标签:
在xcode中打开一个app,在想要break的行号上单击,即可生成一个深色的箭头标识--断点。如下图,在viewDidLoad:中设置了断点。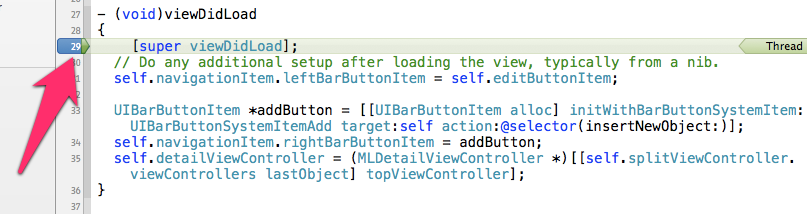
运行app,等待。。。就可以看到xcode在断点处进入调试模式,现在让我们把视线移到xcode右下角的控制台,有木有看到(lldb)这样一行,鼠标移到此行,输入
1 |
po [self view] |
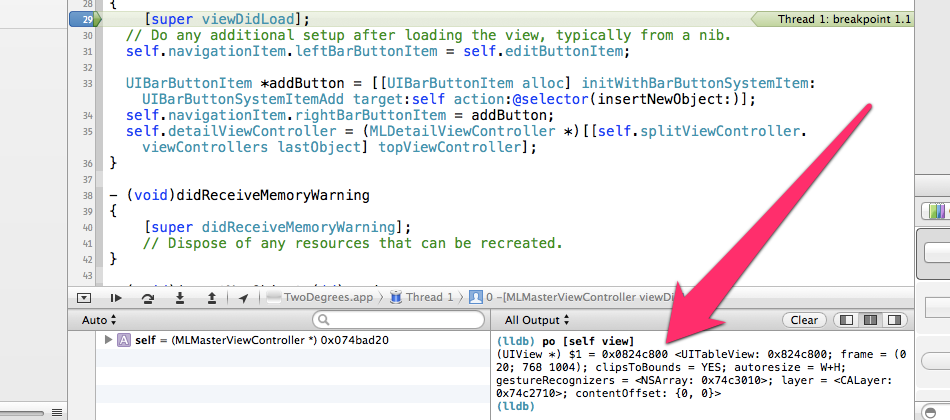
po(print object)是LLDB的一个命令,其主要功能是输出objective-c中对象(objects)的信息,与之相似的另外一个命令是 p(print),其主要功能是输出原生类型(boolean、integer、float、etc)的信息。
控制台输入
p (int)[[[self view] subviews] count]
结果如下
(int) $2 = 2
注意这个使用了类型转换告知调试器应该如何处理返回值。
你以前怎么验证是不是某个变量的值导致整段程序不能正常工作?修改代码中的变量的值,然后cmd+r重新启动app?现在你不需要这么做了,只需要设置一个断点,当程序在这进入调试模式后,使用expr命令即可在运行时修改变量的值。
假如有一个loginWithUsername:方法,需要两个参数:username,password。
首先设置好断点,如下图所示:
运行app,进入断点模式后,在(lldb)后输入
1 |
expr username = @"username" |
2 |
expr password = @"badpassword" |
1 |
(NSString *) $0 = 0x3d3504c4 @"username" |
2 |
(NSString *) $1 = 0x1d18ef60 @"badpassword" |
1 |
(0x1c59aae0) A line for the breakpoint |
2 |
(0x1c59aae0) Username and Password after: username:badpassword |
右击断点选择“Edit Breakpoint...”(或者按住cmd+option,单击断点),然后如下图所示设置断点
注意选中了最后一行(“Automatically continue after evaluating”)的选择框,这就保证运行到这个断点的时,填充变量的值,然后继续运行,并不在此处断点进入调试模式。
运行app,你会得到和上述手动设置变量的值一样的输出。
接下来单击断点,使其处于禁用状态,现在箭头的颜色应该是浅蓝色的,重新运行app,你会发现username和password的值没有在运行时被改变了。
断点的另外一个重要作用,是可以设置触发断点生效的条件,这样我们就可以在运行时针对特定的数据进行分析,观察app是否运行在正确的轨道上。如下图:
上述截图可以看到如下语句
1 |
(BOOL)[(NSString*)[item valueForKey:@"ID"] isEqualToString:@"93306"] |
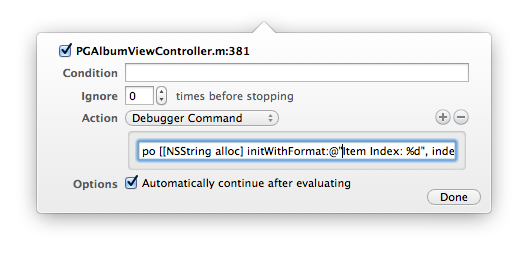
如果你厌倦了代码里无穷无尽的NSLog,幸运的是我们可以在编辑断点使其输出格式化字符串就像平常编码时一样。不过有一点需要注意,平常编码时可能会使用NSString‘s stringWithFormat:输出格式化字符串,不过这个方法貌似在断点中木有效果,你需要使用alloc/init形式的方法,如下:
1 |
po [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"Item index is: %d", index] |
运行app,就能在控制台看到想要的输出啦!
