标签:style blog http color 使用 strong
2014.07.04 20:43
简介:
给定一个有向图,如果每一条边u->v代表一根水管,定义能从u流向v的最大水流量。那么选定起点s和终点t,如果让水从s流入,从t流出,最多能达到多少流量而不挤爆水管?
图示:
Capacity是容量的意思,那么我们用C(u, v)来表示u->v这条边,也就是u流向v的最大流量。
下面是一张容量图:
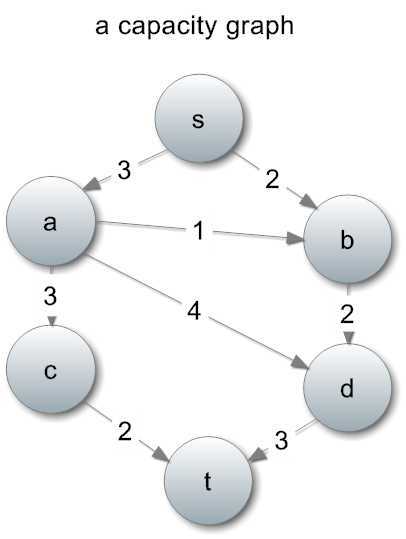
Ford-Fulkerson方法的思路:每次从图中找出一条增广路径,直到找不出来为止。
什么是增广路径呢?是一条从起点s到终点t的权值大于0的路径。比如这条:
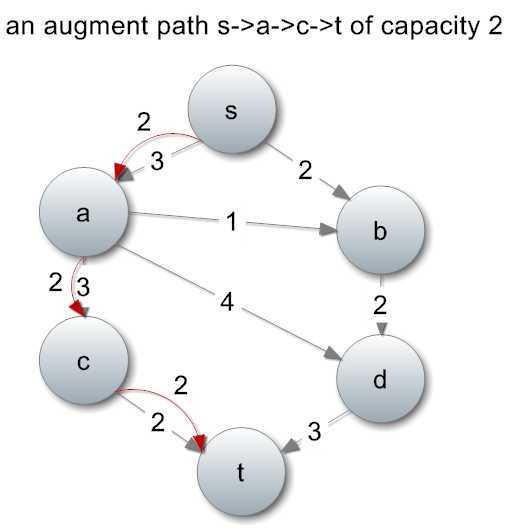
为什么这条路径的流量是2?因为我们只能去路径上的最小容量,这样水管才不会挤爆。
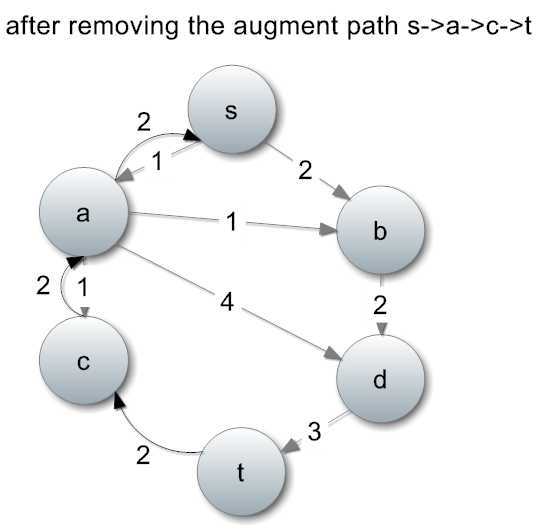
找到增广路径之后怎么办呢?我们把沿路的边扣除掉对应的流量,并增加一条反向的边(最大流的需要证明的地方就在这儿了,问题就是:最大流与最小割等价)。
目前我们已经有了2单位的流量,流量图也发生了变化:
继续寻找增广路径,比如找到一条路径:s->a->b->d->t:
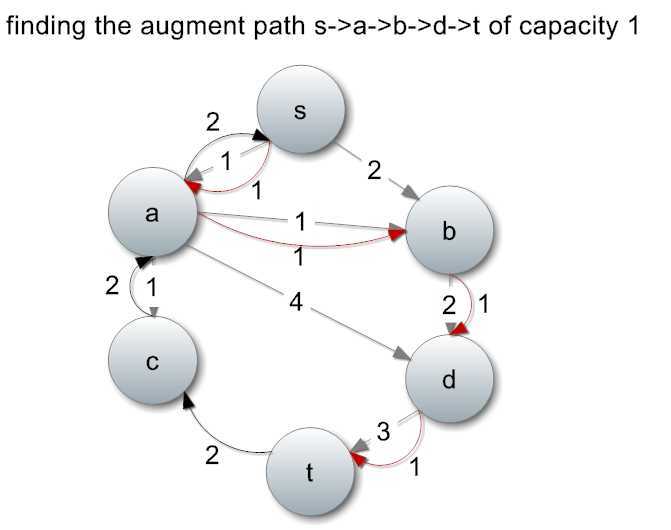
找到以后,增加流量,修改流量图:
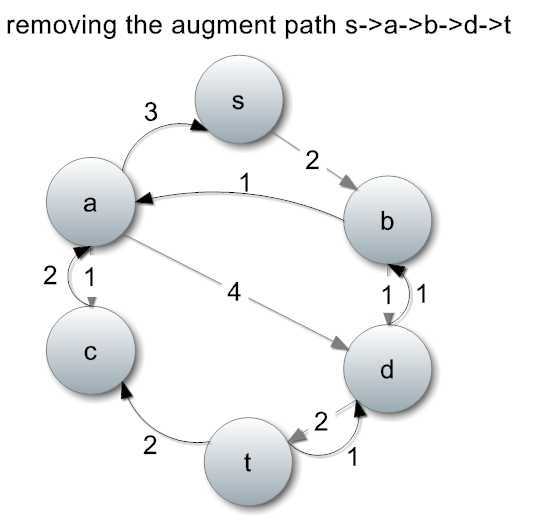
继续找到下一条增广路径:s->b->a->d->t,流量为1。
增加1单位流量,并且修改流量图。
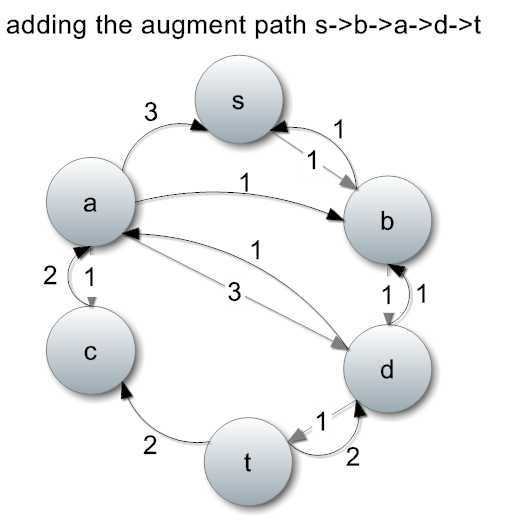
继续找到一条增广路径:s->b->d->t,流量为1。
增加1单位流量,并且修改流量图。
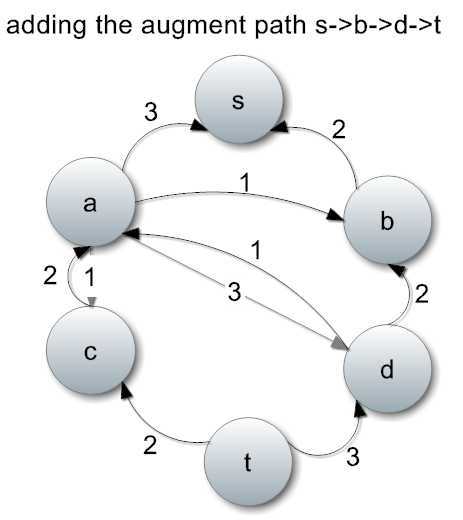
到此为止,没有更多从s到t的增广路径了。总共的流量是2+1+1+1=5。
因此最大流量为5。
在这样的流量模型里,s作为入口,t作为出口,其他顶点的流入和流出一定会保持平衡。这仅仅是最简单的一种模型,如果允许多个入口或者多个出口的话,那么问题的复杂程度就不是几句话能说清楚的了。
Ford-Fulkerson方法是基于这种增广路径思想的解法,用于处理这类问题。之所以叫“方法”而不是“算法”,是因为如何寻找增广路径并没有具体说明。
那到底怎么找呢?可以用BFS、DFS、排序等等手段来组合使用。简单的来说,就是靠搜。根据寻找增广路径的方法不同,就有了几种不同的对应算法。
实现:
我的实现版本,使用BFS来寻找增广路径,所以属于Edmonds-Karp算法。
1 // My first practice on maximum flow problem. This is an implementation using Edmonds-Karp Algorithm. 