标签:
Question: 为何sql解析和高大上有关系?
Answer:因为数据库永远都是系统的核心,CRUD如此深入码农的内心。。。如果能把CRUD改造成高大上技术,如此不是造福嘛。。。
CRUD就是Create, Read, Update, Delete,转换成sql语句就是insert, select, update, delete
普通场景下,insert也就是一个insert了,没什么高深。。。
高并发场景下,insert就不是一个insert了,而是千千万万个insert。。。可以用到的技术有排队、分表、分区、分仓、缓存同步
普通场景下,select也就是一个select了,没什么高深。。。
高并发场景下,select就不是一个select了,而是千千万万,再千千万万个select。。。可以用到的技术有缓存、普通读写分离、深入读写分离、不锁、past锁、还有分表、分区、分仓。。。
你说这么多东西,是全部在一个sql中全部自动化掉好呢,还是让我们码农一个一个考虑,再一个一个写成代码逻辑的好?
肯定两种声音都有,还肯定有第三种声音。。。所以我还是照着我自己的思路来说吧,你们随便发挥想象。。。
我要让一个sql全部解决上面的效果,或者接近上面的效果
如何解决,那就是,以SELECT语句为例
比如有2个SELECT语句:
很简单的两句sql,可是Users是个虚拟表,真实表有16个表:Users.[A-F], Users.[0-9],分表策略为根据主键ID的第一个字母来分表, 因此:
其他:
由于只是个demo,所以没有实现上述全部功能,我们只说下关键原理、和代码。。。
我们用antlr来做词法解析、语法解析,然后再用tree walker把antlr解析出来的东西转换为我们要的数据结构,比如:SelectTerms, TableName, WhereClause, OrderByClause等
奥,我们还得写一个规则文件让Antlr吃进去,然后antlr就能调用tree walker生成我们要的数据结构了
(大家赶紧补下编译原理之类的基础知识以及ANTLR知识)
grammar SelectSQL; /* * Parser Rules */ compileUnit : start ; /* * Lexer Rules */ WS : [ \t\n\r]+ -> skip ; COMMA:‘,‘; SELECT: ‘SELECT‘; STAR:‘*‘; FROM:‘FROM‘; WHERE:‘WHERE‘; ORDERBY:‘ORDER BY‘; DIRECTION:‘ASC‘|‘DESC‘; CHAR: ‘a‘..‘z‘|‘A‘..‘Z‘; NUM: ‘0‘..‘9‘; STRING:‘\‘‘ .*? ‘\‘‘; LB:‘(‘; RB:‘)‘; LBRACE:‘[‘; RBRACE:‘]‘; CONDITIONS_OPERATOR :‘AND‘ |‘OR‘ ; CONDITION_OPERATOR :‘=‘ |‘>‘ |‘<‘ |‘<>‘ |‘!=‘ |‘>=‘ |‘<=‘ ; FCOUNT:‘COUNT‘; start :statement_list ; statement_list :statement statement* ; statement :selectStatement ; selectStatement :selectStmt fromStmt whereStmt? orderbyStmt? ; selectStmt :SELECT columns ; columns :column (COMMA column)* ; column : identifier | LBRACE identifier RBRACE | functionStmt | STAR ; functionStmt :function LB (parameters) RB ; function :FCOUNT ; parameters : parameter (COMMA parameter)* ; parameter : identifier | integer | string | STAR ; fromStmt :FROM table ; table : identifier | LBRACE identifier RBRACE ; whereStmt : WHERE conditions ; conditions : condition (CONDITIONS_OPERATOR condition)* ; condition :left CONDITION_OPERATOR right ; left : parameter ; right : parameter ; orderbyStmt :ORDERBY sortStmt ; sortStmt : sortCondition (COMMA sortCondition)* ; sortCondition :sortColumn DIRECTION ; sortColumn : identifier | LBRACE identifier RBRACE ; identifier :CHAR (CHAR|NUM)* ; integer :NUM+ ; string : STRING ;
真心呼唤广大开发人员深入编译原理之类的基础技术!
