标签:
1.TCP/IP协议
在Internet中TCP/IP协议是使用最广泛的通讯协议。“传输控制协议/网际协议”/Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
2.TCP协议
TCP(transmission control protocol)传输控制协议。
TCP是一种面向连接的通信协议,TCP连接提供两台计算机之间可靠无差错的字节流数据传输。
3.IP地址和端口号
IP地址:网络中每台计算机的一个标识符,是一个逻辑地址。127.0.0.1代表本机地址。
端口号:具有网络功能的应用软件的标识符。
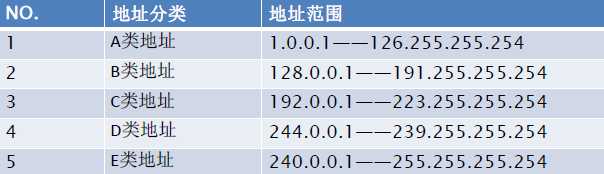
4.IP地址
IP地址是使用32位(4个字节)二进制表示。一般用十进制显示如:182.168.1.3。
IP地址分类:5类,A类:给政府机构用。B类:给中等规模公司用。C类:给有任何需要的人用
D类:用于组播。E类:用于实验。
在实际中可以使用127.0.0.1表示本机(本机IP地址或回路地址),或者直接使用localhost代表本机。
ping 127.0.0.1 是用来测试网卡是否正常。
后三位都为0的和后三位都为255的不在其中,另有他用。
4.1 域名
http://www.sina.com.cn 域名
http:协议
www:www组织
sina:主机名
com;商业 net :非盈利组织 org:政府,edu:教育
cn:中国
5.Socket套接字
6.网络编程的四个基本步骤
演示Demo
public class TCPServer //Server端
{
public static void main (String []args)
{
try{
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket (8888);//建立服务端
while(true)
{
Socket s1=ss.accept();//返回Socket端
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter //建立写入流;
(new OutputStreamWriter(s1.getOutputStream()));
//向写入流写入内容
bw.write("你好"+s1.getInetAddress()+":"+s1.getPort());
//关闭资源
bw.close();
s1.close();
}
}catch (Exception e)
{
}
}}
public class TCPClient //客户端
{
public static void main (String []args)
{
try{
Socket s=new Socket ("127.0.0.1",8888);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
System.out.println("服务器说:"+br.readLine());
br.close();
s.close();
}catch (Exception e)
{
}
}}
7.TCP Socket通信模型
java.net包中定义了两个类:Socket和ServerSocket ,分别用来实现TCP的Client和Server端
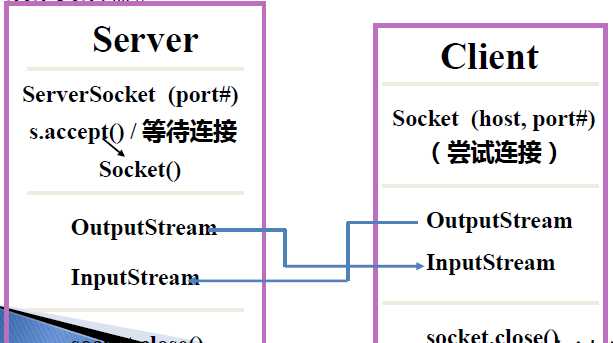
7.1 TCP/IP中的协议
8.UDP网络编程
UDP编程所需要的类。
DatagramSocket 此类表示用来发送和接收数据报包的套接字
DatagramSocket (int port) ;//创建本地主机的指定端口
DatagramSocket (int port ,InetAddress laddr) ;//
DatagramPacket 此类表示数据报包。(多个包发送时会选择不同的路由发送,且按不同的顺序到达)
DatagramPacket (byte[] buf,int length,InetAddress address,int port);
DatagramPacket(byte[] buf,int length,SocketAddress address);
InetAddress类。
static InetAddress getByName(String host);//静态方法,其没有构造方法
//eg: InetAddress ia=InetAddress.getByName("192.168.1.1");返回一个指定iP的对象。
SocketAddress是抽象类,其实现的子类为InetSocketAddress。
构造方法:
InetSocketAddress (InetAddress addr,int port);
InetSocketAddress (int port);//创建套接字地址,其中IP地址为通配符地址。
InetSocketAddress (String hostname,int port);//hostname为IP地址
发送端: 1:建立DatagramSocket,(此socket端口随机)。
2:建立DatagramPacket,(指定发送地址的ip和端口)。
3:使用socket的send方法发送。
4:关闭资源
接收端:1:建立DatagramSocket,(监听的端口为发送端packet的指定端口)。
2:建立DatagramPacket,(无需指定ip和端口)。
3:使用socket的receive方法接收。
4:关闭资源
发送端代码:
import java.io.IOException ;
import java.net.*;
//发送端
public class UDPSender
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
String str="你好吗!";
DatagramSocket ds=null;
DatagramPacket dp=null;
try{
//定义一个发送包的socket ,端口使用9999
ds=new DatagramSocket(9999);
//要发送的数据包,一定要指定ip和port
String ip="127.0.0.1";
byte[]buf=str.getBytes();
dp=new DatagramPacket (buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName(ip),8888);
//发送数据
ds.send(dp);
}catch(Exception e)
{}
finally{
if(ds!=null)
ds.close();
}
}
}
接收端代码:
import java.io.IOException ;
import java.net.*;
//发送端
public class UDPSender
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
String str="你好吗!";
DatagramSocket ds=null;
DatagramPacket dp=null;
try{
//定义一个发送包的socket ,端口使用9999
ds=new DatagramSocket(9999);
//要发送的数据包,一定要指定ip和port
String ip="127.0.0.1";
byte[]buf=str.getBytes();
dp=new DatagramPacket (buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName(ip),8888);
//发送数据
ds.send(dp);
}catch(Exception e)
{}
finally{
if(ds!=null)
ds.close();
}
}
}
//接收端
public class UDPReceiver
{
public static void main (String []args)
{
byte[]buf=new byte[1024];
DatagramSocket ds=null;
DatagramPacket dp=null;
try{
//在8888端口监听并接受数据包
ds=new DatagramSocket("8888");
dp=new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
while(true)
{
//收数据--此方法在接收到数据报前一直阻塞
ds.receive(dp);
//dp.getLength();得到dp里的有效数据的长度
System.out.println(new String (buf,0,dp.getLength()));
}
}catch(Exception e)
{}
finally
{
if(ds!=null)
ds.close();
}
}
}
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/beyondbycyx/p/4643285.html