标签:
LinkedList是一种可以在任何位置进行高效地插入和移除操作的有序序列,它是基于双向链表实现的。
ps:这里有一个问题,就是关于实现LinkedList的数据结构是否为循环的双向链表,上网搜了有很多文章都说是循环的,并且有的文章中但是我看了源代码觉得应该不是循环的?
例如在删除列表尾部节点的代码:
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l)
{ final E element = l.item; final Node<E> prev = l.prev; l.item = null; l.prev = null; // help GC last = prev; if (prev == null) first = null; else prev.next = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
这里删除尾节点l后,将l前面的节点prev的next置为null,而并没有指向head节点。不知道是不是因为代码版本的原因(我的源代码是在下载的jdk1.8.0_45文件中获取的),如果读者看到知道原因,希望能够帮忙解答!
在源码中定义了节点的基本结构:
private static class Node<E> { E item; //表示该节点包含的值 Node<E> next; //表达当前节点的下一个节点 Node<E> prev; //表示当前节点的上一个节点 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
LinkedList的类图如下所示:
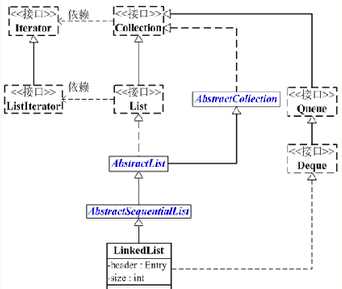
LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能对它进行队列操作。
LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
LinkedList 是非同步的。
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { //实现Serilizable接口时,将不需要序列化的属性前添加关键字transient,序列化对象的时候,这个属性就不会序列化到指定的目的地中。 transient int size = 0; //指向首节点 transient Node<E> first; //指向最后一个节点 transient Node<E> last; //构建一个空列表 public LinkedList() { } //构建一个包含集合c的列表 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); } //将节点值为e的节点作为首节点 private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; //构建一个prev值为null,next为f,节点值为e的节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); //将newNode作为首节点 first = newNode; //如果newNode后面没有节点就将newNode作为最后一个节点 if (f == null) last = newNode; //否则就将newNode赋给其prev else f.prev = newNode; //列表长度加一 size++; modCount++; } //将节点值为e的节点作为最后一个节点 void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; //构建一个prev值为l,next为null,节点值为e的节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } //在非空节点succ之前插入节点e void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; //将succ前面的节点和succ作为其prev和next final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); //然后将newNode作为succ的prev succ.prev = newNode; //如果原来succ是首节点,则将newNode设置为首节点 if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } //释放非空的首节点f private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { final E element = f.item; final Node<E> next = f.next; f.item = null; f.next = null; // help GC //将first节点后面的节点设为首节点 first = next; if (next == null) last = null; else next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } //释放非空的尾节点l private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { final E element = l.item; final Node<E> prev = l.prev; l.item = null; l.prev = null; // help GC last = prev; if (prev == null) first = null; else prev.next = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } //删除非空节点x E unlink(Node<E> x) { final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; //x后面的节点 final Node<E> prev = x.prev; //x前面的节点 if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } //返回列表首节点元素值 public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; } //返列表尾节点元素值 public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; } //移除首节点 public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); } //删除尾节点 public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); } //在列表首部插入节点e public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); } //在列表尾部插入节点e public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); } //判断列表中是否包含有元素o public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; } //返回列表长度大小 public int size() { return size; } //在列表尾部插入元素 public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } //删除元素为o的节点 public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } //将集合c中所有元素添加到列表的尾部 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } //从指定的位置index开始,将集合c中的元素插入到列表中 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //首先判断插入位置的合法性 checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) {//说明在列表尾部插入集合元素 succ = null; pred = last; } else { //否则,找到index所在的节点 succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; } //删除列表中所有节点 public void clear() { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; } //获取指定索引位置节点的元素值 public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } //替换指定索引位置节点的元素值 public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; } //在指定索引位置之前插入元素e public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } //删除指定位置的元素 public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); } //判断指定索引位置的元素是否存在 private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size; } private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size; } //构建 IndexOutOfBoundsException详细信息 private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; } private void checkElementIndex(int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { if (!isPositionIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } //返回指定索引位置的节点 Node<E> node(int index) { //此处是一个小技巧,当index<size/2时,从列表前半部分开始,否则从后半部分开始 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }//返回列表中第一次出现o的位置,若不存在则返回-1 public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; } //逆向搜索,返回第一出现o的位置,不存在则返回-1 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (x.item == null) return index; } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; } } return -1; } //获取列表首节点元素值 public E peek() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } //获取列表首节点元素值,若为空则抛异常 public E element() { return getFirst(); } //检索首节点,若空则返回null,不为空则返回其元素值并删除首节点 public E poll() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } //检索首节点,若空则抛异常,不为空则返回其元素值并删除首节点 public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } //在列表尾部增加节点e public boolean offer(E e) { return add(e); } //在列表首部插入节点e public boolean offerFirst(E e) { addFirst(e); return true; } //在列表尾部插入节点e public boolean offerLast(E e) { addLast(e); return true; } public E peekFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } //获取列表尾节点元素值 public E peekLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : l.item; } public E pollFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } public E pollLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); } //入栈 public void push(E e) { addFirst(e); } //出栈 public E pop() { return removeFirst(); } //删除列表中第一出现o的节点 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { return remove(o); } //逆向搜索,删除第一次出现o的节点 public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
Node<E> node(int index) { if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
该方法返回双向链表中指定位置处的节点,而链表中是没有下标索引的,要指定位置出的元素,就要遍历该链表,从源码的实现中,我们看到这里有一个加速动作。源码中先将index与长度size的一半比较,如果index<size/2,就只从位置0往后遍历到位置index处,而如果index>size/2,就只从位置size往前遍历到位置index处。这样可以减少一部分不必要的遍历。
LinkedList与ArrayList在性能上各有优缺点,都有各自适用的地方,总结如下:
总之,当操作是在一列数据的后面添加数据而不是在前面或中间,并且需要随机地访问其中的元素时,使用ArrayList会提供比较好的性能,当你的操作是在一列数据的前面或中间添加或删除数据,并且按照顺序访问其中的元素时,就应该使用LinkedList了。
在查找和删除时,源代码如下所示:
public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }
推荐一篇介绍LinkedList基本用法的博文http://blog.csdn.net/i_lovefish/article/details/8042883,这里不再赘述。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xujian2014/p/4630785.html