标签:
开始之前
系统环境
监控内容
使用CRT上传软件包
安装邮件服务
常用到的命令
启动nrpe
配置开发环境
在首次配置了nagios监控端后,在浏览器输入地址后连接不上
安装pnp4nagios后出现The requested URL /pnp4nagios/graph was not found on this server.
出现“CHECK_NRPE: Error - Could not complete SSL handshake.”的错误
执行 ./configure时报错:configure error cannot find ssl headers
解压./configure 后,在nagios-4.0.8进行make all报错
错误:perfdata directory "/usr/local/pnp4nagios/var/perfdata/" is empty
声明:本文中的命令都经过了测试,但难免有所纰漏,如果你发现命令粘贴后运行有错,可能是由于符号的格式(尤其是破折号)导致的,此时你应该自己手打一遍命令。对于本文中发现的错误和建议,请发送邮件给我:
kylinlingh@foxmail.com,请在邮件主题里注明“关于nagios的问题(建议)”。
一共3台机器,全都按照CentOS7最小化模式安装系统
| 系统版本号 | [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.0.1406 (Core) |
| 监控主机 (一台) | IP地址:192.168.1.204 主机名称:nagios_server_204 |
| 远程主机 (两台) | IP地址:192.168.1.112 主机名称:nagios_slave_112
IP地址:192.168.1.113 主机名称:nagios_slave_113 |
| 分区情况 | 安装时使用默认分区(使用 df 命令来查看) [root@localhost ~]# df -h |
| 要监控的服务 | 监控命令 |
| cpu负载 | (check_linux_state.pl -C) |
| 当前用户登录数量 | (check_users) |
| 磁盘使用情况 | (check_disk) |
| 总进程数 | (check_procs) |
| 内存使用情况 | (check_linux_stats.pl -M) |
| 负载均衡 | (check_load) |
| 磁盘IO | (check_linux_stats.pl -I) |
| 网络流量 | (check_linux_stats.pl -N) |
| 打开的文件数量 | (check_linux_stats.pl -F) |
| socket连接数 | (check_linux_stats.pl -S) |
| 进程使用的内存和CPU | (check_linux_stats.pl -T) |
| 指定的网站是否可连接 | (check_http) |
| 系统在线时长 | (check_uptime) |
监控主机
| 软件包 | 下载地址 |
| nagios-4.0.8.tar.gz | 请到我的github地址里下载: https://github.com/Kylinlin/install_nagios_automatically/tree/master/nagios_tools_for_server 注明:我的github项目install_nagios_automatically是一个一键自动化安装nagios的项目(能运行,但还在完善中) |
| nagios-plugins-2.0.3.tar.gz | |
| nrpe-2.15.tar.gz | |
| pnp-0.4.14.tar.gz | |
| Sys-Statistics-Linux-0.66.tar.gz | |
| libxml2-2.7.1.tar.gz |
远程主机
| 软件包 | 下载地址 |
| nagios-plugins-2.0.3.tar.gz | 请到我的github地址里下载: https://github.com/Kylinlin/install_nagios_automatically/tree/master/nagios_tools_for_client |
| nrpe-2.15.tar.gz | |
| Sys-Statistics-Linux-0.66.tar.gz |
Centos7相比较以前的Centos有一些涉及到常用命令的变化,如果不事先了解,会在使用命令的时候造成巨大的困扰
l Centos7默认没有ifconfig和netstat两个命令了,ip addr命令代替了ifconfig,只要安装上net-tools包就可以继续使用ifconfig和netstat两个命令了
l systemctl命令的出现(systemctl可以看作是service和chkconfig的组合),虽然仍然可以使用以前的命令,但是会重定向到新的命令中,下面以http服务为例
| job | 以前的系统 | CentOS7 |
| 服务开机启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd on | systemctl enable httpd.service |
| 服务不开机启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd off | systemctl disable httpd |
| 服务状态 | service httpd status | systemctl status httpd |
| 所有服务的启动状态 | chkconfig --list | systemctl |
| 启动服务 | service httpd start | systemctl start httpd.service |
| 停止服务 | service httpd stop | systemctl stop httpd.service |
| 重启服务 | service httpd restart | systemctl restart httpd.service |
把监控系统里的所有机器都同步一次网络时间(非常重要)
[root@localhost ~]timedatectl #该命令用来检查当前时间和时区
如果发现所有机器的时区不一致,此时就要使用命令
[root@localhost ~]timedatectl list-timezones #该命令列出了所有的时区
[root@localhost ~]timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai #该命令把时区设置为上海
ntpdate time.nist.gov #该命令同步网络当前的时间
如果提示没有ntpdate命令,则安装ntp,并且配置系统自动更新时间
[root@localhost ~]# yum install ntp -y
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov
[root@localhost ~]# echo ‘#time sync‘>>/var/spool/cron/root
