标签:
/*
程序功能:
1、构造arp包,并发送。程序参数顺序:源IP、目的IP、mac地址、flag
2、获取网络中的ARP数据包,解析数据包的内容。程序参数:日志文件名
winpacp中文技术文档(基本是英文的):http://www.ferrisxu.com/WinPcap/html/index.html
*/
一、构造arp包
在构造之前先了解一下arp包的结构,先从网上找了张图
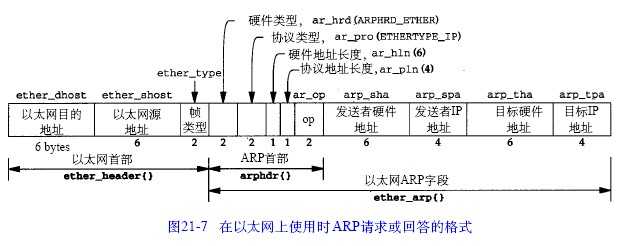
从图中可以看出以太网首部占14字节,以太网ARP字段占28字节。其中op字段为操作类型,1表示ARP请求、2表示ARP应答
再介绍几个要用到的pcap函数
函数功能:列出当前所有可用的网络设备(网卡),将设备信息存入pcap_if_t结构列表中
参数:1、alldevsp 指向pcap_if_t结构列表的指针的地址(注意这里是pcap_if_t指针的地址,而不是pcap_if_t结构的地址)
有些地方这里可能会写pcap_if结构,其实pcap_if和pcap_if_t就是同一个东西,我们来看看在pcap.h中是怎么定义的
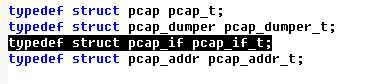
pcap_if结构体成员:
Struct pcap_if {
struct pcap_if *next; //指向下一个链表成员
char *name; //网卡名称
chat *description; //网卡描述信息
struct pcap_addr address;
u_int flags; //接口标志
}
2、errbuf 错误缓冲区,要求长度至少为PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE 字节,那么PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE是多大呢
这在pcap.h中宏定义的,如下图

这个错误缓冲区用来做什么呢?在函数错误返回时(返回值为-1)会向错误缓冲中填充错误信息,错误信息为可打印ASCII码
函数正确时返回0
2、pcap_t * pcap_open_live ( char * device, int snaplen, int promisc,int to_ms, char * errbuf )
函数功能:在网络中打开一个活动的捕获<这是winpcap技术文档给出的说明,也就是指定从一个网络设备捕获数据包,我是这么理解的>
函数的返回值为一个结构体指针pcap_t即为struct pcap。pcap_t结构体有点长就不做说明了,里面就是捕获句柄的一些信息
参数: <文档是英文的不知道有没有翻译对>
device 设备名
snaplen 单包最大捕捉字节数(若数据包大于snaplen,只有前面snaplen字节大小的数据被捕获)
promisc 混杂模式(即使该参数是false,也可能由其他原因导致网络接口为混杂模式)
to_ms 指定毫秒级读超时(当一个数据包被发现时,并不一定立即返回数据包,它会等待一段时间,允许一个操作从系统内核读取多个数据 包。不是所有的平台都支持读超时,在不支持的平台上读超时会被忽略。)<在支持读超时的平台上若读超时为0,将导致永不超时>
errbuf 用于返回错误或警告信息
3、void pcap_close ( pcap_t *p )
关闭pcap_open_live()获取的包捕获句柄,释放相关资源
源码:
1 /* 2 构造并发送ARP包 3 2015年6月24日15:44:21 4 blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/wd1001/ 5 */ 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <pcap.h> 9 10 #pragma comment(lib, "wpcap.lib") 11 #pragma comment(lib, "wsock32.lib") 12 #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib") 13 14 main(int argc, char **argv) 15 { 16 u_char packet[100]; 17 pcap_if_t *alldevs; 18 pcap_if_t *d; 19 int inum; 20 int i=0,j,k,temp[3]; 21 pcap_t * adhandle; 22 char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; 23 /* 获取设备列表 */ 24 25 if (argc != 5)//argc==5,及程序后面有四个参数 26 { 27 printf("usage: %s inerface", argv[0]); 28 return -1; 29 } 30 31 32 if (pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) == -1) 33 { 34 fprintf(stderr,"Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s\n", errbuf); 35 exit(1); 36 } 37 /* 数据列表 */ 38 for(d=alldevs; d; d=d->next) 39 { 40 printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name); 41 if (d->description) 42 printf(" (%s)\n", d->description); 43 else 44 printf(" (No description available)\n"); 45 } 46 if(i==0) 47 { 48 printf("\n找不到网卡! 