标签:
HashSet是Set接口典型实现,它按照Hash算法来存储集合中的元素,具有很好的存取和查找性能。主要具有以下特点:
当向HashSet集合中存入一个元素时,HashSet会调用该对象的hashCode()方法来得到该对象的hashCode值,然后根据该值确定对象在HashSet中的存储位置。在Hash集合中,不能同时存放两个相等的元素,而判断两个元素相等的标准是两个对象通过equals方法比较相等并且两个对象的HashCode方法返回值也相等。
下面的例子说明了上述特性:
public class Person { String name; int age; public Person(String name,int age) { this.name=name; this.age=age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } //当对象的名字和姓名相同即返回true public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(obj==null) return false; if((this.name.equals(((Person)obj).name) && this.age==((Person)obj).age)) return true; else return false; } }
此时添加两个name和age均相同的Person对象实例到HashSet中:
public class HashSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Person> hs = new HashSet<>(); Person p1=new Person("xujian", 23); Person p2=new Person("xujian", 23); hs.add(p1); hs.add(p2); for(Person p:hs) { System.out.println(p.name+"---"+p.age); } } }
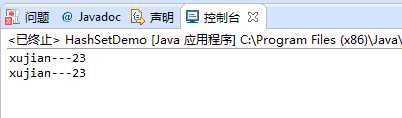
可见,HashSet中存放了两个name和age均相同的Person对象。
接下来我们重写一下Person类的hashCode方法,使其返回相同的HashCode。
public class Person { String name; int age; public Person(String name,int age) { this.name=name; this.age=age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int hashCode() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 return 1; } //当对象的名字和姓名相同即返回true public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(obj==null) return false; if((this.name.equals(((Person)obj).name) && this.age== ((Person)obj).age)) return true; else return false; } }
再次执行向HashSet添加元素操作,会发现此时HashSet只保存了一个。
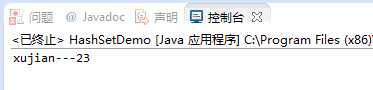
HashSet中每一能存储元素的槽位通常称为“桶”,如果有多个元素的hashCode相同,但是通过equals方法比较返回false,就需要在一个桶上存放多个元素。
HashSet的底层实际上是由HashMap实现的。其四个构造函数分别对应相应的HashMap。
//构造一个新的,空的HashSet,其底层 HashMap实例的默认初始容量是 16,加载因子是 0.75 public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); } //构造一个包含指定 collection 中的元素的新 set public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) { map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16)); addAll(c); } //构造一个新的空 set,其底层 HashMap 实例具有指定的初始容量和指定的加载因子 public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor); } //构造一个新的空 set,其底层 HashMap 实例具有指定的初始容量和默认的加载因子0.75 public HashSet(int initialCapacity) { map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity); }
boolean add(E e): 如果此 set 中尚未包含指定元素,则添加指定元素
public boolean add(E e) { //调用map的put方法,其中value值为静态的Object对象 return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; }
void clear():从此 set 中移除所有元素
public void clear() { map.clear(); }
Object clone():返回此 HashSet 实例的浅表副本
public Object clone() { try { //调用父类的clone方法 HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone(); newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone(); return newSet; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new InternalError(e); } }
boolean contains(Object o):如果此 set 包含指定元素,则返回 true
public boolean contains(Object o) { return map.containsKey(o); }
boolean isEmpty():如果此 set 不包含任何元素,则返回 true
public boolean isEmpty() { return map.isEmpty(); }
Iterator<E> iterator():返回对此 set 中元素进行迭代的迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return map.keySet().iterator(); }
boolean remove(Object o):如果指定元素存在于此 set 中,则将其移除
public boolean remove(Object o) { return map.remove(o)==PRESENT; }
int size():返回此 set 中的元素的数量
public int size() { return map.size(); }
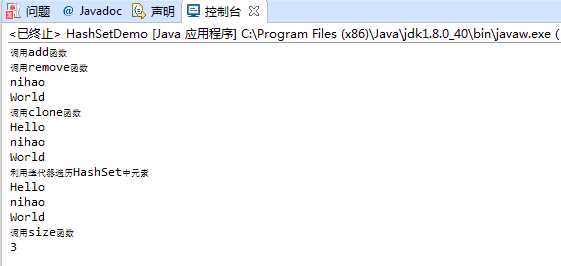
public class HashSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<String> hs1 = new HashSet<>(); //无参构造函数新建一个默认大小为16,装载因子为0.75的HashSet System.out.println("调用add函数"); hs1.add("Hello"); hs1.add("World"); hs1.add("nihao"); HashSet<String> hs2 = new HashSet<>(hs1); //构造一个包含hs1中元素的HashSet System.out.println("调用remove函数"); hs1.remove("Hello"); for(String str:hs1) System.out.println(str); System.out.println("调用clone函数"); HashSet<String> hs3=(HashSet<String>) hs2.clone(); for(String str:hs3) System.out.println(str); System.out.println("利用迭代器遍历HashSet中元素"); Iterator<String> it=hs2.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } System.out.println("调用size函数"); System.out.print(hs2.size()); } }
执行结果如图:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xujian2014/p/4643759.html