标签:android style class blog code http
在android中应用的界面是以xml来组织的,这一点和WPF相似,通过配置xml文件我们可以灵活的构建出你自己想要的界面。
而在所有的xml界面文件中,根节点必须是布局,即先有布局,然后在布局中组织控件或嵌套布局,android中的布局有5种,熟悉各种布局的使用对我们以后开发中更好的组织界面大有益处,以下简单介绍。
表格布局,就是类似我们在网页中以表格来组织控件的布局。以N行N列的形式排列出相应的控件。
1 <TableLayout
2 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
3 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
4 android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView1"
5 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
6 android:layout_centerVertical="true" >
7
8 <TableRow
9 android:id="@+id/tableRow1"
10 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
11 android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
12
13 <Button
14 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
15 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
16 android:text="1行1列" />
17
18 <Button
19 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
20 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
21 android:text="1行2列" />
22 </TableRow>
23
24 <TableRow
25 android:id="@+id/tableRow2"
26 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
27 android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
28
29 <Button
30 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
31 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
32 android:text="2行1列" />
33
34 <Button
35 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
36 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
37 android:text="2行2列" />
38 </TableRow>
39
40 <TableRow
41 android:id="@+id/tableRow3"
42 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
43 android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
44
45 <Button
46 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
47 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
48 android:text="3行1列" />
49
50 <Button
51 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
52 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
53 android:text="3行2列" />
54 </TableRow>
55 </TableLayout>
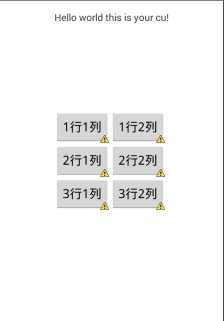
线性布局,比较简单,就是以水平或垂直的方式一行一个或一列一个的形式摆放控件。
1 <LinearLayout
2 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
3 android:layout_height="fill_parent"
4 android:orientation="vertical" >//水平或垂直
5
6 <Button
7 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
8 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
9 android:text="1行" />
10
11 <Button
12 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
13 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
14 android:text="2行" />
15
16 <Button
17 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
18 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
19 android:text="3行" />
20 </LinearLayout>
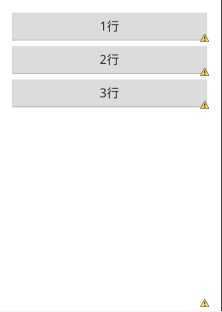
相对布局,最为灵活得分一种布局,用于组织一些复杂界面,在此布局中的子元素里与位置相关的属性将生效。例如android:layout_below, android:layout_above, android:layout_centerVertical等。注意在指定位置关系时,引用的ID必须在引用之前,先被定义,否则将出现异常。
1 <RelativeLayout
2 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
3 android:layout_height="fill_parent"
4 android:orientation="vertical" >
5
6 <Button
7 android:id="@+id/text_01"
8 android:layout_width="50dp"
9 android:layout_height="50dp"
10 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
11 android:gravity="center"
12 android:text="1" />
13
14 <Button
15 android:id="@+id/text_02"
16 android:layout_width="50dp"
17 android:layout_height="50dp"
18 android:layout_above="@id/text_01"//相对布局中的特有属性,xx之上/之下/之左/之右等
19 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
20 android:gravity="center"
21 android:text="2" />
22
23 <Button
24 android:id="@+id/text_03"
25 android:layout_width="50dp"
26 android:layout_height="50dp"
27 android:layout_above="@id/text_01"
28 android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/text_02"//相对布局中的特有属性,在xx的左边
29 android:gravity="center"
30 android:text="3" />
31 </RelativeLayout>

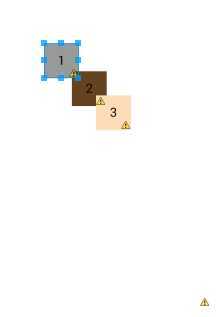
绝对布局,在此布局中的子元素的android:layout_x和android:layout_y属性将生效,用于描述该子元素的坐标位置,一经设置变不能改变位置,适用一些不经常变化的控件或界面。
1 <AbsoluteLayout
2 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
3 android:layout_height="fill_parent"
4 android:orientation="vertical" >
5
6 <Button
7 android:layout_width="50dp"
8 android:layout_height="50dp"
9 android:layout_x="50dp"
10 android:layout_y="50dp"
11 android:background="#999999"
12 android:gravity="center"
13 android:text="1" />
14
15 <Button
16 android:layout_width="50dp"
17 android:layout_height="50dp"
18 android:layout_x="90dp"
19 android:layout_y="90dp"
20 android:background="#ff654321"
21 android:gravity="center"
22 android:text="2" />
23
24 <Button
25 android:layout_width="50dp"
26 android:layout_height="50dp"
27 android:layout_x="125dp"
28 android:layout_y="125dp"
29 android:background="#fffedcba"
30 android:gravity="center"
31 android:text="3" />
32 </AbsoluteLayout>
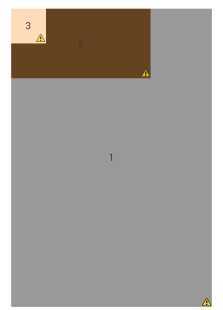
帧布局,网上说的有些别扭,我自己理解就类似css中的z-index,可以实现遮罩,即有层的效果。注意:所有的帧默认都是从屏幕左上角开始绘制,然后按照控件的声明顺序,依次叠加,层级逐渐升高。
1 <FrameLayout
2 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
3 android:layout_height="fill_parent"
4 android:orientation="vertical" >
5
6 <TextView
7 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
8 android:layout_height="fill_parent"
9 android:background="#999999"
10 android:gravity="center"
11 android:text="1" />
12
13 <TextView
14 android:layout_width="200dp"
15 android:layout_height="100dp"
16 android:background="#ff654321"
17 android:gravity="center"
18 android:text="2" />
19
20 <TextView
21 android:layout_width="50dp"
22 android:layout_height="50dp"
23 android:background="#fffedcba"
24 android:gravity="center"
25 android:text="3" />
26 </FrameLayout>
五大布局已经介绍完毕,有些简单,(因为这个布局我觉得确实也没什么好说的,结合配图我觉得已经很能说明问题了)。我在写这个系列之前也说了“我并不想做重复性的工作”,类似这种基础的东西,网上很多人写的比我好也很详细,我只是想把自己在学习过程中认为有必要和大家分享的一些经验和技巧写出来,所以你可以看到我并没有写什么HelloWorld之类的,因为与其把时间花在这种已经泛滥的内容上,倒不如多花时间去贡献一些独有的,或被大家忽略的内容上。
写技术博客真的很费时间,得理顺思路、组织语言、写Demo、截图、排版等等,有时候真羡慕那些可以一周一篇甚至几天一篇得大牛们。最近学的内容和点都比较多,看着大篇凌乱的笔记,一时间都不知道该从哪去写,自己更新的有些慢,不过自己还是会坚持的,一起加油!
.Net码农学Android---五分钟了解布局,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:android style class blog code http
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/clownvary/p/3809525.html