIZE sizeof(struct PassWord) # define PASS_WORD_COUNT BLOCK_SIZE/PASSWORD_SIZE//最多保存用户数 # define FILE_NAME_SIZE 15//文件、目录名的长度(字节) # define DIR_FIL_SIZE sizeof(struct DirFil) # define FILE_NUMBER_IN_DIRECTORY BLOCK_SIZE/DIR_FIL_SIZE//一个目录下的最多子目录或文件的总个数 //全局变量 const char fileSystemName[20]="FileSystem.txt";//模拟硬盘的文件名 FILE *fileSystemPointer;//模拟硬盘的文件的文件指针 struct SuperBlock superBlock;//超级块 struct INode *currentINode;//指向当前【目录】的inode struct INode *tempINode;//跟多时候,是指向当前要处理的【文件】的inode struct PassWord passWord[PASS_WORD_COUNT];//passWord区的用户账号和密码及用户组 struct PassWord curPW;//保存当前登陆的用户的账号和密码及用户组 struct DirFil currentDirFil[FILE_NUMBER_IN_DIRECTORY];//保存当前【目录】中的目录项 char abDir[200];//当前绝对路径 char curTime[30]; int iBM_lock=0;//inode位图锁 可能会多个进程同时访问 INodeAlloc int dbBM_lock=0;//datablock位图锁 可能会多个进程同时访问 DatablockAlloc
8、增加文件:(思想:申请并初始化该文件的inode、datablock;更新文件父目录的inode、datablock;更新超块。)

int createFile() { int i; char fileName[20]; if(currentINode->i_size<FILE_NUMBER_IN_DIRECTORY) { printf("input file name:"); fflush(stdin); scanf("%s",fileName); for(i=0;i<FILE_NUMBER_IN_DIRECTORY;i++) { if(strcmp(currentDirFil[i].df_name,fileName)==0) { printf("文件名已存在\n"); return 0; } } char *input=(char *)malloc(BLOCK_SIZE*sizeof(char)); printf("0:自己输入内容\n"); printf("1:自动输入内容\n"); printf("请选择:"); fflush(stdin); scanf("%d",&i); if(i==0) { printf("自己输入内容,以“#”结束\n"); while(1) { input[i]=getchar(); if(input[i]==‘#‘) { break; } i++; if(i%BLOCK_SIZE==0) { input=(char *)realloc(input,BLOCK_SIZE*(i/BLOCK_SIZE+1)*sizeof(char)); } } input[i]=‘\0‘; } else { i=0; while(i<1000) { input[i]=i%10+‘0‘; i++; if(i%BLOCK_SIZE==0) { input=(char *)realloc(input,BLOCK_SIZE*(i/BLOCK_SIZE+1)*sizeof(char)); } } input[i]=‘\0‘; } printf("input length is %d\n",strlen(input)); printf("您输入的信息为:%s",input); //申请inode和datablock记录这些信息 int ikey=INodeAlloc(); if(ikey==-1) { return 0; } int datablockStartNumber=DatablockAlloc(strlen(input)/BLOCK_SIZE+1); if(datablockStartNumber==-1) { return 0; } else//将新建的文件的inode和datablock的信息补充完整 { tempINode->i_key=ikey; tempINode->i_type=TYPE_FILE; tempINode->i_size=strlen(input)+1;//+1,把“\0”也要写进去 tempINode->i_group_id=curPW.p_group_id; GetTime(); strcpy(tempINode->i_create_time,curTime); strcpy(tempINode->i_modify_time,curTime); tempINode->i_datablock_count=(strlen(input)/BLOCK_SIZE+1); for(i=0;i<tempINode->i_datablock_count;i++) { tempINode->i_datablock[i]=datablockStartNumber+i; } fseek(fileSystemPointer,(DATABLOCK_START_BLOCK+datablockStartNumber)*BLOCK_SIZE,SEEK_SET);//将新建的文件内容写入datablock区 //fwrite(input,sizeof(input),1,fileSystemPointer);不能sizeof(input),否则只能写进去4个============================= fwrite(input,strlen(input)+1,1,fileSystemPointer);//+1,把“\0”也要写进去 fseek(fileSystemPointer,(INODE_START_BLOCK+ikey)*BLOCK_SIZE,SEEK_SET);//将新建的文件inode写入inode区 