检查是否安装WinPcap.\n"); 49 return -1; 50 } 51 printf("Enter the interface number (1-%d):",i); 52 scanf("%d", &inum); 53 if(inum < 1 || inum > i) 54 { 55 printf("\nInterface number out of range.\n"); 56 /* 释放设备列表 */ 57 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 58 return -1; 59 } 60 /* 转到选择的设备 */ 61 for(d=alldevs, i=0; i< inum-1;d=d->next, i++); 62 /* 打开设备 */ 63 if ( (adhandle= pcap_open_live(d->name, //设备名 64 65536, // 最大捕捉字节数 65 1, // 混杂模式 66 1000, // 读入超时 67 errbuf // 错误缓冲 68 ) ) == NULL) 69 { 70 /*打开失败*/ 71 fprintf(stderr,"\n打开失败. %s 不被winpcap支持\n",d->name); 72 /* 释放列表 */ 73 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 74 return -1; 75 } 76 /* 释放设备列表 */ 77 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 78 79 /* 填充数据段 */ 80 81 //flag为1表示ARP请求 82 if(‘1‘==argv[4][0]) 83 { 84 //源MAC地址 85 k=0; 86 for(i=0;i<18;i=i+3) 87 { 88 temp[0]=(int)argv[3][i]; 89 temp[1]=(int)argv[3][i+1]; 90 if(temp[0]>96) //当输入mac为小写字母时字符转换为16进制 91 temp[0]=temp[0]-87; 92 else if(temp[0]>64) 93 temp[0]=temp[0]-55;//当输入mac为大写字母时字符转换为16进制 94 else 95 temp[0]=temp[0]-48;//当输入mac为数字时字符转换为16进制 96 if(temp[1]>96) 97 temp[1]=temp[1]-87; 98 else if(temp[1]>64) 99 temp[1]=temp[1]-55; 100 else 101 temp[1]=temp[1]-48; 102 packet[22+k]=packet[6+k]=temp[0]*16+temp[1]; 103 k++; 104 } 105 106 //发送ARP请求时目的MAC全置为ff 107 for(i=0;i<6;i++) 108 { 109 packet[i]=packet[32+i]=0xff; 110 } 111 } 112 113 //flag=2:ARP应答 114 else 115 { 116 //目的MAC地址 117 k=0; 118 for(i=0;i<18;i=i+3) 119 { 120 temp[0]=(int)argv[3][i]; 121 temp[1]=(int)argv[3][i+1]; 122 if(temp[0]>96) 123 temp[0]=temp[0]-87; 124 else if(temp[0]>64) 125 temp[0]=temp[0]-55; 126 else 127 temp[0]=temp[0]-48; 128 if(temp[1]>96) 129 temp[1]=temp[1]-87; 130 else if(temp[1]>64) 131 temp[1]=temp[1]-55; 132 else 133 temp[1]=temp[1]-48; 134 packet[k]=packet[32+k]=temp[0]*16+temp[1]; 135 k++; 136 } 137 //应答ARP请求时把源MAC置为0 138 for(i=0;i<6;i++) 139 { 140 packet[6+i]=packet[22+i]=0x00; 141 } 142 } 143 144 //源IP地址 145 k=0; 146 temp[2]=0; //指向每个字节初始位置 147 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 148 { 149 temp[0]=0; 150 temp[1]=0; 151 for(j=0;j<4;j++) 152 { 153 if(argv[1][j+temp[2]]>=‘0‘&&argv[1][j+temp[2]]<=‘9‘) 154 { 155 temp[0]=(int)argv[1][j+temp[2]]-48; 156 temp[1]=temp[1]*10+temp[0]; 157 //printf("%d %d\n",temp[0],temp[1]); 158 } 159 else 160 { 161 //当遇到点时j自加1目的是让temp[2]+j指向下一字节的第一位 162 j++; 163 break; 164 } 165 } 166 packet[28+k]=temp[1]; 167 k++; 168 temp[2]+=j; 169 } 170 //目标IP地址 171 k=0; 172 temp[2]=0; 173 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 174 { 175 temp[0]=0; 176 temp[1]=0; 177 for(j=0;j<4;j++) 178 { 179 if(argv[2][j+temp[2]]>=‘0‘&&argv[2][j+temp[2]]<=‘9‘) 180 { 181 temp[0]=(int)argv[2][j+temp[2]]-48; 182 temp[1]=temp[1]*10+temp[0]; 183 //printf("%d %d\n",temp[0],temp[1]); 184 } 185 else 186 { 187 j++; 188 break; 189 } 190 } 191 packet[38+k]=temp[1]; 192 k++; 193 temp[2]+=j; 194 } 195 //ARP首部 196 packet[12]=0x08;//12、13位为帧类型 197 packet[13]=0x06; 198 packet[14]=0x00;//14、15位为硬件类型 199 packet[15]=0x01; 200 packet[16]=0x08;//16、17位为协议类型 201 packet[17]=0x00; 202 packet[18]=0x06;//硬件地址长度 203 packet[19]=0x04;//协议地址长度 204 packet[20]=0x00;//op 205 packet[21]=(int)argv[4][0]-48;//op(1为请求2为应答) 206 207 208 /* 填充发送包的剩余部分 */ 209 for(i=0;i<18;i++) 210 { 211 packet[42+i]=0; 212 } 213 //这里后四个字节本应该是校验位,这里就不算了,写个日期纪念一下 214 packet[60]=0x20; 215 packet[61]=0x15; 216 packet[62]=0x6; 217 packet[63]=0x24; 218 /* 发送包 */ 219 pcap_sendpacket(adhandle, packet, 64); 220 printf("Success!\n"); 221 222 return 0; 223 }
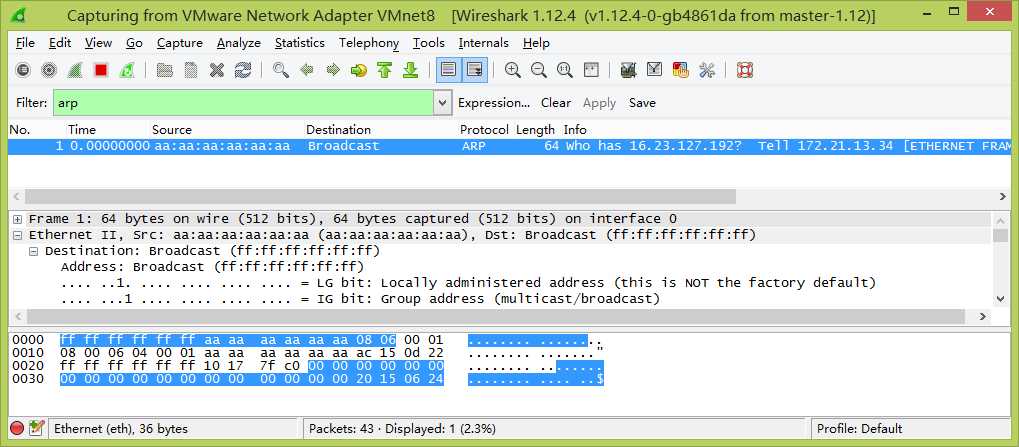
运行结果:
输入参数:随意设置源IP,目的IP和mac地址

选择网卡并发送,抓包结果如下
二、获取网络中的ARP数据包,解析数据包的内容
在上面的基础上再解析ARP数据包就简单了
同样在解析前先介绍几个要用到的函数
1、int pcap_compile ( pcap_t * p, struct bpf_program * fp, char * str,int optimize , bpf_u_int32 netmask )
函数功能:将字符串str编译进一个过滤程序,将程序中高级的过滤表达式,转换成能被内核级的过滤引擎所处理的东西
参数:1、p为pcap_open_live返回的一个捕获句柄
2、fp为一个指向bpf_program结构的指针,由pcap_compile()函数填写
bpf_program结构为:
struct bpf_program {
u_int bf_len;
struct bpf_insn *bf_insns;
};
bpf_insn结构为:
struct bpf_insn {
u_short code;
u_char jt;
u_char jf;
bpf_int32 k;
};
3、str 过滤串表达式
4、optimize 优化控制,是否执行结果代码优化(optimize controls whether optimization on the resulting code is performed)
5、netmask 子网掩码
2、int pcap_setfilter (pcap_t *p, struct bpf_program *fp)
函数功能:在捕获过程中绑定一个过滤器
源码:
1 /* 2 获取网络中的ARP数据包,解析数据包的内容 3 2015年6月24日19:36:36 4 blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/wd1001/ 5 */ 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <pcap.h> 9 #pragma comment(lib, "wpcap.lib") 10 #pragma comment(lib, "wsock32.lib") 11 #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib") 12 //定义ARP包数据 13 typedef struct arppkt 14 { 15 unsigned short hdtyp;//硬件类型 16 unsigned short protyp;//协议类型 17 unsigned char hdsize;//硬件地址长度 18 unsigned char prosize;//协议地址长度 19 unsigned short op;//(操作类型)操作值:ARP/RARP 20 u_char smac[6];//源MAC地址 21 u_char sip[4];//源IP地址 22 u_char dmac[6];//目的MAC地址 23 u_char dip[4];//目的IP地址 24 }arpp; 25 int main(int argc,char * argv[] ) 26 { 27 struct tm * timeinfo; 28 struct tm *ltime; 29 time_t rawtime; 30 FILE * fp=NULL; 31 int result; 32 int i=0,inum; 33 pcap_if_t * alldevs;//指向pcap_if_t结构列表指针 34 pcap_if_t * d; 35 pcap_t * adhandle;//定义包捕捉句柄 36 char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];//错误缓冲最小为256 37 u_int netmask; //定义子网掩码 38 char packet_filter[]="ether proto \\arp"; 39 struct bpf_program fcode; 40 struct pcap_pkthdr * header; 41 const u_char * pkt_data; 42 //打开日志文件 43 if((fp=fopen(argv[1],"a"))==NULL) 44 { 45 printf("打开文件失败!\n"); 46 exit(0); 47 } 48 if (argc != 2)//argc==2,及程序后面有1个参数 49 { 50 printf("程序%s需要一个日志文件名参数!\n", argv[0]); 51 return -1; 52 } 53 //当前所有可用的网络设备 54 if (pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) == -1) 55 { 56 fprintf(stderr,"Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s\n", errbuf); 57 exit(1); 58 } 59 //列出网络设备 60 for(d=alldevs; d; d=d->next) 61 { 62 printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name); 63 if (d->description) 64 printf(" (%s)\n", d->description); 65 else 66 printf(" (没有描述可用)\n"); 67 } 68 if(i==0) 69 { 70 printf("\n找不到网卡! 检查是否安装WinPcap.\n"); 71 return -1; 72 } 73 printf("选择对应网卡编号 (1-%d):",i); 74 scanf("%d", &inum); 75 if(inum < 1 || inum > i) 76 { 77 printf("\n输入的编号超出范围!\n"); 78 /* 释放设备列表 */ 79 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 80 return -1; 81 } 82 /* 转到选择的设备 */ 83 i=0; 84 d=alldevs; 85 while(i<inum-1) 86 { 87 d=d->next; 88 i++; 89 } 90 if ( (adhandle= pcap_open_live(d->name,65536, 1,1000,errbuf) ) == NULL) 91 { 92 /*打开失败*/ 93 fprintf(stderr,"\n打开失败. %s 不被winpcap支持\n",d->name); 94 /* 释放设备列表 */ 95 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 96 return -1; 97 } 98 /* 释放设备列表 */ 99 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 100 101 //获得子网掩码 102 netmask=((sockaddr_in *)(d->addresses->netmask))->sin_addr.S_un.S_addr; 103 //编译过滤器,只捕获ARP包 104 if(pcap_compile(adhandle,&fcode,packet_filter,1,netmask)<0) 105 { 106 printf("\nUnable to compile the packet filter.Check the syntax.