[root@localhost ~]# echo ‘*/10**** /usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1‘>>/var/spool/cron/root
不关闭selinux可能会导致一些难以察觉的错误,为了保险起见,首先关闭selinux:
[root@localhost ~]vi /etc/selinux/config
重启机器
检查selinux是否关闭:
[root@localhost ~]getenforce #如果显示enforcing则没有关闭
我在这里使用的SSH连接工具是SecureCRT7.2,通过这个工具上传文件到Linux的步骤如下:
1. 首先在Linux中安装传送文件命令:
[root@localhost ~] yum install lrzsz -y
2. 然后在Linux中跳转到/usr/local/src目录下
[root@localhost ~] cd /usr/local/src
3. 运行CRT的传送文件命令
因为邮件报警服务需要安装mail功能
[root@localhost ~]yum install –y mailx
[root@localhost ~]yum install –y sendmail
[root@localhost ~]systemctl restart sendmail.service
[root@localhost ~]mail –s Test xxx@xxx.com (你的邮箱地址)
#此时进入输入模式,输入完邮件内容后按ctrl + d退出并且发送
| 命令内容 | 命令格式 |
| 检查nagios的配置文件是否有错 | /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig 或者 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg |
| 启动nagios | systemctl start nagios.service 或者 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg |
| 修改了nagios的配置文件后重新加载配置文件 | /etc/init.d/nagios reload |
[root@localhost ~]# yum install gcc glibc glibc-common -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install php php-gd perl -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install httpd gd gd-devel openssl openssl-devel -y
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service #设置CentOS开机启动服务
使用CRT上传所需的软件包(软件包在这里)
[root@localhost ~]useradd -m nagios
并将nagios以及apache用户加入到nagcmd组中
[root@localhost ~]groupadd nagcmd
[root@localhost ~]usermod -G nagcmd nagios
[root@localhost ~]usermod -a -G nagcmd apache #把apace用户添加到与nagios的一个组(apache用户会在安装apache时自动创建)
[root@localhost src]# tar -zxvf nagios-4.0.8.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# cd nagios-4.0.8
首先初始化和建立编译的环境
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]#./configure --with-command-group=nagcmd
如果能看到下面的基本配置信息则说明初始的环境已经成功配置完成:
之后按照提示执行命令来进行编译:
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]# make all
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]# make install
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]# make install-init
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]# make install-config
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]# make install-commandmode
[root@localhost nagios-4.0.8]# make install-webconf
安装完成之后,在/usr/local/nagios目录下如果能够看到这些目录:
就表示Naigos安装成功了。
Nagios的样例配置文件默认安装在/usr/local/nagios/etc目录下,配置这些文件就可以使得nagios按要求运行(详细的配置过程请参考我的另一篇博文:nagios服务配置详解)
此时应该为email指定您想用来接收nagios警告信息的邮件地址,默认是本机的nagios用户:
[root@localhost]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
email nagios@localhost #把描红的地方修改为你的email地址
创建一个登录nagios web程序的用户(用户名配置为nagiosadmin则不需要配置权限,设置为其他用户名就要配置权限),我在这里把用户名设置为kylinlin,密码为123456,这个用户帐号在以后通过web登录nagios认证时所用:
[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -bc /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users kylinlin 123456 #把描红的地方修改为你的用户名和密码
如果在上面创建登陆nagios web程序的用户名不是nagiosadmin(我在上面已经设置为kylinlin),在登陆nagios的web界面后(此时我们还不能登录,但如果你忽略了这一小节的配置,那么在后面的登陆中就会看到如下的界面),点击Hosts或Services会显示图片红色的错误提示
|
|
是因为nagios默认把全部的权限给nagiosadmin,所以可以通过修改cgi.cfg文件赋予kylinlin权限,切换到/usr/local/nagios/etc目录下
[root@localhost etc]# sed -i ‘s#nagiosadmin#kylinlin#g‘ cgi.cfg #这条命令将nagiosadmin用户名替换为kylinlin
