标签:
1 // GO 2 private static Map<Map<Integer,String>,Integer> GO 3 = new HashMap<Map<Integer,String>,Integer>(); 4 5 // 规范族集 C 6 private static Map<Integer,Map<String,List<String>>> C 7 = new HashMap<Integer, Map<String, List<String>>>(); 8 9 // 文法 G 10 private static Map<String,List<String>> G = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); 11 12 // 文法 G’ 13 private static List<String> Gc = new ArrayList<String>(); 14 15 // 文法的项目 16 private static Map<String,List<String>> GItems = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); 17 18 // ACTION 表 19 private static Map<Map<Integer,String>,String> ACTION 20 = new HashMap<Map<Integer,String>,String>(); 21 22 // GOTO 表 23 private static Map<Map<Integer,String>,Integer> GOTO 24 = new HashMap<Map<Integer,String>,Integer>();
这个结构很清晰,不解释
在每个文法适当位置插入特殊字符圈,构成新的文法的项目GItems,这一步可以在输入的时候完成
例如有文法产生式为
E=[aA, bB]
则得到的文法的项目应该是,这里用*号代表圈
E=[*aA, a*A, aA*, *bB, b*B, bB*]
根据文法的项目构造识别活前缀的有限自动机DFA,如图
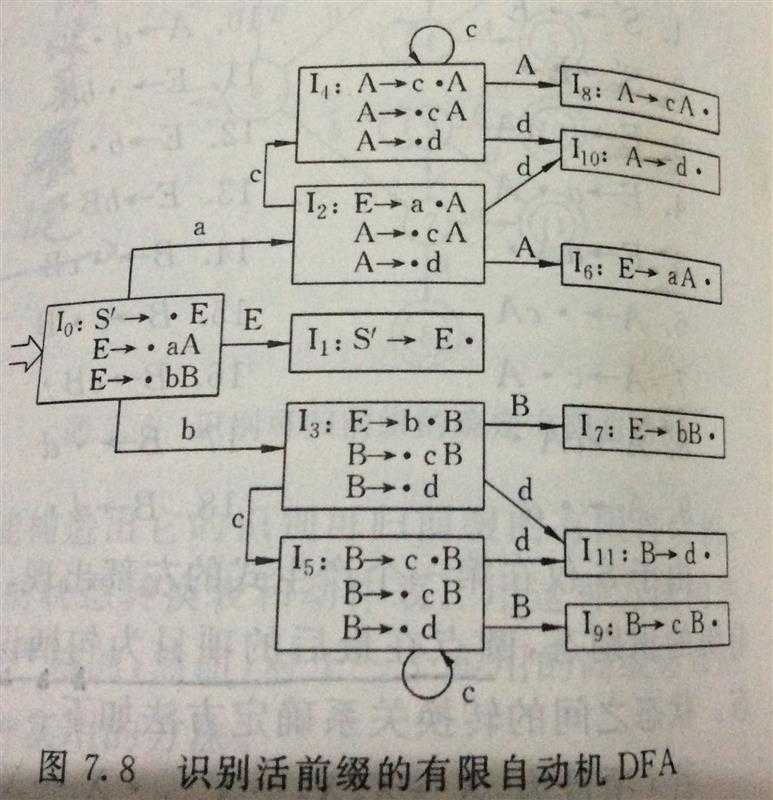
构造文法的规范族集
按图以对其中的每一项编号即可得到规范族集C={I0,I1,I2,....,In}
1 S‘->E 2 E->aA|bB 3 A->cA|d 4 B->cB|d
1 package org.lyh.app; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.util.*; 5 6 public class Main { 7 8 private static Integer I = 0; 9 // GO 10 private static Map<Map<Integer,String>,Integer> GO 11 = new HashMap<Map<Integer,String>,Integer>(); 12 13 // 规范族集 C 14 private static Map<Integer,Map<String,List<String>>> C 15 = new HashMap<Integer, Map<String, List<String>>>(); 16 17 // 文法 G 18 private static Map<String,List<String>> G = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); 19 20 // 文法 G’ 21 private static List<String> Gc = new ArrayList<String>(); 22 23 // 文法的项目 24 private static Map<String,List<String>> GItems = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); 25 26 // ACTION 表 27 private static Map<Map<Integer,String>,String> ACTION 28 = new HashMap<Map<Integer,String>,String>(); 29 30 // GOTO 表 31 private static Map<Map<Integer,String>,Integer> GOTO 32 = new HashMap<Map<Integer,String>,Integer>(); 33 34 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 35 36 37 FileReader fr = new FileReader("main.in"); 38 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); 39 40 String line = null; 41 while((line = br.readLine()) != null){ 42 43 // 构造文法 44 45 String [] pLine = line.split("->"); 46 List<String> pLineValues = G.get(pLine[0]); 47 if(null == pLineValues) pLineValues = new ArrayList<String>(); 48 pLineValues.addAll(Arrays.asList(pLine[1].split("\\|"))); 49 G.put(pLine[0], pLineValues); 50 51 for (String val : pLineValues){ 52 String pStr = pLine[0]+"->"+val; 53 if(!Gc.contains(pStr)) Gc.add(pStr); 54 } 55 // 构造文法的项目,这里以*代替书上的圆点 56 57 List<String> pItemValues = GItems.get(pLine[0]); 58 if(null == pItemValues) pItemValues = new ArrayList<String>(); 59 for(Iterator<String> iterator = pLineValues.iterator();iterator.hasNext();){ 60 String pValueItem = iterator.next(); 61 for (int i=0;i<pValueItem.length();i++){ 62 String newItem = new StringBuilder(pValueItem).insert(i, "*").toString(); 63 pItemValues.add(newItem); 64 } 65 pItemValues.add(pValueItem+"*"); 66 } 67 GItems.put(pLine[0], pItemValues); 68 } 69 fr.close(); 70 br.close(); 71 72 System.out.println("文法G:" + G); 73 System.out.println("文法G‘:"+Gc); 74 System.out.println("文法G的项目:"+GItems); 75 76 // 构造项目集规范族 77 // 这里将问题稍稍简化,假设S‘对应的第一个项目为初态 78 initC("S‘", "*E"); 79 System.out.println("C:"+C); 80 System.out.println("GO:"+GO); 81 82 // 构造ACTION表和GOTO表 83 // 首先考虑最开始的情况 84 Map<Integer,String> acKey = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 85 acKey.put(0,"#"); 86 ACTION.put(acKey,"acc"); 87 // 遍历 项目集规范族 C 88 for(Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer,Map<String,List<String>>>> iterator 89 = C.entrySet().iterator(); 90 iterator.hasNext();){ 91 Map.Entry<Integer,Map<String,List<String>>> CI 92 = iterator.next(); 93 //System.out.println(iterator.next()); 94 // 扫描 CI ,switch判断每条文法 95 int k = CI.getKey(); 96 Map<String,List<String>> values = CI.getValue(); 97 for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String,List<String>>> mapIterator 98 = values.entrySet().iterator();mapIterator.hasNext();){ 99 Map.Entry<String,List<String>> value = mapIterator.next(); 100 String pLeft = value.getKey(); 101 List<String> pRightValues = value.getValue(); 102 for(int x = 0;x<pRightValues.size();x++){ 103 String pRightVal = pRightValues.get(x); 104 System.out.println("K:"+k+" "+pLeft+"->"+pRightVal); 105 String a = null; 106 Integer GOka = 0; 107 Map<Integer,String> ka = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 108 109 if(pRightVal.matches("\\w*\\*[a-z]{1}\\w*")){ 110 // 形如 A-> 。。。。 书上第一种情况 111 a = pRightVal.charAt(pRightVal.indexOf("*")+1)+""; 112 // System.out.println(a); 113 ka.put(k, a); 114 int j = GO.get(ka); 115 // System.out.println(j); 116 Map<Integer,String> key = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 117 key.put(k,a); 118 ACTION.put(key,"S"+j); 119 } 120 else if(pRightVal.matches("\\w*\\*$")){ 121 // 形如书上第二种情况 122 // 扫描这个文法串 123 int j = 0; 124 j = Gc.indexOf(pLeft+"->" 125 +pRightVal.substring(0,pRightVal.length()-1)); 126 for(int r = 0;r<pRightVal.length();r++){ 127 char vti = pRightVal.charAt(r); 128 if(vti >= ‘a‘ && vti <= ‘z‘){ 129 // 是非终结符 130 // 置ACTION[k,a] 为 rj 131 Map<Integer,String> key = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 132 key.put(k,vti+""); 133 // 在G‘中查找A->r 得到j 134 135 if(j>=0) ACTION.put(key,"r"+j); 