简单!强大!这就是LLDB给你的选择,从此代码里可以不用再有NSLog满天飞的情况了,代码变得更干净了,心情变得更愉悦了!
LLDB还有很多强大的地方,本教程只不过揭开了它的面纱,即便如此,仍让我们沉醉不已。
如此你有让xcode中debug变的更轻松加简单的方法,请在评论中尽情的分享!
命令总结:
| LLDB | GDB |
| Launch a process no arguments. | |
| (lldb) process launch (lldb) run (lldb) r |
(gdb) run (gdb) r |
Launch a process with arguments <args>. |
|
|
(lldb) process
launch — <args> (lldb) r <args> |
(gdb) run
<args> (gdb) r <args> |
Launch a process for with arguments a.out
1 2 3 without having to supply the args every time. |
|
|
% lldb
— a.out 1 2 3 (lldb) run … (lldb) run … |
% gdb
–args a.out 1 2 3 (gdb) run … (gdb) run … |
| Launch a process with arguments in new terminal window (Mac OS X only). | |
|
(lldb) process
launch –tty — <args> (lldb) pro la -t — <args> |
|
| Launch a process with arguments in existing terminal /dev/ttys006 (Mac OS X only). | |
|
(lldb) process
launch –tty=/dev/ttys006 — <args> (lldb) pro la -t/dev/ttys006 — <args> |
|
| Attach to a process with process ID 123. | |
|
(lldb) process
attach –pid 123 (lldb) attach -p 123 |
(gdb) attach 123 |
| Attach to a process named “a.out”. | |
|
(lldb) process
attach –name a.out (lldb) pro at -n a.out |
(gdb) attach a.out |
| Wait for a process named “a.out” to launch and attach. | |
|
(lldb) process
attach –name a.out –waitfor (lldb) pro at -n a.out -w |
(gdb) attach -waitfor a.out |
| Do a source level single step in the currently selected thread. | |
|
(lldb) thread
step-in (lldb) step (lldb) s |
(gdb) step (gdb) s |
| Do a source level single step over in the currently selected thread. | |
|
(lldb) thread
step-over (lldb) next (lldb) n |
(gdb) next (gdb) n |
| Do an instruction level single step in the currently selected thread. | |
|
(lldb) thread
step-inst (lldb) si |
(gdb) stepi (gdb) si |
| Do an instruction level single step over in the currently selected thread. | |
|
(lldb) thread
step-inst-over (lldb) ni |
(gdb) nexti (gdb) ni |
| Step out of the currently selected frame. | |
|
(lldb) thread
step-out (lldb) finish |
(gdb) finish |
| Backtrace and disassemble every time you stop. | |
|
(lldb) target
stop-hook add Enter your stop hook command(s). Type ‘DONE’ to end. > bt > disassemble –pc > DONE Stop hook #1 added. |
|
| LLDB | GDB |
| Set a breakpoint at all functions named main. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
set –name main (lldb) br s -n main (lldb) b main |
(gdb) break main |
| Set a breakpoint in file test.c at line 12. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
set –file test.c –line 12 (lldb) br s -f test.c -l 12 (lldb) b test.c:12 |
(gdb) break test.c:12 |
| Set a breakpoint at all C++ methods whose basename is main. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
set –method main (lldb) br s -M main |
(gdb) break
main (Hope that there are no C funtions named main). |
| Set a breakpoint at and object C function: -[NSString stringWithFormat:]. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
set –name “-[NSString stringWithFormat:]” (lldb) b -[NSString stringWithFormat:] |
(gdb) break -[NSString stringWithFormat:] |
| Set a breakpoint at all Objective C methods whose selector is count. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
set –selector count (lldb) br s -S count |
(gdb) break
count (Hope that there are no C or C++ funtions namedcount). |
| List all breakpoints. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
list (lldb) br l |
(gdb) info break |
| Delete a breakpoint. | |
|
(lldb) breakpoint
delete 1 (lldb) br del 1 |
(gdb) delete 1 |
| LLDB | GDB |
| Set a watchpoint on a variable when it is written to. | |
|
(lldb) watchpoint
set variable -w write global_var (lldb) watch set var -w write global_var |
(gdb) watch global_var |
| Set a watchpoint on a memory location when it is written into. The size of the region to watch for defaults to the pointer size if no ‘-x byte_size’ is specified. This command takes raw input, evaluated as an expression returning an unsigned integer pointing to the start of the region, after the ‘–’ option terminator. | |