[root@localhost etc]# grep kylinlin cgi.cfg #这条命令检查是否修改成功
以上过程配置结束以后需要重新启动httpd:
[root@localhost etc]# systemctl restart httpd.service
检查其主配置文件的语法是否正确:
[root@localhost etc]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
或者使用下面这个命令来检查语法
[root@localhost etc]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig
| 显示错误数为0才正确 |
配置成功
刚才已经提到Nagios主程序只是一个控制中心,而能够起到服务监测和系统监测等功能的是众多Nagios的插件,没有插件的Nagios系统其实只是一个空壳。因此在安装了Nagios平台之后我们还需要安装插件。
Nagios插件同样是在其官方网站下载,目前版本是1.4.15。我将下载的源码包放到/usr/local目录下,按照下面的步骤进行解压,编译和安装:
[root@localhost src]# tar zxf nagios-plugins-2.0.3.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# cd nagios-plugins-2.0.3
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]# ./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]#make
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]#make install
通过下面的命令查看安装了多少个插件
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]#ls /usr/local/nagios/libexec/|wc -l
然后把Nagios加入到服务列表中以使之在系统启动时自动启动:
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]# chkconfig --add nagios
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]# chkconfig nagios on
执行下面的命令来验证Nagios的样例配置文件:
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
在防火墙中打开http端口
firewall-cmd --add-service=http (即时打开)
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http(写入配置文件)
firewall-cmd --reload (重启防火墙)
启动nagios服务
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
之后可以在浏览器上访问链接http://192.168.1.204/nagios,输入登陆名和密码,如果能够正常看到页面,证明主程序和插件都安装和配置成功(如上图所示)!点击“Service”的链接来查看你本机的监视详情。此时可能需要给点时间让Nagios来检测你机器上所依赖的服务。
注意上图中出现了一个处于WARNING状态的服务,所以我配置过的邮箱里已经收到了报警信息,如果你没有收到报警信息,此时检查你是否已经配置了接收报警信息的邮箱,同时检查是否被当做垃圾邮件而屏蔽了。
[root@localhost src]# tar -zxf nrpe-2.15.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# cd nrpe-2.15
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# ./configure --with-nrpe-user=nagios \
--with-nrpe-group=nagios \
--with-nagios-user=nagios \
--with-nagios-group=nagios \
--enable-command-args \
--enable-ssl
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make all
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make install-plugin
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make install-daemon
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make install-daemon-config
检查一下/usr/local/nagios/libexec目录下是否已经安装了check_nrpe插件
[root@localhost libexec]# ls | grep check_nrpe
check_nrpe
至此,监控主机已经完成了nagios的安装
| 命令内容 | 命令格式 |
| 关闭nrpe | pkill nrpe |
| 启动nrpe | /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d |
| 启动nrpe(只适用于有编写nrpe脚本的情况) | systemctl start nrpe.service |
| 检查nrpe是否启动 | netstat -lnt (通过检查5666端口是否打开) |
首先关闭防火墙:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# yum install gcc glibc glibc-common -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install gd gd-devel openssl openssl-devel -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install php php-gd perl net-tools -y
使用CRT上传所需的软件包(软件包在这里)
1)先添加nagios用户
[root@localhost ~]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin nagios #禁止nagios用户登录
2)NRPE依赖于nagios-plugins,因此,需要先安装之
进入到/usr/local/src目录下开始执行下面的命令