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <queue> 5 #include <vector> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const int INFINITY = 1000000000; 9 10 bool findAugmentPath(const vector<vector<int> > &rg, vector<int> &path, 11 const int start, const int end) 12 { 13 // Find an augment path with BFS. 14 queue<int> q; 15 vector<int> back_trace; 16 int n; 17 int i; 18 19 n = rg.size(); 20 back_trace.resize(n, -1); 21 22 int tmp; 23 24 back_trace[start] = start; 25 q.push(start); 26 while (!q.empty()) { 27 if (back_trace[end] >= 0) { 28 // An augment path is found. 29 break; 30 } 31 tmp = q.front(); 32 q.pop(); 33 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 34 if (rg[tmp][i] == INFINITY) { 35 continue; 36 } 37 if (i == tmp || back_trace[i] >= 0) { 38 continue; 39 } 40 back_trace[i] = tmp; 41 q.push(i); 42 } 43 } 44 45 if (q.empty()) { 46 return false; 47 } 48 49 path.clear(); 50 tmp = end; 51 while (tmp != start) { 52 path.push_back(tmp); 53 tmp = back_trace[tmp]; 54 } 55 path.push_back(tmp); 56 reverse(path.begin(), path.end()); 57 58 while (!q.empty()) { 59 q.pop(); 60 } 61 back_trace.clear(); 62 63 return true; 64 } 65 66 void addFlow(vector<vector<int> > &rg, const vector<int> &path, const int flow) 67 { 68 int i; 69 70 for (i = 0; i < (int)path.size() - 1; ++i) { 71 if (rg[path[i]][path[i + 1]] == flow) { 72 rg[path[i]][path[i + 1]] = INFINITY; 73 } else { 74 rg[path[i]][path[i + 1]] -= flow; 75 } 76 77 if (rg[path[i + 1]][path[i]] == INFINITY) { 78 rg[path[i + 1]][path[i]] = flow; 79 } else { 80 rg[path[i + 1]][path[i]] += flow; 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 85 int maximumFlow(const vector<vector<int> > &graph, int start, int end) 86 { 87 // The