标签:
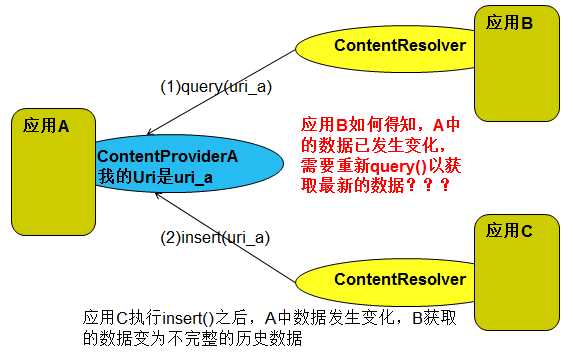
现在有这样一个应用A通过ContentProvider提供自己的数据给其他应用,应用B通过ContentResolver获取应用A中提供的数据,并将其展示在ListView中,而应用C通过ContentResolver修改应用A中的数据,或者添加新的数据。现在的问题是应用C修改A中数据后,应用B的ListView中显示的还是历史数据……
具体程序如下:
ContentProvider和插入数据的应用分别复用上一篇中的两个应用,然后新建一个应用,用于获取ContentProvider中的数据,并在一个ListView中展示:
布局文件activity _main.xml中添加一个ListView:
1 <ListView 2 3 android:id="@+id/lv" 4 5 android:layout_width="match_parent" 6 7 android:layout_height="wrap_content"></ListView>
布局文件item_layout.xml用于显示ListView中的条目:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 3 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 4 5 android:layout_width="match_parent" 6 7 android:layout_height="match_parent" 8 9 android:orientation="horizontal" > 10 11 <TextView 12 13 android:id="@+id/tv_id" 14 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 17 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 18 19 android:layout_weight="1"/> 20 21 <TextView 22 23 android:id="@+id/tv_name" 24 25 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 26 27 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 28 29 android:layout_weight="1"/> 30 31 <TextView 32 33 android:id="@+id/tv_gender" 34 35 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 36 37 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 38 39 android:layout_weight="1"/> 40 41 <TextView 42 43 android:id="@+id/tv_age" 44 45 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 46 47 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 48 49 android:layout_weight="1"/> 50 </LinearLayout>
MainActivity添加获取数据并显示到ListView的代码:
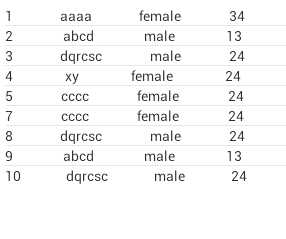
1 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 2 3 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 4 5 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 6 7 uri = Uri.parse("content://cn.csc.content_provider/t_student"); 8 9 Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, new String[]{"id as _id","name","gender","age"}, null, null, null); 10 11 lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv); 12 13 lv.setAdapter(new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,R.layout.item_layout,cursor, 14 15 new String[]{"_id","name","gender","age"},new int[]{R.id.tv_id,R.id.tv_name,R.id.tv_gender,R.id.tv_age})); 16 17 }
运行结果:
上面使用到了SimpleCursorAdapter这个Adapter类,其构造的参数说明:
第一个参数指明应用上下文实例
第二个参数指明ListView中每个条目显示的布局id
第三个参数指明存放要显示数据的Cursor结果集对象
第四和第五个参数共同指明Cursor结果集中每一个字段放在布局文件中的那个控件中,这两个数组中的元素时按顺序一一对应的。第四个参数是String[]类型的,每个元素为结果集中的字段名,第五个参数时int[]类型的,每个参数时布局文件中每个控件的资源id。
在这里需要特别注意的一点是,SimpleCursorAdapter要求表中必须存在名为_id的字段,否则会报错,从而停止正常运行。
但是我之前所建立的表中并没有_id字段,id字段倒是有一个,但是又不想去改变表的定义,这时,就可以在query()方法中,用于指定要查询的字段的第二个参数中使用别名:如上面的写法是:
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, new String[]{"id as _id","name","gender","age"}, null, null, null);
这样结果集中的字段名就由id变为了_id,SimpleCursorAdapter就能正常使用了。
但是,此时由充当应用C角色的应用通过insert()方法添加数据,当前应用中的ListView并没有变化,还是显示不完整的历史数据!!!
