标签:
前面小试了一下scrapy抓取博客园的博客(您可在此查看scrapy爬虫成长日记之创建工程-抽取数据-保存为json格式的数据),但是前面抓取的数据时保存为json格式的文本文件中的。这很显然不满足我们日常的实际应用,接下来看下如何将抓取的内容保存在常见的mysql数据库中吧。
说明:所有的操作都是在“scrapy爬虫成长日记之创建工程-抽取数据-保存为json格式的数据”的基础上完成,如果您错过了这篇文章可以移步这里查看scrapy爬虫成长日记之创建工程-抽取数据-保存为json格式的数据
环境:mysql5.1.67-log
操作步骤:
1、检查python是否支持mysql
[root@bogon ~]# python Python 2.7.10 (default, Jun 5 2015, 17:56:24) [GCC 4.4.4 20100726 (Red Hat 4.4.4-13)] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import MySQLdb Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ImportError: No module named MySQLdb
如果出现:ImportError: No module named MySQLdb则说明python尚未支持mysql,需要手工安装,请参考步骤2;如果没有报错,请调到步骤3
2、python安装mysql支持
[root@bogon ~]# pip install mysql-python Collecting mysql-python Downloading MySQL-python-1.2.5.zip (108kB) 100% |████████████████████████████████| 110kB 115kB/s Building wheels for collected packages: mysql-python Running setup.py bdist_wheel for mysql-python Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/8c/0d/11/d654cad764b92636ce047897dd2b9e1b0cd76c22f813c5851a Successfully built mysql-python Installing collected packages: mysql-python Successfully installed mysql-python-1.2.5
安装完以后再次运行步骤1,检查python是否已经支持mysql
如果还有问题您可以尝试:LC_ALL=C pip install mysql-python
如果依然报错:error: Python.h: No such file or directory
您可以尝试先安装python-devel:
yum install python-devel
3、创建数据库和表
CREATE DATABASE cnblogsdb DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; CREATE TABLE `cnblogsinfo` ( `linkmd5id` char(32) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘url md5编码id‘, `title` text COMMENT ‘标题‘, `description` text COMMENT ‘描述‘, `link` text COMMENT ‘url链接‘, `listUrl` text COMMENT ‘分页url链接‘, `updated` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘最后更新时间‘, PRIMARY KEY (`linkmd5id`) ) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
注意:
a)、创建数据库的时候加上DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci,这样才不至于出现乱码。我就因为这个问题折腾了很久。
b)、数据库表的编码为utf8
4、设置mysql配置信息
根据前面的文章(scrapy爬虫成长日记之创建工程-抽取数据-保存为json格式的数据)我们可以知道,最终scrapy是通过pipelines.py对抓取的结果进行处理的。很显然要保存到mysql数据库中的话,修改pipelines.py这个文件是在所难免的了。然而在进行mysql操作的时候,我们需要先连上数据库,这时候就设计到数据库连接字符串的问题了。我们可以直接写死在pipelines.py文件中,但是这样又不利于程序的维护,因此我们可以考虑将配置信息写在项目的配置文件settings.py中。
settings.py中添加如下配置项
# start MySQL database configure setting MYSQL_HOST = ‘localhost‘ MYSQL_DBNAME = ‘cnblogsdb‘ MYSQL_USER = ‘root‘ MYSQL_PASSWD = ‘root‘ # end of MySQL database configure setting
5、修改pipelines.py
修改完的结果如下,需要注意的pipelines.py中定义了两个类。JsonWithEncodingCnblogsPipeline是写入json文件用的,而MySQLStoreCnblogsPipeline(需要记住,后面会用到哦!)才是写入数据库用的。
MySQLStoreCnblogsPipeline类做的主要功能有
a)、读取数据库配置文件,并生成数据库实例,主要通过类方法from_settings实现,
b)、如果url不存在则直接写入,如果url存在则更新,通过自定义的方法_do_upinsert实现,
c)、确保url唯一性的md5函数_get_linkmd5id 。
