标签:
java中关于泛型的有关知识
一.为什么要有泛型(Generic)
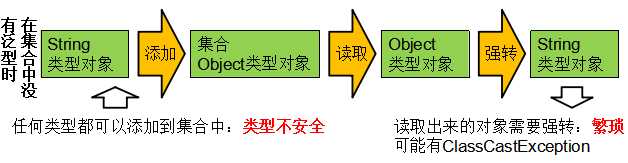
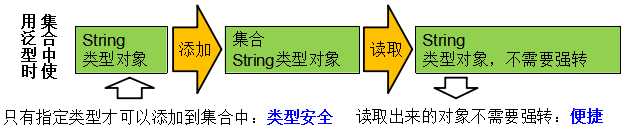
1.解决元素存储的安全性问题
2.解 决获取数据元素时,需要类型强转的问题
决获取数据元素时,需要类型强转的问题
二.在集合中使用泛型
public class TestGeneric {
//1.在集合中不用泛型的情况
public void Test1(){
List list=new ArrayList();
list.add(87);
list.add(89);
list.add(95);
//1.没有使用泛型,任何Object及其子类的对象都可以添加进来
list.add(new String("aa"));
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
//2.强转为int型时,可能报ClassCastException的异常
int score=(Integer)list.get(i);
System.out.println(score);
}
}
//2.在集合中使用泛型
public void test2(){
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(89);
list.add(87);
//list.add("aa");
//输出list中存储的整数
Iterator<Integer> it=list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next());
}
//3.在Map中使用泛型
public void test3(){
Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("aa", 87);
map.put("bb", 90);
map.put("cc", 95);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set=map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o:set){
System.out.println(o.getKey()+"---->"+o.getValue());
}
}
}
三.自定义泛型类
1.实例化泛型类的对象时,指明泛型的类型,则对应的类中所有使用泛型的位置,都变为实例化中指定的泛型类型。
2.如果我们自定义了泛型类,对象实例化时没有指定泛型,默认为Object型的。
3.继承泛型类或泛型接口时,可以指明泛型的类型,也可以不指明
class SubOrder extendx Order<Integer> {}
class SubOrder<T> extendx Order<T>{}
4.加入集合中的对象类型必须与指定的泛型类型一致
class Person<T>{
//使用T类型定义变量
private T info;
//使用T类型定义一般方法
public T getInfo(){
return info;
}
public void setInfo(T info){
this.info = info;
}
//使用T类型定义构造器
public Person(){}
public Person(T info){
this.info = info;
}
//static的方法中不能声明泛型
//public static void show(T t){
//}
//不能在try-catch中使用泛型定义
//try{}
//catch(T t){}
}


标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xujiming/p/4636238.html