在eclipse中输入解析sql文本后,会被解析成tree
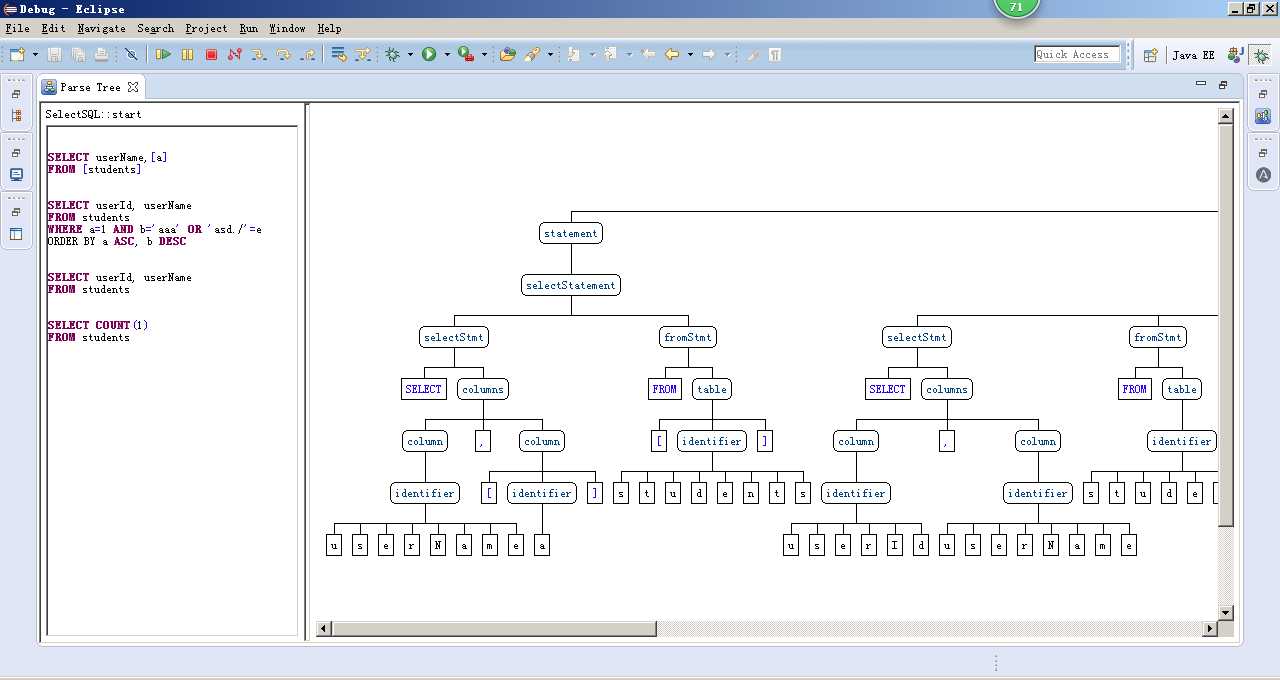
开源世界真强大啊,有yacc, flex, bison, antlr这些现成的解析工具。
我们先在eclipse中把规则测试通过后,再把这个.g4规则文件拷贝到我们的visual studio中,如下:
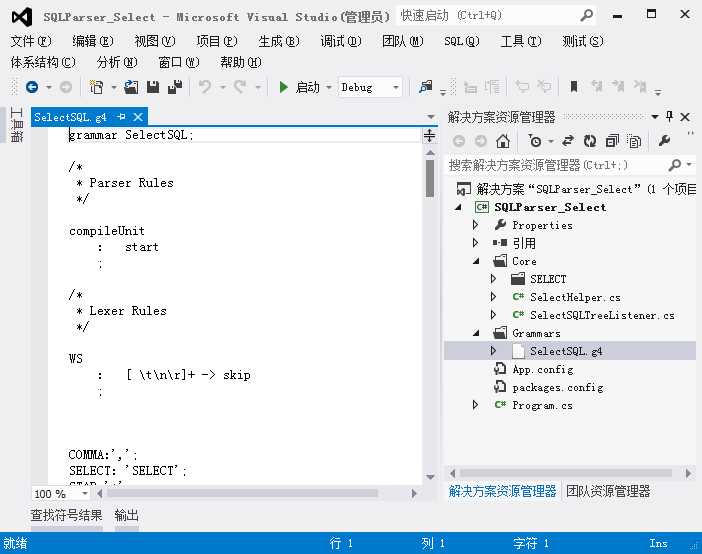
然后只要这个g4文件一保存,antlr的vs插件就会自动根据规则文件生成相关名称的词法解析类、文法解析类、以及我们即将要改写的TreeListener
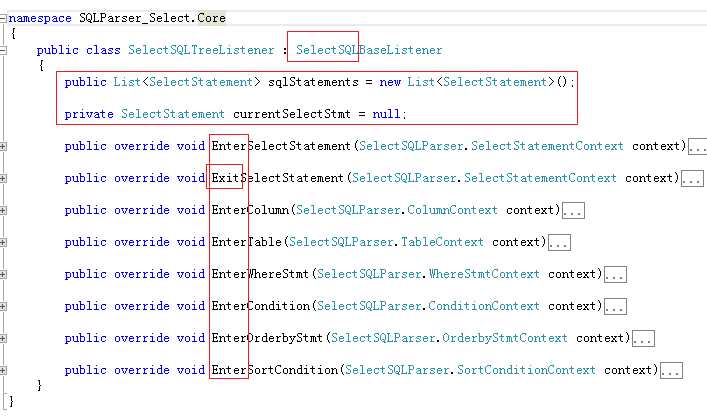
SelectSQLBaseListener:就是antlr插件自动生成的抽象类,我们的改动都是基于这个类,来做override改写(针对规则的enter/exit)
EnterXXXXX/ExitXXXX: 对应规则文件中的规则名称,Enter/Exit代表进入规则以及离开规则之前的行为动作
demo控制台程序运行输出效果:
输入SQL: SELECT * FROM users SELECT userId, userName FROM users SELECT COUNT(1) FROM users SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users SELECT userId, userName FROM users ORDER BY userName DESC SELECT userId, userName FROM users WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ ORDER BY userName DESC 输出SQL: select * from [users.0] select * from [users.1] select * from [users.2] select * from [users.3] select * from [users.4] select * from [users.5] select * from [users.6] select * from [users.7] select * from [users.8] select * from [users.9] select * from [users.a] select * from [users.b] select * from [users.c] select * from [users.d] select * from [users.e] select * from [users.f] select userId, userName from [users.0] select userId, userName from [users.1] select userId, userName from [users.2] select userId, userName from [users.3] select userId, userName from [users.4] select userId, userName from [users.5] select userId, userName from [users.6] select userId, userName from [users.7] select userId, userName from [users.8] select userId, userName from [users.9] select userId, userName from [users.a] select userId, userName from [users.b] select userId, userName from [users.c] select userId, userName from [users.d] select userId, userName from [users.e] select userId, userName from [users.f] select COUNT(1) from [users.0] select COUNT(1) from [users.1] select COUNT(1) from [users.2] select COUNT(1) from [users.3] select COUNT(1) from [users.4] select COUNT(1) from [users.5] select COUNT(1) from [users.6] select COUNT(1) from [users.7] select COUNT(1) from [users.8] select COUNT(1) from [users.9] select COUNT(1) from [users.a] select COUNT(1) from [users.b] select COUNT(1) from [users.c] select COUNT(1) from [users.d] select COUNT(1) from [users.e] select COUNT(1) from [users.f] select COUNT(*) from [users.0] select COUNT(*) from [users.1] select COUNT(*) from [users.2] select COUNT(*) from [users.3] select COUNT(*) from [users.4] select COUNT(*) from [users.5] select COUNT(*) from [users.6] select COUNT(*) from [users.7] select COUNT(*) from [users.8] select COUNT(*) from [users.9] select COUNT(*) from [users.a] select COUNT(*) from [users.b] select COUNT(*) from [users.c] select COUNT(*) from [users.d] select COUNT(*) from [users.e] select COUNT(*) from [users.f] select userId, userName from [users.0] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.1] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.2] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.3] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.4] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.5] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.6] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.7] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.8] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.9] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.a] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.b] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.c] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.d] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.e] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.f] order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.0] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.1] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.2] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.3] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.4] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.5] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.6] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.7] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.8] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.9] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.a] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.b] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.c] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.d] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.e] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC select userId, userName from [users.f] WHERE userId=‘1212121‘ order by userName DESC
希望大家能对基础技术真正感兴趣,赶紧学习编译原理、antlr吧。
很抱歉没能提供详细原理说明,大家baidubaidu就都有了。
代码下载 http://files.cnblogs.com/files/aarond/SQLParser_Select.rar
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/aarond/p/sqlparser.html