[root@bogon cnblogs]# more pipelines.py # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don‘t forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html from scrapy import signals import json import codecs from twisted.enterprise import adbapi from datetime import datetime from hashlib import md5 import MySQLdb import MySQLdb.cursors class JsonWithEncodingCnblogsPipeline(object): def __init__(self): self.file = codecs.open(‘cnblogs.json‘, ‘w‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) def process_item(self, item, spider): line = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + "\n" self.file.write(line) return item def spider_closed(self, spider): self.file.close() class MySQLStoreCnblogsPipeline(object): def __init__(self, dbpool): self.dbpool = dbpool @classmethod def from_settings(cls, settings): dbargs = dict( host=settings[‘MYSQL_HOST‘], db=settings[‘MYSQL_DBNAME‘], user=settings[‘MYSQL_USER‘], passwd=settings[‘MYSQL_PASSWD‘], charset=‘utf8‘, cursorclass = MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor, use_unicode= True, ) dbpool = adbapi.ConnectionPool(‘MySQLdb‘, **dbargs) return cls(dbpool) #pipeline默认调用 def process_item(self, item, spider): d = self.dbpool.runInteraction(self._do_upinsert, item, spider) d.addErrback(self._handle_error, item, spider) d.addBoth(lambda _: item) return d #将每行更新或写入数据库中 def _do_upinsert(self, conn, item, spider): linkmd5id = self._get_linkmd5id(item) #print linkmd5id now = datetime.utcnow().replace(microsecond=0).isoformat(‘ ‘) conn.execute(""" select 1 from cnblogsinfo where linkmd5id = %s """, (linkmd5id, )) ret = conn.fetchone() if ret: conn.execute(""" update cnblogsinfo set title = %s, description = %s, link = %s, listUrl = %s, updated = %s where linkmd5id = %s """, (item[‘title‘], item[‘desc‘], item[‘link‘], item[‘listUrl‘], now, linkmd5id)) #print """ # update cnblogsinfo set title = %s, description = %s, link = %s, listUrl = %s, updated = %s where linkmd5id = %s #""", (item[‘title‘], item[‘desc‘], item[‘link‘], item[‘listUrl‘], now, linkmd5id) else: conn.execute(""" insert into cnblogsinfo(linkmd5id, title, description, link, listUrl, updated) values(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s) """, (linkmd5id, item[‘title‘], item[‘desc‘], item[‘link‘], item[‘listUrl‘], now)) #print """ # insert into cnblogsinfo(linkmd5id, title, description, link, listUrl, updated) # values(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s) #""", (linkmd5id, item[‘title‘], item[‘desc‘], item[‘link‘], item[‘listUrl‘], now) #获取url的md5编码 def _get_linkmd5id(self, item): #url进行md5处理,为避免重复采集设计 return md5(item[‘link‘]).hexdigest() #异常处理 def _handle_error(self, failue, item, spider): log.err(failure)
6、启用MySQLStoreCnblogsPipeline类,让它工作起来
修改setting.py配置文件,添加MySQLStoreCnblogsPipeline的支持
ITEM_PIPELINES = { ‘cnblogs.pipelines.JsonWithEncodingCnblogsPipeline‘: 300, ‘cnblogs.pipelines.MySQLStoreCnblogsPipeline‘: 300, }
至此,所有的需要修改的文件都修改好了,下面测试看结果如何。
7、测试
[root@bogon cnblogs]# scrapy crawl CnblogsSpider
查看数据库结果:
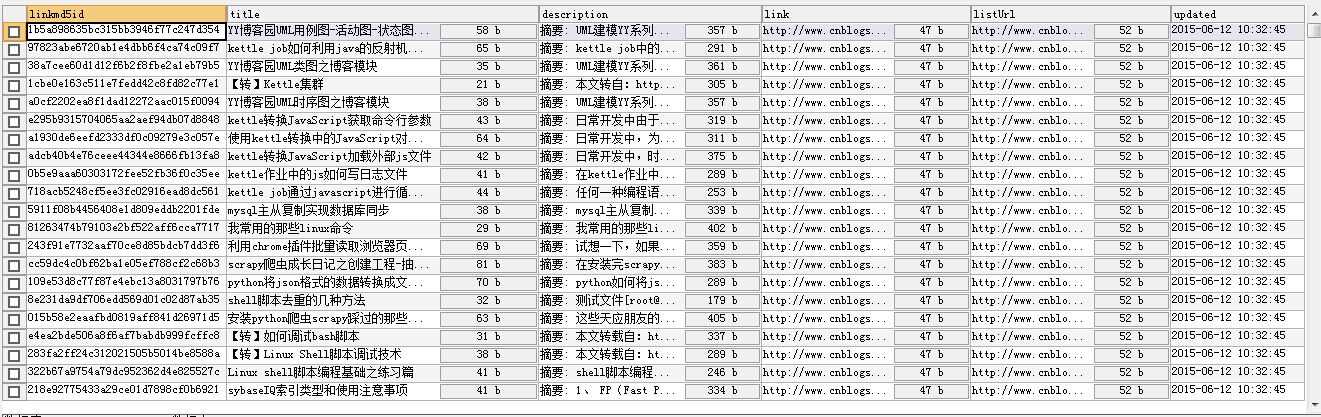
至此,scrapy抓取网页内容写入数据库的功能就已经实现了。然而这个爬虫的功能还太弱小了,最基本的文件下载、分布式抓取等都功能都还不具备;同时也试想一下现在很多网站的反爬虫抓取的,万一碰到这样的网站我们要怎么处理呢?接下来的一段时间里我们来逐一解决这些问题吧。随便畅想一下,如果爬虫足够强,内容足够多;我们是不是可以打造一个属于自己的垂直搜索引擎呢?想想就兴奋,尽情YY去吧!!!
最后源码更新至此:https://github.com/jackgitgz/CnblogsSpider
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/rwxwsblog/p/4572367.html