标签:
------Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! -------
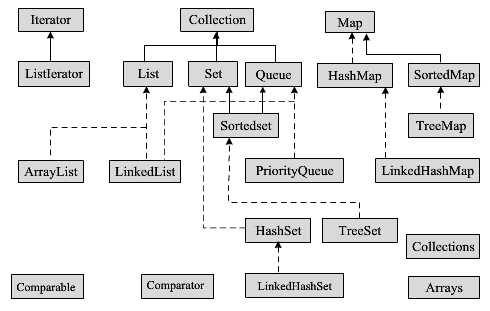
一、基本概念
1)Collection:一个独立元素的序列,这些元素都服从一条或多条规则。List必须按照插入的顺序
保存元素,而Set不能有重复元素。Queue按照排队规则了确定对象产生的顺序(通常与它们被插
入的顺序相同)。
2)Map:一组成对的“键值对”对象,允许你使用键来查找值。ArrayList允许你使用数字来查找值
,因此在某种意义上讲,他讲数字与对象关联在了一起。映射表允许我们使用另一个对象来查找某
个对象,它也被称为“关联数组”,因为它将某些对象与另外一些对象关联在了一起;或者被称为“字
典”,因为你可以使用键对象来查找值对象,就像在字典中使用单词来定义一样。Map是强大的编程
工具。
Collection vs Collections
首先,Collection 和 Collections 是两个不同的概念。之所以放在一起,是为了更好的比较。
Collection是容器层次结构中根接口。而Collections是一个提供一些处理容器类静态方法的类。
JDK不提供Collection接口的具体实现,而是提供了更加具体的子接口(如Set和List)实现。
那Collection接口存在有何作用呢?存在即是道理。
原因在于:所有容器的实现类(如ArrayList实现了List接口,HashSet实现了Set接口)提供
了两个‘标准’的构造函数来实现:1、一个无参的构造方法(void)2、一个带有Collection类型单
参数构造方法,用于创建一个具有其参数相同元素新的Collection及其实现类等。实际上:因为所
有通用的容器类遵从Collection接口,用第二种构造方法是允许容器之间相互的复制。
Conllection接口概括了序列的概念——一种存放一组对象的方式。下面用Integer对象填充一个
Collection(这里用ArrayList表示)示例,然后打印所产生的容器中的所有元素:
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 4 5 public class SimpleCollection { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 Collection<Integer> c = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 10 11 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 12 13 c.add(i); 14 15 } 16 17 for(Integer i : c) { 18 19 System.out.print(i + ", "); 20 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 }
因为这个示例只使用了Collection方法,因此任何继承自Collection的类的对象都可以正常
工作,但是ArrayList是最基本的序列类型。
add()方法的名称就表明它是要将一个新元素放置到Collection中。但是,文档中非常仔细
地叙述到:“要确保这个Collection包含指定的元素。”这个因为考虑到了Set的含义,因为在Set
中只有元素不存在的情况下才会添加。在使用ArrayList,或者任何种类的List时,add()总是表
示“把它放进去”,因为List不关心是否存在重复。
二、容器的打印
对TreeSet,HashSet,LinkedList,ArrayList,TreeMap,HashMap的例子如下:
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class CollectionAll 4 { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) 7 { 8 printLists(); 9 10 printSets(); 11 12 printMaps(); 13 } 14 15 private static void printLists() 16 { 17 List<String> a1 = new ArrayList<String>(); 18 a1.add("List"); 19 a1.add("Set"); 20 a1.add("Queue"); 21 a1.add("Map"); 22 a1.add("List"); 23 System.out.println("ArrayList Elements:"); 24 System.out.println(" " + a1); 25 26 List<String> l1 = new LinkedList<String>(); 27 l1.add("List"); 28 l1.add("Set"); 29 l1.add("Queue"); 30 l1.add("Map"); 31 l1.add("List"); 32 System.out.println("LinkedList Elements:"); 33 System.out.println(" " + l1); 34 } 35 private static void printSets() 36 { 37 Set<String> h1 = new HashSet<String>(); 38 h1.add("List"); 39 h1.add("Set"); 40 h1.add("Queue"); 41 h1.add("Map"); 42 h1.add("List"); 43 System.out.println("HashSet Elements:"); 44 System.out.println(" " + h1); 45 46 Set<String> t1 = new TreeSet<String>(); 47 t1.add("List"); 48 t1.add("Set"); 49 t1.add("Queue"); 50 t1.add("Map"); 51 t1.add("List"); 52 System.out.println("TreeSet Elements:"); 53 System.out.println(" " + t1); 54 } 55 56 private static void printMaps() 57 { 58 Map<String, String> h1 = new HashMap<String, String>(); 59 h1.put("List", "ArrayList"); 60 h1.put("Set", "HashSet"); 61 h1.put("Queue", "PriorityQueue"); 62 h1.put("Map", "HashMap"); 63 h1.put("List", "ArrayList"); 64 System.out.println("HashMap Elements:"); 65 System.out.println(" " + h1); 66 67 Map<String, String> t1 = new TreeMap<String,String>(); 68 t1.put("List", "ArrayList"); 69 t1.put("Set", "HashSet"); 70 t1.put("Queue", "PriorityQueue"); 71 t1.put("Map", "HashMap"); 72 t1.put("List", "ArrayList"); 73 System.out.println("TreeMap Elements:"); 74 System.out.println(" " + t1); 75 76 } 77 }
运行结果:
ArrayList Elements: [List, Set, Queue, Map, List] LinkedList Elements: [List, Set, Queue, Map, List] HashSet Elements: [Map, Queue, Set, List] TreeSet Elements: [List, Map, Queue, Set] HashMap Elements: {Map=HashMap, Queue=PriorityQueue, Set=HashSet, List=ArrayList} TreeMap Elements: {List=ArrayList, Map=HashMap, Queue=PriorityQueue, Set=HashSet}
这里展示了Java容器类库中的两种主要类型,它们的区别在于容器中每个“槽”保存的元素个
数。Collection在每个槽中只能保存一个元素。此类容器包含:
List:它以特定的顺序保存一组元素;
Set:元素不能重复;
Queue:值允许在容器的一“端”插入对象,并从另外一“端”移除对象。Map在每个槽内保存了两
个对象,即键和与之相关的值。
从打印结果来看,ArrayList和LinkedList都是List类型,它们都按照被插入的顺序保存元素
。两者的不同之处不仅在于执行某些类型的操作时的性能,而且LinkedList包含的操作也多于
ArrayList。
HashSet、TreeSet和LinkedHashSet都是Set类型,每个相同的项只有保存一次,但输出
也显示了不同的Set实现存储元素的方式也不同。HashSet使用的是相当复杂的方式来存储元素
的,因此,存储的顺序看起来并无实际意义。如果存储顺序很重要,那么可以使用TreeSet,它
按照比较结果的升序保存对象;或者使用LinkedHashSet,它按照被添加的顺序保存对象。
本例使用了三种基本风格的Map:HashMap、TreeMap和LinkedHashSet。与HashSet一
样,HashMap也提供了最快的查找技术,也没有按照任何明显的顺序来曹操其元素。TreeMap
按照比较结果的升序保存键,而LinkedHashMap则按照插入顺序保存键,同时还保留了HashMap
的查询速度。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiongxuesong/p/4560400.html