标签:
static关键字:
用法:用于修饰成员(成员变量,成员函数)
特点
1随着类的加载而加载,随着类的消失而消失。说明生命周期最长。
2优先于对象存在,静态先存在,对象后存在。
3被所有对象共享
4可以直接被类名调用 Persion.country ;
使用注意事项:
1,静态方法只能访问静态成员(因为static先存在),非静态即可以,又可以访问非静态成员
2,静态中不可以定义this,super
3,主函数时静态的
利:对对象的共享的数据进行单独空间存储,节省空间,没必要所有对象都存储一份,可以直接被类名调用。
弊:生命周期过长,访问出现局限性。
特有内容随着对象在堆内存中存储,共有内容用static修饰存储在共享区。
静态的内容被对象所共享,只在内存(栈)中建立一个·内容,可以节省内存。
class Zx {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Persion p = new Persion();
p.name = "zhangsan";
p.show();
}
}
class Persion
{
String name;
static String country = "CN";
public void show()
{
System.out.println(name+"::"+country);
}
}
使用场景
1,对象中出现共享数据时,被静态所修饰,特有数据定义成非静态,存在于堆内存中
2,当功能没有访问到非静态数据,可以把功能定义成静态的
class Zx {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Persion p = new Persion();
p.show();
}
}
class Persion
{
String name;
static String country = "CN";
public static void show()
{
System.out.println("haha");
}
}
虽然可以用ArrayTool建立对象使用这些工具的方法,但是有问题:
1,对象时用于封装数据的,可ArrayTool对象并未封装特有数据
2,操作数组的每一个方法都没有用到ArrayTool对象中的特有数据
考虑让程序更严谨,不需要对象,可以将ArrayTool中的方法都定义成静态的,直接用类名调用方法
例:
public class ArrayTool
{
public int getMax(int [] arr)
{
int max=0;
for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++)
if(arr[x]>max)
max=arr[x];
return max;
}
public int getMain(int [] arr)
{
int min=arr[0];
for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++)
if(arr[x]< min)
min=arr[x];
return min;
}
public void selectSort(int [] arr)
{
for(int x=0;x<arr.length-1;x++)
for(int y=x+1;y<arr.length;y++)
if(arr[x]>arr[y])
{
swap(arr,x,y);
}
}
public void bubbleSort(int []arr)
{
for(int x=0;x<arr.length-1;x++)
for(int y=0;y<arr.length-x-1;y++)
if(arr[y]>arr[y+1])
{
swap(arr,y,y+1);
}
}
public void swap(int []arr,int a,int b)
{
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
class Zx
{
public static void main(String []arr)
{
int[] p = {1,9,99,66,2,33,6,88,44,66,78,26};
ArrayTool tool = new ArrayTool();
int max = tool.getMax(p);
System.out.println("max"+max);
tool.selectSort(p);
for(int x=0;x<p.length;x++)
{
System.out.println(p[x]);
}
tool.bubbleSort(p);
for(int x=0;x<p.length;x++)
{
System.out.println(p[x]);
}
}
}
修改后:
public class ArrayTool
{
public static int getMax(int [] arr)
{
int max=0;
for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++)