\n"); 107 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 108 return -1; 109 } 110 //设置过滤器 111 if(pcap_setfilter(adhandle,&fcode)<0) 112 { 113 printf("\nError setting the filter.\n"); 114 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); 115 return -1; 116 } 117 //输出每次修改文件时间 118 time ( &rawtime ); 119 timeinfo = localtime ( &rawtime ); 120 printf("--------------修改时间:%s",asctime (timeinfo)); 121 fprintf(fp,"-----------修改时间:%s",asctime (timeinfo)); 122 fflush(fp);//刷新缓冲流 123 while((result=pcap_next_ex(adhandle,&header,&pkt_data))>=0) 124 { 125 //循环解析ARP数据包 126 if(result==0) 127 continue; 128 //解析ARP包,结果输出到屏幕与文件 129 arppkt* arph = (arppkt *)(pkt_data +14); 130 //输出操作时间 131 ltime=localtime(&header->ts.tv_sec); 132 printf("时间:%s",asctime (ltime)); 133 fprintf(fp,"时间:%s",asctime (ltime)); 134 //输出源IP 135 printf("源IP:"); 136 fprintf(fp,"源IP:"); 137 for(i=0;i<3;i++) 138 { 139 printf("%d.",arph->sip[i]); 140 fprintf(fp,"%d.",arph->sip[i]); 141 } 142 printf("%d\t",arph->sip[3]); 143 fprintf(fp,"%d.\t",arph->sip[3]); 144 //输出目的IP 145 printf("目的IP:"); 146 fprintf(fp,"目的IP:"); 147 for(i=0;i<3;i++) 148 { 149 printf("%d.",arph->dip[i]); 150 fprintf(fp,"%d.",arph->dip[i]); 151 } 152 printf("%d\t",arph->dip[3]); 153 fprintf(fp,"%d\t",arph->dip[3]); 154 //输出源mac 155 printf("源mac:"); 156 fprintf(fp,"源mac:"); 157 for(i=0;i<5;i++) 158 { 159 printf("%x-",arph->smac[i]); 160 fprintf(fp,"%x-",arph->smac[i]); 161 } 162 printf("%x\t",arph->smac[5]); 163 fprintf(fp,"%x\t",arph->smac[5]); 164 //输出目的mac 165 printf("目的mac:"); 166 fprintf(fp,"目的mac:"); 167 for(i=0;i<5;i++) 168 { 169 printf("%x-",*(pkt_data+i)); 170 fprintf(fp,"%x-",*(pkt_data+i)); 171 } 172 printf("%x\t",*(pkt_data+5)); 173 fprintf(fp,"%x\t",*(pkt_data+5)); 174 //输出操作类型 175 printf("操作类型(ARP/RARP):"); 176 fprintf(fp,"操作类型(ARP/RARP):"); 177 if(arph->op==256) 178 { 179 printf("ARP\t"); 180 fprintf(fp,"ARP\t"); 181 } 182 else 183 { 184 printf("RARP\t"); 185 fprintf(fp,"RARP\t"); 186 } 187 printf("\n"); 188 fprintf(fp,"\n"); 189 printf("--------------------------------------\n"); 190 fprintf(fp,"--------------------------------------\n"); 191 fflush(fp); 192 } 193 fclose(fp); 194 return 0; 195 }
(OS.png)
(OS.png)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wd1001/p/4596945.html