136 } 137 } 138 Map<Integer,String> key = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 139 key.put(k,"#"); 140 ACTION.put(key,"r"+j); 141 } 142 } 143 } 144 145 } 146 147 // GOTO表 148 // 判断 GO(Ik,A) == Ij 149 // 扫描 GO 表 150 for (Iterator<Map.Entry<Map<Integer,String>,Integer>> goit = GO.entrySet().iterator(); 151 goit.hasNext();){ 152 Map.Entry<Map<Integer,String>,Integer> goi = goit.next(); 153 Map<Integer,String> gKey = goi.getKey(); 154 //System.out.println("gKey:"+gKey); 155 int k =((Integer) gKey.keySet().toArray()[0]); 156 char A = ((String)gKey.values().toArray()[0]).charAt(0); 157 // System.out.println(A); 158 if(A >= ‘A‘ && A <= ‘Z‘){ 159 Map<Integer,String> gotoKey = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 160 gotoKey.put(k,A+""); 161 GOTO.put(gotoKey,goi.getValue()); 162 } 163 } 164 165 System.out.println("ACTION 表:"+ACTION); 166 System.out.println("GOTO 表:"+GOTO); 167 } 168 169 private static void initC(String start, String pValue) { 170 171 Map<String,List<String>> CI = new HashMap<String,List<String>>(); 172 //List<String> pValues = GItems.get(start); 173 List<String> startCIValues = new ArrayList<String>(); 174 startCIValues.add(pValue); 175 CI.put(start, startCIValues); 176 177 System.out.println(start + "->" + pValue); 178 179 180 int new_index = pValue.indexOf("*") + 1; 181 if(new_index != pValue.length()){ 182 // 找到key为E(newStart)的右部以*a(这里a是终结符)的产生式,一并加到CI中 183 String newStart = pValue.substring(new_index,new_index+1); 184 List<String> seValues = GItems.get(newStart); 185 186 List<String> newStartCIValues = newStart.equals(start) 187 ? startCIValues : new ArrayList<String>(); 188 189 //System.out.println(seValues); 190 for (String value : seValues){ 191 if(value.matches("^\\*[a-z]{1}\\w*")){ 192 newStartCIValues.add(value); 193 System.out.println(newStart+"->"+value); 194 } 195 } 196 197 CI.put(newStart, newStartCIValues); 198 199 C.put(I,CI); 200 int curI = I; 201 I++; 202 203 String VC = ""+pValue.charAt(new_index); 204 Map<Integer,String> GOI = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 205 GOI.put(curI,VC); 206 GO.put(GOI,I); 207 208 209 System.out.println("------------"); 210 // 将第一条程式的圆点移动到下一位 211 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(pValue); 212 sb.deleteCharAt(new_index-1).insert(new_index, "*"); 213 String newPValue = sb.toString(); 214 // 对第一条程式进行递归查找 215 initC(start, sb.toString()); 216 217 // 将下面程式的原点移动到下一位 218 for(String value : newStartCIValues){ 219 220 221 222 sb.delete(0, sb.length()); 223 sb.append(value); 224 int x_index = sb.indexOf("*"); 225 226 VC = ""+value.charAt(x_index+1); 227 GOI = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); 228 GOI.put(curI,VC); 229 // 下移一位 230 sb.deleteCharAt(x_index).insert(x_index + 1, "*"); 231 if(!pValue.equals(sb.toString())){ 232 // 判断C当中是否已经存在这个程式 233 Map<String,List<String>> _this = new HashMap<String,List<String>>(); 234 List<String> v = new ArrayList<String>(); 235 v.add(sb.toString()); 236 _this.put(newStart,v); 237 // 查找是否已经存在这个CI了 238 boolean has = false; 239 int exist_key = 0; 240 Set<Integer> keys = C.keySet(); 241 for (Integer key : keys){ 242 // 找到这个ID 243 if(C.get(key).equals(_this)){ 244 //System.out.println("存在重复"); 245 has = true; 246 exist_key = key; 247 break; 248 } 249 } 250 if(has){ 251 //System.out.println("存在重复"); 252 // 将 GO 的值 指向这个已经存在的 253 GO.put(GOI,exist_key); 254 } 255 else{ 256 // 正常新建一个CI 257 GO.put(GOI,I); 258 initC(newStart, sb.toString()); 259 } 260 }else{ 261 // 指向自身 262 //System.out.println("指向自身"); 263 GO.put(GOI,curI); 264 } 265 } 266 } 267 else{ 268 System.out.println("------------"); 269 C.put(I,CI); 270 I++; 271 } 272 273 } 274 275 }
1 文法G:{E=[aA, bB], S‘=[E], A=[cA, d], B=[cB, d]} 2 文法G‘:[S‘->E, E->aA, E->bB, A->cA, A->d, B->cB, B->d] 3 文法G的项目:{E=[*aA, a*A, aA*, *bB, b*B, bB*], S‘=[*E, E*], A=[*cA, c*A, cA*, *d, d*], B=[*cB, c*B, cB*, *d, d*]} 4 S‘->*E 5 E->*aA 6 E->*bB 7 ------------ 8 S‘->E* 9 ------------ 10 E->a*A 11 A->*cA 12 A->*d 13 ------------ 14 E->aA* 15 ------------ 16 A->c*A 17 A->*cA 18 A->*d 19 ------------ 20 A->cA* 21 ------------ 22 A->d* 23 ------------ 24 E->b*B 25 B->*cB 26 B->*d 27 ------------ 28 E->bB* 29 ------------ 30 B->c*B 31 B->*cB 32 B->*d 33 ------------ 34 B->cB* 35 ------------ 36 B->d* 37 ------------ 38 C:{0={E=[*aA, *bB], S‘=[*E]}, 1={S‘=[E*]}, 2={E=[a*A], A=[*cA, *d]}, 3={E=[aA*]}, 4={A=[c*A, *cA, *d]}, 5={A=[cA*]}, 6={A=[d*]}, 7={E=[b*B], B=[*cB, *d]}, 8={E=[bB*]}, 9={B=[c*B, *cB, *d]}, 10={B=[cB*]}, 11={B=[d*]}} 39 GO:{{2=d}=6, {7=B}=8, {4=c}=4, {4=A}=5, {0=E}=1, {7=c}=9, {0=b}=7, {7=d}=11, {4=d}=6, {2=c}=4, {2=A}=3, {0=a}=2, {9=d}=11, {9=c}=9, {9=B}=10} 40 K:0 E->*aA 41 K:0 E->*bB 42 K:0 S‘->*E 43 K:1 S‘->E* 44 K:2 E->a*A 45 K:2 A->*cA 46 K:2 A->*d 47 K:3 E->aA* 48 K:4 A->c*A 49 K:4 A->*cA 50 K:4 A->*d 51 K:5 A->cA* 52 K:6 A->d* 53 K:7 E->b*B 54 K:7 B->*cB 55 K:7 B->*d 56 K:8 E->bB* 57 K:9 B->c*B 58 K:9 B->*cB 59 K:9 B->*d 60 K:10 B->cB* 61 K:11 B->d* 62 ACTION 表:{{1=#}=r0, {2=d}=S6, {5=c}=r3, {0=#}=acc, {4=c}=S4, {7=c}=S9, {3=#}=r1, {6=d}=r4, {0=b}=S7, {3=a}=r1, {5=#}=r3, {7=d}=S11, {4=d}=S6, {6=#}=r4, {0=a}=S2, {2=c}=S4, {11=d}=r6, {8=#}=r2, {11=#}=r6, {10=#}=r5, {9=d}=S11, {9=c}=S9, {8=b}=r2, {10=c}=r5} 63 GOTO 表:{{0=E}=1, {4=A}=5, {7=B}=8, {2=A}=3, {9=B}=10} 64 65 Process finished with exit code 0
求LR(0)文法的规范族集和ACTION表、GOTO表的构造算法
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lvyahui/p/4600951.html