[root@localhost src]# tar zxf nagios-plugins-2.0.3.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# cd nagios-plugins-2.0.3
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]# ./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]# make all
[root@localhost nagios-plugins-2.0.3]# make install
进入到/usr/local/src目录下开始执行下面的命令
[root@localhost src]# tar -zxf nrpe-2.15.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# cd nrpe-2.15
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# ./configure --with-nrpe-user=nagios \
--with-nrpe-group=nagios \
--with-nagios-user=nagios \
--with-nagios-group=nagios \
--enable-command-args \
--enable-ssl
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make all
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make install-plugin
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make install-daemon
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# make install-daemon-config
[root@localhost nrpe-2.15]# ls /usr/local/nagios/libexec/ #如果安装成功里面有好多NRPE的插件
注意是否有check_nrpe这个插件(没有的话就说明了nrpe没有安装成功)
方法一:用命令启动nrpe
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
#这条命令启动nrpe
如果要重启nrpe,先执行命令:
[root@localhost ~]# pkill nrpe #关闭nrpe
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -lnt #这条命令用来检查端口,看5666端口是否已经被关闭
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
#重启nrpe进程
方法二:创建启动nrpe的脚本
为了便于NRPE服务的启动,可以将如下内容定义为/etc/init.d/nrpe脚本,在/etc/init.d目录下新建一个名为nrpe的文件,把下面内容复制进去
| #!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 88 12 # description: NRPE DAEMON
NRPE=/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe NRPECONF=/usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
case "$1" in start) echo -n "Starting NRPE daemon..." $NRPE -c $NRPECONF -d echo " done." ;; stop) echo -n "Stopping NRPE daemon..." pkill -u nagios nrpe echo " done." ;; restart) $0 stop sleep 2 $0 start ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 start|stop|restart" ;; esac exit 0 |
然后添加运行权限:
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nrpe
启动nrpe
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nrpe.service
检查5666端口是否成功启动
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -tnlp
5666端口已经成功启动
在/usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg文件中添加监控主机的ip地址
[root@localhost etc]# vi nrpe.cfg +81
将allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1 修改为 allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.1.204(这是监控主机的ip地址,本机的ip地址为192.168.1.112)
然后重启nrpe
[root@localhost ~]# pkill nrpe
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
在监控主机上(ip地址为192.168.1.204)输入下面的命令来检查两个机器之间是否成功通信
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nagios/libexec/
[root@localhost libexec]# ./check_nrpe -H 192.168.1.113
NRPE v2.15 #通信成功
至此,远程主机安装nagios完毕
重要提醒:看清楚你要安装的php4nagios的版本,因为0.4和0.6的配置方式是不一致的
[root@localhost ~]# yum install rrdtool librrds-perl -y
进入到/usr/local/src目录下开始执行下面的命令
[root@localhost src]# tar zxf pnp4nagios-0.6.25.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# cd pnp4nagios-0.6.25
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# ./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make all
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make install