针对这个问题,android提供了一个名为ContentObserver的类,用于观察特定uri的数据有无变化,有变化时,则可以根据自己需要做相应的处理。
ContentObserver的使用:

第一步:在应用B中注册ContentObserver,声明要观察的uri,并重写其onChange方法完成需要的业务逻辑。
具体代码如下:
1 uri = Uri.parse("content://cn.csc.content_provider/t_student"); 2 3 getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(uri, true, new ContentObserver(new Handler()) { 4 5 @Override 6 7 public void onChange(boolean selfChange) { 8 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 11 super.onChange(selfChange); 12 13 Log.i("Test","changed"); 14 15 Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, new String[]{"id as _id","name","gender","age"}, null, null, null); 16 17 lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv); 18 19 lv.setAdapter(new SimpleCursorAdapter(MainActivity.this,R.layout.item_layout,cursor, 20 21 new String[]{"_id","name","gender","age"},new int[]{R.id.tv_id,R.id.tv_name,R.id.tv_gender,R.id.tv_age})); 22 23 Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "数据有变化,已然刷新ListView显示", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 24 25 } 26 27 28 29 });
第二步:在应用A中的insert()、update()、delete()方法中,通知观察这些uri的内容观察者,告知数据发生变化,会触发其对应的onChange方法,完成数据变化的业务。
具体代码如下:
1 getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
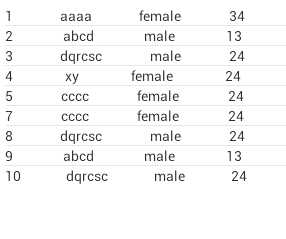
当前ListView状态:
在应用C中测试增删改方法,观察应用B中的运行:
增:
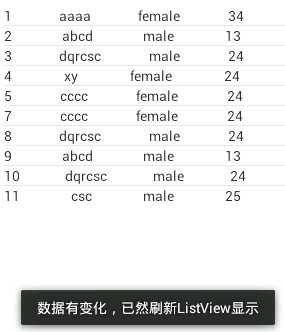
1 public void testInsert(){ 2 3 Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://cn.csc.content_provider/t_student"); 4 5 ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); 6 7 values.put("name", "csc"); 8 9 values.put("gender", "male"); 10 11 values.put("age", 25); 12 13 Uri uri2 = getContext().getContentResolver().insert(uri, values); 14 15 Log.i("Test",uri2.toString()); 16 17 }
运行结果:
删:
1 public void testDelete(){ 2 3 Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://cn.csc.content_provider/t_student"); 4 5 int i = getContext().getContentResolver().delete(uri, "id>?", new String[]{"7"}); 6 7 Log.i("Test",i+""); 8 9 }
运行结果:
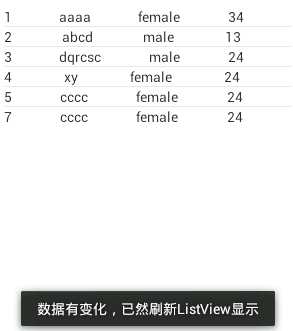
改:
1 public void testUpdate(){ 2 3 Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://cn.csc.content_provider/t_student"); 4 5 ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); 6 7 values.put("name", "dqrcsc"); 8 9 values.put("gender", "male"); 10 11 values.put("age", 24); 12 13 int i = getContext().getContentResolver().update(uri, values, "id>?", new String[]{"3"}); 14 15 Log.i("Test",i+""); 16 17 }
运行结果:
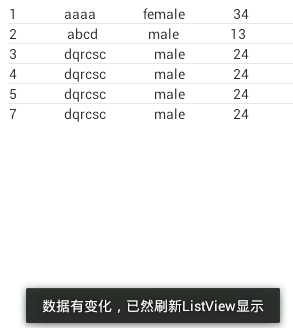
以上,就是ContentObserver的简单使用啦。
android菜鸟学习笔记22----ContentProvider(二)ContentObserver的简单使用
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dqrcsc/p/4640509.html