|
(lldb) watchpoint
set expression -w write — my_ptr (lldb) watch set exp -w write — my_ptr |
(gdb) watch -location g_char_ptr |
| Set a condition on a watchpoint. | |
|
(lldb) watch
set var -w write global (lldb) watchpoint modify -c ‘(global==5)’ (lldb) c … (lldb) bt * thread #1: tid = 0x1c03, 0x0000000100000ef5 a.out modify
+ 21 at main.cpp:16, stop reason = watchpoint 1modify + 21 at main.cpp:16frame #1: 0x0000000100000eac a.out main
+ 108 at main.cpp:25start + 1(lldb) frame var global (int32_t) global = 5 |
|
| List all watchpoints. | |
|
(lldb) watchpoint
list (lldb) watch l |
(gdb) info break |
| Delete a watchpoint. | |
|
(lldb) watchpoint
delete 1 (lldb) watch del 1 |
(gdb) delete 1 |
| LLDB | GDB |
| Show the arguments and local variables for the current frame. | |
| (lldb) frame variable |
(gdb) info
args and (gdb) info locals |
| Show the local variables for the current frame. | |
|
(lldb) frame
variable –no-args (lldb) fr v -a |
(gdb) info locals |
| Show the contents of local variable “bar”. | |
|
(lldb) frame
variable bar (lldb) fr v bar (lldb) p bar |
(gdb) p bar |
| Show the contents of local variable “bar” formatted as hex. | |
|
(lldb) frame
variable –format x bar (lldb) fr v -f x bar |
(gdb) p/x bar |
| Show the contents of global variable “baz”. | |
|
(lldb) target
variable baz (lldb) ta v baz |
(gdb) p baz |
| Show the global/static variables defined in the current source file. | |
|
(lldb) target
variable (lldb) ta v |
n/a |
| Display a the variable “argc” and “argv” every time you stop. | |
|
(lldb) target
stop-hook add –one-liner “frame variable argc argv” (lldb) ta st a -o “fr v argc argv” (lldb) display argc (lldb) display argv |
(gdb) display
argc (gdb) display argv |
| Display a the variable “argc” and “argv” only when you stop in the function named main. | |
|
(lldb) target
stop-hook add –name main –one-liner “frame variable argc argv” (lldb) ta st a -n main -o “fr v argc argv” |
|
| Display the variable “*this” only when you stop in c class named MyClass. | |
|
(lldb) target
stop-hook add –classname MyClass –one-liner “frame variable *this” (lldb) ta st a -c MyClass -o “fr v *this” |
|
| LLDB | GDB |
| Show the stack backtrace for the current thread. | |
|
(lldb) thread
backtrace (lldb) bt |
(gdb) bt |
| Show the stack backtraces for all threads. | |
|
(lldb) thread
backtrace all (lldb) bt all |
(gdb) thread apply all bt |
| Select a different stack frame by index for the current thread. | |
| (lldb) frame select 12 | (gdb) frame 12 |
| List information about the currently selected frame in the current thread. | |
| (lldb) frame info | |
| Select the stack frame that called the current stack frame. | |
|
(lldb) up (lldb) frame select –relative=1 |
(gdb) up |
| Select the stack frame that is called by the current stack frame. | |
|
(lldb) down (lldb) frame select –relative=-1 (lldb) fr s -r-1 |
(gdb) down |
| Select a different stack frame using a relative offset. | |
|
(lldb) frame
select –relative 2 (lldb) fr s -r2
(lldb) frame
select –relative -3 |
(gdb) up
2 (gdb) down 3 |
| Show the general purpose registers for the current thread. | |
| (lldb) register read | (gdb) info registers |
| Show the general purpose registers for the current thread formatted as signed decimal. LLDB tries to use the same format characters as printf(3) when possible. Type “help format” to see the full list of format specifiers. | |
|
(lldb) register
read –format i (lldb) re r -f i
LLDB
now supports the GDB shorthand format syntax but there can’t be space after the command: |
|
| Show all registers in all register sets for the current thread. | |
|
(lldb) register
read –all (lldb) re r -a |
(gdb) info all-registers |
| Show the values for the registers named “rax”, “rsp” and “rbp” in the current thread. | |