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make install-webconf
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make install-config
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make install-init
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# cd ./sample-config
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make install-webconf
[root@localhost pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# cd /usr/local/pnp4nagios/etc/
[root@localhost etc]# mv misccommands.cfg-sample misccommands.cfg
[root@localhost etc]# mv rra.cfg-sample rra.cfg
[root@localhost etc]# mv nagios.cfg-sample nagios.cfg
[root@localhost etc]# cd pages/
[root@localhost pages]# mv web_traffic.cfg-sample web_traffic.cfg
[root@localhost pages]# cd ../check_commands/
[root@localhost check_commands]# mv check_all_local_disks.cfg-sample check_all_local_disks.cfg
[root@localhost check_commands]# mv check_nrpe.cfg-sample check_nrpe.cfg
[root@localhost check_commands]# mv check_nwstat.cfg-sample check_nwstat.cfg
[root@localhost check_commands]# /etc/init.d/npcd start
[root@localhost check_commands]# chkconfig npcd on
配置Nagios数据输出接口(以BULK模式运行)详情参考官网 https://docs.pnp4nagios.org/pnp-0.6/config#bulk_mode:
[root@localhost ~]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
| process_performance_data=1 #默认为0,修改为1 并在该文件中添加下面的内容 # # service performance data # service_perfdata_file=/usr/local/pnp4nagios/var/service-perfdata service_perfdata_file_template=DATATYPE::SERVICEPERFDATA\tTIMET::$TIMET$\tHOSTNAME::$HOSTNAME$\tSERVICEDESC::$SERVICEDESC$\tSERVICEPERFDATA::$SERVICEPERFDATA$\tSERVICECHECKCOMMAND::$SERVICECHECKCOMMAND$\tHOSTSTATE::$HOSTSTATE$\tHOSTSTATETYPE::$HOSTSTATETYPE$\tSERVICESTATE::$SERVICESTATE$\tSERVICESTATETYPE::$SERVICESTATETYPE$ service_perfdata_file_mode=a service_perfdata_file_processing_interval=15 service_perfdata_file_processing_command=process-service-perfdata-file # # host performance data starting with Nagios 3.0 # host_perfdata_file=/usr/local/pnp4nagios/var/host-perfdata host_perfdata_file_template=DATATYPE::HOSTPERFDATA\tTIMET::$TIMET$\tHOSTNAME::$HOSTNAME$\tHOSTPERFDATA::$HOSTPERFDATA$\tHOSTCHECKCOMMAND::$HOSTCHECKCOMMAND$\tHOSTSTATE::$HOSTSTATE$\tHOSTSTATETYPE::$HOSTSTATETYPE$ host_perfdata_file_mode=a host_perfdata_file_processing_interval=15 host_perfdata_file_processing_command=process-host-perfdata-file |
配置command.cfg
[root@localhost ~]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
| 在该文件中添加下面的内容
define command{ command_name process-service-perfdata-file command_line /usr/local/pnp4nagios/libexec/process_perfdata.pl --bulk=/usr/local/pnp4nagios/var/service-perfdata }
define command{ command_name process-host-perfdata-file command_line /usr/local/pnp4nagios/libexec/process_perfdata.pl --bulk=/usr/local/pnp4nagios/var/host-perfdata } |
在模板配置文件中添加图表图标模板:
[root@localhost ~]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/templates.cfg
| 在该文件中添加下面的内容 define host { name host-pnp action_url /pnp4nagios/index.php/graph?host=$HOSTNAME$&srv=_HOST_ register 0 }
define service { name service-pnp action_url /pnp4nagios/index.php/graph?host=$HOSTNAME$&srv=$SERVICEDESC$ register 0 } |
在监控主机和服务中调用图表模板(在主机和服务后面添加新的模板):