fwrite(tempINode,sizeof(struct INode),1,fileSystemPointer); currentDirFil[currentINode->i_size].df_inode_key=ikey;//当前目录中添加一项子文件目录项 strcpy(currentDirFil[currentINode->i_size].df_name,fileName); fseek(fileSystemPointer,(DATABLOCK_START_BLOCK+currentINode->i_datablock[0])*BLOCK_SIZE,SEEK_SET);//将当前目录更新后的信息写回datablock区 fwrite(currentDirFil,sizeof(currentDirFil),1,fileSystemPointer); currentINode->i_size++;//当前目录的子文件数+1 fseek(fileSystemPointer,(INODE_START_BLOCK+currentINode->i_key)*BLOCK_SIZE,SEEK_SET);//将当前inode更新后的inode写回inode区 fwrite(currentINode,sizeof(struct INode),1,fileSystemPointer); fseek(fileSystemPointer,0,SEEK_SET);//将更新后的superBlock写回superBlock区 fwrite(&superBlock,sizeof(struct SuperBlock),1,fileSystemPointer); free(input); } } else { printf("当前目录的子文件数目已达到最大\n"); return 0; } printf("创建文件成功...\n"); return 1; }
9、删除目录:

int deleteFile() { int i; char fileName[20]; printf("input file name:"); fflush(stdin); scanf("%s",fileName); for(i=0;i<FILE_NUMBER_IN_DIRECTORY;i++) { if(strcmp(currentDirFil[i].df_name,fileName)==0) { break; } } if(i==FILE_NUMBER_IN_DIRECTORY) { printf("当前目录下下没有文件%s\n",fileName); return 0; } else { ReadINode(currentDirFil[i].df_inode_key); if(tempINode->i_type!=TYPE_FILE) { printf("%s不是用户文件,可能是目录或系统文件,您不能使用该命令删除\n",fileName); return 0; } if(Authority()==0) { printf("您没有权限删除文件%s\n",fileName); return 0; } else { while(i<currentINode->i_size)//删除文件,更新当前目录datablock区 { strcpy(currentDirFil[i].df_name,currentDirFil[i+1].df_name); currentDirFil[i].df_inode_key=currentDirFil[i+1].df_inode_key; i++; } fseek(fileSystemPointer,(DATABLOCK_START_BLOCK+currentINode->i_datablock[0])*BLOCK_SIZE,SEEK_SET);//将当前目录更新后的信息写回datablock区 fwrite(currentDirFil,sizeof(currentDirFil),1,fileSystemPointer); currentINode->i_size--;//删除文件,更新当前目录indoe区 fseek(fileSystemPointer,(INODE_START_BLOCK+currentINode->i_key)*BLOCK_SIZE,SEEK_SET);//将当前目录更新后的inode写回inode区 fwrite(currentINode,sizeof(struct INode),1,fileSystemPointer); for(i=0;i<tempINode->i_datablock_count;i++)//删除文件,回收datablock区 { superBlock.s_datablock_bitmap[tempINode->i_datablock[i]]=0; } superBlock.s_free_datablock_count+=tempINode->i_datablock_count; superBlock.s_inode_bitmap[tempINode->i_key]=0;//删除文件,回收inode区 superBlock.s_free_inode_count++; fseek(fileSystemPointer,0,SEEK_SET);//将更新后的superBlock写回superBlock区 fwrite(&superBlock,sizeof(struct SuperBlock),1,fileSystemPointer); } } printf("删除文件成功...\n"); return 1; }
10、注意事项:
1)永远让currentINode指向当前目录的inode;tempINode指向当前要访问的子文件/子目录的inode;currentDirFile永远只想当前目录的datablock。
2)注意文件的读写方式,是wb、rb+还是什么,否则一定出错。
操作系统——linux文件系统初实现,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style class blog code http tar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mmcmmc/p/3809416.html