if(arr[x]>max)
max=arr[x];
return max;
}
public static int getMain(int [] arr)
{
int min=arr[0];
for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++)
if(arr[x]< min)
min=arr[x];
return min;
}
public static void selectSort(int [] arr)
{
for(int x=0;x<arr.length-1;x++)
for(int y=x+1;y<arr.length;y++)
if(arr[x]>arr[y])
{
swap(arr,x,y);
}
}
public static void bubbleSort(int []arr)
{
for(int x=0;x<arr.length-1;x++)
for(int y=0;y<arr.length-x-1;y++)
if(arr[y]>arr[y+1])
{
swap(arr,y,y+1);
}
}
public static void swap(int []arr,int a,int b)
{
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
class Zx
{
public static void main(String []arr)
{
int[] p = {1,9,99,66,2,33,6,88,44,66,78,26};
//ArrayTool tool = new ArrayTool();
int max = ArrayTool.getMax(p);
System.out.println("max"+max);
ArrayTool.selectSort(p);
for(int x=0;x<p.length;x++)
{
System.out.println(p[x]);
}
ArrayTool.bubbleSort(p);
for(int x=0;x<p.length;x++)
{
System.out.println(p[x]);
}
}
}
当方法都静态后,可以方便使用,但是该类还是可以被其他程序建立对象的,为了更为严谨,让该类不能建立对象,可以提供将构造函数私有化完成。这样就不能再建立对象。因为构造函数在对象初始化的时候初始化,构造函数不能初始化了就无法建立新对象。
public class ArrayTool
{
private ArrayTool (){}
public static int getMax(int [] arr)
{
int max=0;
for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++)
if(arr[x]>max)
max=arr[x];
return max;
}
public static int getMain(int [] arr)
{
int min=arr[0];
for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++)
if(arr[x]< min)
min=arr[x];
return min;
}
public static void selectSort(int [] arr)
{
for(int x=0;x<arr.length-1;x++)
for(int y=x+1;y<arr.length;y++)
if(arr[x]>arr[y])
{
swap(arr,x,y);
}
}
public static void bubbleSort(int []arr)
{
for(int x=0;x<arr.length-1;x++)
for(int y=0;y<arr.length-x-1;y++)
if(arr[y]>arr[y+1])
{
swap(arr,y,y+1);
}
}
private public static void swap(int []arr,int a,int b) //隐藏
{
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
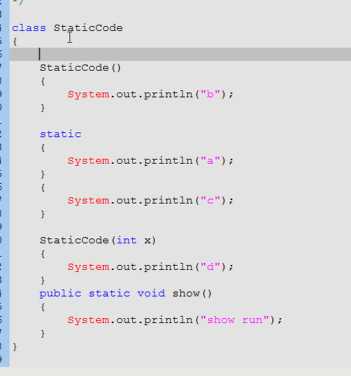
静态代码块:随着类的加载而加载,只执行一次。用于给类进行初始化。优先于给对象初始化的构造构造代码块,优先于给对应对象初始化的构造函数,并优先于主函数。
会打印:a,c,d
下面是
new StaticCode(5);
格式:
static
{
System.out,println("a")
}
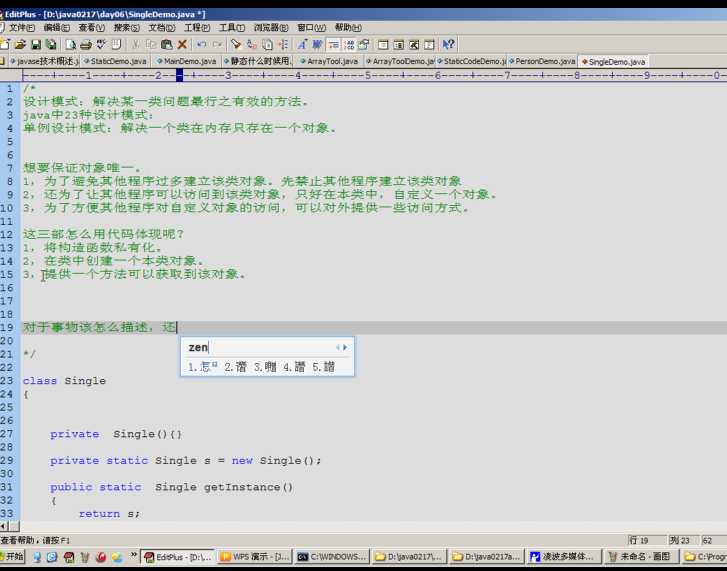
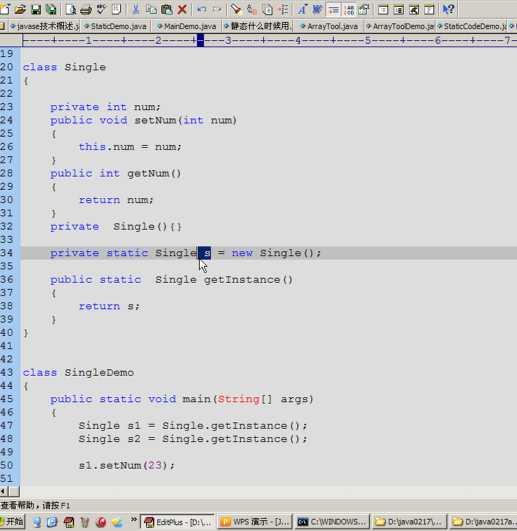
单例设计模式:
JAVA 6(对象)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hitxx/p/4631417.html