标签:
In information retrieval, Okapi BM25 (BM stands for Best Matching) is a ranking function used by search engines to rank matching documents according to their relevance to a given search query. It is based on the probabilistic retrieval framework developed in the 1970s and 1980s byStephen E. Robertson, Karen Spärck Jones, and others.
The name of the actual ranking function is BM25. To set the right context, however, it usually referred to as "Okapi BM25", since the Okapi information retrieval system, implemented at London‘s City University in the 1980s and 1990s, was the first system to implement this function.
BM25, and its newer variants, e.g. BM25F (a version of BM25 that can take document structure and anchor text into account), represent state-of-the-art TF-IDF-like retrieval functions used in document retrieval, such as web search.
BM25 is a bag-of-words retrieval function that ranks a set of documents based on the query terms appearing in each document, regardless of the inter-relationship between the query terms within a document (e.g., their relative proximity). It is not a single function, but actually a whole family of scoring functions, with slightly different components and parameters. One of the most prominent instantiations of the function is as follows.
Given a query 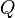 , containing keywords
, containing keywords 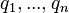 , the BM25 score of a document
, the BM25 score of a document  is:
is:
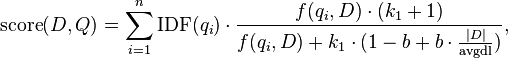
where  is
is  ‘s term frequency in the document
‘s term frequency in the document  ,
,  is the length of the document
is the length of the document  in words, and
in words, and 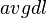 is the average document length in the text collection from which documents are drawn.
is the average document length in the text collection from which documents are drawn. 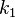 and
and  are free parameters, usually chosen, in absence of an advanced optimization, as
are free parameters, usually chosen, in absence of an advanced optimization, as 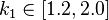 and
and 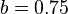 .[1]
.[1] 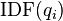 is the IDF (inverse document frequency) weight of the query term
is the IDF (inverse document frequency) weight of the query term  . It is usually computed as:
. It is usually computed as:
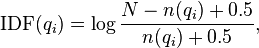
where 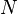 is the total number of documents in the collection, and
is the total number of documents in the collection, and 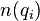 is the number of documents containing
is the number of documents containing  .
.
There are several interpretations for IDF and slight variations on its formula. In the original BM25 derivation, the IDF component is derived from the Binary Independence Model.
Please note that the above formula for IDF shows potentially major drawbacks when using it for terms appearing in more than half of the corpus documents. These terms‘ IDF is negative, so for any two almost-identical documents, one which contains the term and one which does not contain it, the latter will possibly get a larger score. This means that terms appearing in more than half of the corpus will provide negative contributions to the final document score. This is often an undesirable behavior, so many real-world applications would deal with this IDF formula in a different way:
 , to avoid common terms being ignored at all;
, to avoid common terms being ignored at all;Here is an interpretation from information theory. Suppose a query term  appears in
appears in 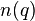 documents. Then a randomly picked document
documents. Then a randomly picked document  will contain the term with probability
will contain the term with probability 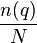 (where
(where 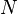 is again the cardinality of the set of documents in the collection). Therefore, the informationcontent of the message "
is again the cardinality of the set of documents in the collection). Therefore, the informationcontent of the message " contains
contains  " is:
" is:

Now suppose we have two query terms  and
and 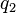 . If the two terms occur in documents entirely independently of each other, then the probability of seeing both
. If the two terms occur in documents entirely independently of each other, then the probability of seeing both  and
and 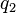 in a randomly picked document
in a randomly picked document  is:
is:

and the information content of such an event is:
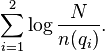
With a small variation, this is exactly what is expressed by the IDF component of BM25.
 BM25 turns into ranking functions known as BM11 (for
BM25 turns into ranking functions known as BM11 (for  ) and BM15 (for
) and BM15 (for  ).[2]
).[2]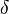 (a default value is
(a default value is 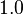 in absence of a training data) as compared with BM25:
in absence of a training data) as compared with BM25: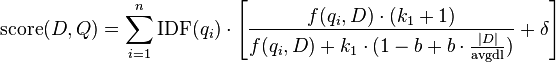
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lvfeilong/p/324dsfdsf.html