residual graph 88 vector<vector<int> > rg; 89 vector<int> path; 90 int flow, maximum_flow; 91 int i; 92 93 if (graph.size() < 2 || start == end) { 94 return 0; 95 } 96 97 rg = graph; 98 maximum_flow = 0; 99 while (findAugmentPath(rg, path, start, end)) { 100 flow = rg[path[0]][path[1]]; 101 for (i = 1; i < (int)path.size() - 1; ++i) { 102 flow = min(flow, rg[path[i]][path[i + 1]]); 103 } 104 addFlow(rg, path, flow); 105 maximum_flow += flow; 106 } 107 108 return maximum_flow; 109 } 110 111 int main() 112 { 113 vector<vector<int> > graph; 114 vector<int> dist; 115 vector<bool> reachable; 116 int n; 117 int nk; 118 int i, j; 119 int tmp, tmp_dist; 120 int maximum_flow; 121 int start, end; 122 123 while (cin >> n && n > 0) { 124 graph.resize(n); 125 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 126 graph[i].resize(n, INFINITY); 127 } 128 129 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 130 cin >> nk; 131 for (j = 0; j < nk; ++j) { 132 cin >> tmp >> tmp_dist; 133 graph[i][tmp] = tmp_dist; 134 } 135 } 136 137 cin >> start >> end; 138 maximum_flow = maximumFlow(graph, start, end); 139 140 cout << "Maximum flow is " << maximum_flow << "." << endl; 141 142 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 143 graph[i].clear(); 144 } 145 graph.clear(); 146 } 147 148 return 0; 149 }
《数据结构与算法分析:C语言描述》复习——第九章“图论”——最大流问题,布布扣,bubuko.com
《数据结构与算法分析:C语言描述》复习——第九章“图论”——最大流问题
标签:style blog http color 使用 strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhuli19901106/p/3825152.html