[root@localhost ~]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/localhost.cfg
| 按下面的内容修改(不是添加)该文件 define host{ use linux-server,host-pnp host_name localhost alias localhost address 127.0.0.1 } define service{ use local-service,service-pnp host_name localhost service_description PING check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60% } define service{ use local-service,service-pnp host_name localhost service_description Root Partition check_command check_local_disk!20%!10%!/ } … |
重启nagios和apache
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart nagios.service
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd.service
访问nagios界面即可看到图表小图标: 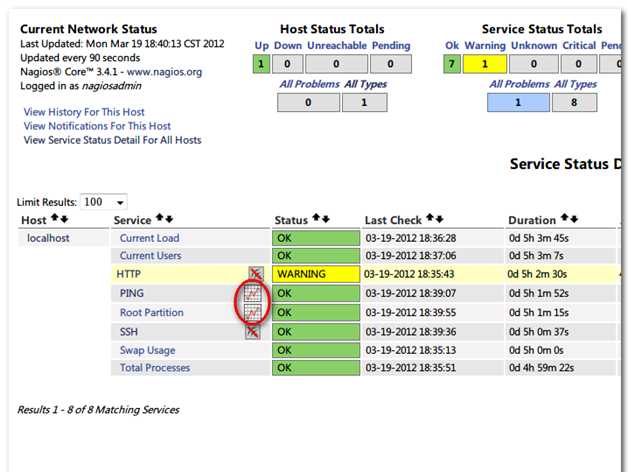
点击图标会显示pnp4nagios测试页面:
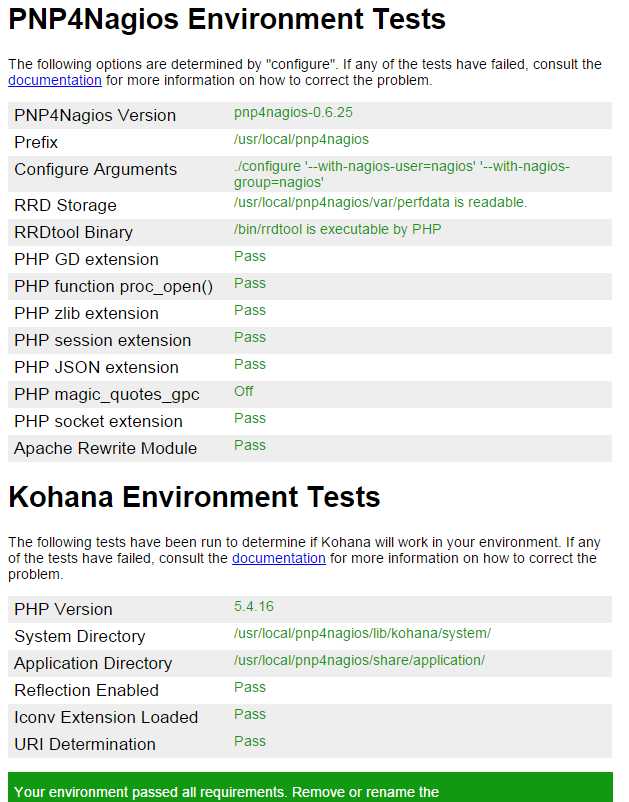
全是绿色代表配置正常,如果不是全绿,要逐个解决错误。然后移除或修改install.php文件:
[root@localhost ~]# rm -rf /usr/local/pnp4nagios/share/install.php
再次点击图标就会显示当前监控服务由pnp4nagios生成的图表了:
至此,nagios监控主机的出图配置已经全部完成
可能是防火墙屏蔽了80端口,此时打开防火墙的80端口即可:
firewall-cmd --add-service=http (即时打开)
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http(写入配置文件)
firewall-cmd --reload (重启防火墙)
如果出现如下错误:
You don‘t have permission to access /nagios/ on this server.nagios
此时要安装php
yum install php –y
然后重启httpd:
systemctl restart httpd.service
首先启动nrpe进程
systemctl restart nrped.service
此时可以检查nrpe绑定的5666端口是否被防火墙屏蔽了:
netstat -tnpl (观察是否有下面的两个服务之一)
如果5666端口没有打开就打开防火墙的5666端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp --permanent (添加5666端口)
firewall-cmd --reload (重启防火墙)
或者直接关闭防火墙
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
原因,当你在pnp4nagios安装的时候执行了make install-webconf,注意它生成了一个apache的配置文件。
你把这个文件:/etc/httpd/conf.d/pnp4nagios.conf 中的所有内容全部添加到apache的httpd.conf文件最后,再重新启动nagios和apache就应该可以啦。
跳转到/usr/local/src/pnp4nagios-0.6.25目录下执行命令
[root@nagios-test pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# make install-webconf
[root@nagios-test pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# cd ./sample-config && make install-webconf
[root@nagios-test pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# service nagios restart
[root@nagios-test pnp4nagios-0.6.25]# systemctl restart httpd.service
先安装开发环境:
yum install openssl openssl-devel
检查nagios监控端的允许地址和目标端的nrpe允许地址配置正确。比如被监控端的配置(命令:vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg):
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.1.112 (两个地址之间只有一个逗号,不能有空格)
原因是缺少openssl-devel包,
yum -y install openssl-devel
报出如下错误:
cd ./base && make
make[1]:Entering directory ‘/tmp/nagios/base‘
make[1]:*** No rule to make target ‘/include/locations.h‘, needed by ‘broker.o‘. Stop.
make[1]:Leaving directory ‘/tmp/nagios/base‘
make:***[all]Error 2
安装好perl就不出这个问题了!命令如下:
yum -y install perl
注意,install perl之后需要重新./configure一下,要不然还是提示这个错误
在监控主机上安装check-nrpe插件时(实际上就是nrpe的整个安装)
./configure 提示报错:
checking for SSL headers... configure: error: Cannot find ssl headers
如果这时运行命令 make all,则会报错:make: *** 没有规则可以创建目标“all”。 停止。
解决办法:
yum -y install openssl-devel
记得:装完openssl-devel之后,要执行 ./configure
然后再make all
make install-plugin
查阅了很多资料,最终根据官网http://docs.pnp4nagios.org/pnp-0.6/config上的Bulk 模式重新配置了PNP的相关文件(可以参照我上文的内容进行)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kylinlin/p/4574207.html