| (lldb) register read rax rsp rbp | (gdb) info all-registers rax rsp rbp |
| Show the values for the register named “rax” in the current thread formatted as binary. | |
|
(lldb) register
read –format binary rax (lldb) re r -f b rax
LLDB
now supports the GDB shorthand format syntax but there can’t be space after the command: |
(gdb) p/t $rax |
| Read memory from address 0xbffff3c0 and show 4 hex uint32_t values. | |
|
(lldb) memory
read –size 4 –format x –count 4 0xbffff3c0 (lldb) me r -s4 -fx -c4 0xbffff3c0 (lldb) x -s4 -fx -c4 0xbffff3c0
LLDB
now supports the GDB shorthand format syntax but there can’t be space after the command: |
(gdb) x/4xw 0xbffff3c0 |
| Read memory starting at the expression “argv[0]“. | |
(lldb) memory
read argv[0]NOTE: any command can inline a scalar expression result (as long as the target is stopped) using backticks around any expression: (lldb) memory read –size sizeof(int) argv[0] |
(gdb) x argv[0] |
| Read 512 bytes of memory from address 0xbffff3c0 and save results to a local file as text. | |
|
(lldb) memory
read –outfile /tmp/mem.txt –count 512 0xbffff3c0 (lldb) me r -o/tmp/mem.txt -c512 0xbffff3c0 (lldb) x/512bx -o/tmp/mem.txt 0xbffff3c0 |
(gdb) set
logging on (gdb) set logging file /tmp/mem.txt (gdb) x/512bx 0xbffff3c0 (gdb) set logging off |
| Save binary memory data starting at 0×1000 and ending at 0×2000 to a file. | |
|
(lldb) memory
read –outfile /tmp/mem.bin –binary 0×1000 0×1200 (lldb) me r -o /tmp/mem.bin -b 0×1000 0×1200 |
|
| (gdb) dump memory /tmp/mem.bin 0×1000 0×2000 | |
| Disassemble the current function for the current frame. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–frame (lldb) di -f |
(gdb) disassemble |
| Disassemble any functions named main. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–name main (lldb) di -n main |
(gdb) disassemble main |
| Disassemble an address range. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–start-address 0x1eb8 –end-address 0x1ec3 (lldb) di -s 0x1eb8 -e 0x1ec3 |
(gdb) disassemble 0x1eb8 0x1ec3 |
| Disassemble 20 instructions from a given address. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–start-address 0x1eb8 –count 20 (lldb) di -s 0x1eb8 -c 20 |
(gdb) x/20i 0x1eb8 |
| Show mixed source and disassembly for the current function for the current frame. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–frame –mixed (lldb) di -f -m |
n/a |
| Disassemble the current function for the current frame and show the opcode bytes. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–frame –bytes (lldb) di -f -b |
n/a |
| Disassemble the current source line for the current frame. | |
|
(lldb) disassemble
–line (lldb) di -l |
n/a |
| LLDB | GDB |
| List the main executable and all dependent shared libraries. | |
| (lldb) image list | (gdb) info shared |
| Lookup information for a raw address in the executable or any shared libraries. | |
|
(lldb) image
lookup –address 0x1ec4 (lldb) im loo -a 0x1ec4 |
(gdb) info symbol 0x1ec4 |
| Lookup information for an address in a.out only. | |
|
(lldb) image
lookup –address 0x1ec4 a.out (lldb) im loo -a 0x1ec4 a.out |
|
Lookup information for for a type Point by
name. |
|
|
(lldb) image
lookup –type Point (lldb) im loo -t Point |
(lldb) ptype Point |
| Dump all sections from the main executable and any shared libraries. | |
| (lldb) image dump sections | (gdb) maintenance info sections |
| Dump all sections in the a.out module. | |
| (lldb) image dump sections a.out | |
| Dump all symbols from the main executable and any shared libraries. | |
| (lldb) image dump symtab | |
| Dump all symbols in a.out and liba.so. | |
| (lldb) image dump symtab a.out liba.so | |
| LLDB | GDB |
| Echo text to the screen. | |
| (lldb) script print “Here is some text” | (gdb) echo Here is some text\n |
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/iCocos/p/4602540.html