标签:
Java知识点总结
1、Java异常处理机制
1.1 Java异常架构图和分类
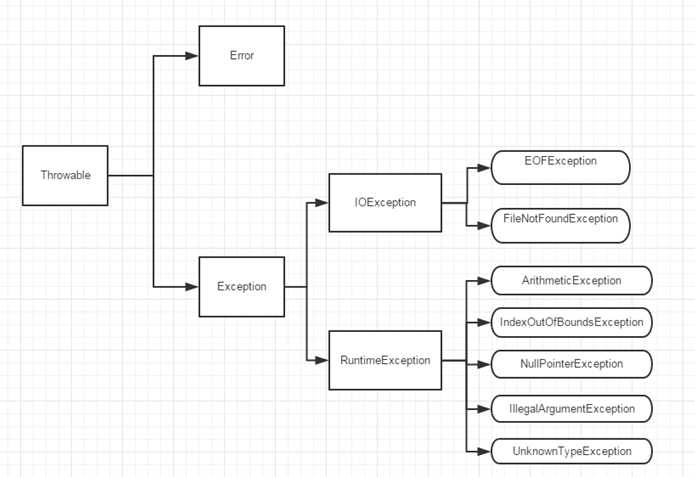
在 Java 中,所有的异常都有一个共同的祖先 Throwable,Throwable有两个重要的子类:Exception(异常)和 Error(错误),二者都是 Java 异常处理的重要子类,各自都包含大量子类。
Error(错误):是程序无法处理的错误,表示运行应用程序中较严重问题。大多数错误与代码编写者执行的操作无关,而表示代码运行时 JVM(Java 虚拟机)出现的问题。例如,Java虚拟机运行错误(Virtual MachineError),当 JVM 不再有继续执行操作所需的内存资源时,将出现 OutOfMemoryError。这些异常发生时,Java虚拟机(JVM)一般会选择线程终止。这些错误表示故障发生于虚拟机自身、或者发生在虚拟机试图执行应用时,如Java虚拟机运行错误(Virtual MachineError)、类定义错误(NoClassDefFoundError)等。这些错误是不可查的,因为它们在应用程序的控制和处理能力之外,而且绝大多数是程序运行时不允许出现的状况。对于设计合理的应用程序来说,即使确实发生了错误,本质上也不应该试图去处理它所引起的异常状况。在 Java中,错误通过Error的子类描述。
Exception(异常):是程序本身可以处理的异常。Exception类有一个重要的子类RuntimeException。RuntimeException 类及其子类表示“JVM 常用操作”引发的错误。例如,若试图使用空值对象引用、除数为零或数组越界,则分别引发运行时异常NullPointerException、ArithmeticException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException。
注意:异常和错误的区别:异常能被程序本身可以处理,错误是无法处理。
Exception 这种异常分两大类运行时异常和非运行时异常(编译异常)。程序中应当尽可能去处理这些异常。
运行时异常:都是RuntimeException类及其子类异常,如NullPointerException(空指针异常)、IndexOutOfBoundsException(下标越界异常)等,这些异常是不检查异常,程序中可以选择捕获处理,也可以不处理。这些异常一般是由程序逻辑错误引起的,程序应该从逻辑角度尽可能避免这类异常的发生。
运行时异常的特点是Java编译器不会检查它,也就是说,当程序中可能出现这类异常,即使没有用try-catch语句捕获它,也没有用throws子句声明抛出它,也会编译通过。
非运行时异常(编译异常):是RuntimeException以外的异常,类型上都属于Exception类及其子类。从程序语法角度讲是必须进行处理的异常,如果不处理,程序就不能编译通过。如IOException、SQLException等以及用户自定义的Exception异常,一般情况下不自定义检查异常。
1.2 Java异常处理机制
在 Java 应用程序中,异常处理机制为:抛出异常,捕捉异常。
1.2.1 抛出异常
当一个方法出现错误引发异常时,方法创建异常对象并交付运行时系统,异常对象中包含了异常类型和异常出现时的程序状态等异常信息。运行时系统负责寻找处置异常的代码并执行。
①throws抛出异常
如果一个方法可能会出现异常,但没有能力处理这种异常,可以在方法声明处用throws子句来声明抛出异常。
methodname throws Exception1,Exception2,..,ExceptionN
{
}
方法名后的throws Exception1,Exception2,...,ExceptionN 为声明要抛出的异常列表。当方法抛出异常列表的异常时,方法将不对这些类型及其子类类型的异常作处理,而抛向调用该方法的方法,由他去处理。
②throw抛出异常
throw总是出现在函数体中,用来抛出一个Throwable类型的异常。程序会在throw语句后立即终止,它后面的语句执行不到,然后在包含它的所有try块中(可能在上层调用函数中)从里向外寻找含有与其匹配的catch子句的try块。
1.2.2 捕获异常
在方法抛出异常之后,运行时系统将转为寻找合适的异常处理器(exception handler)。潜在的异常处理器是异常发生时依次存留在调用栈中的方法的集合。当异常处理器所能处理的异常类型与方法抛出的异常类型相符时,即为合适 的异常处理器。运行时系统从发生异常的方法开始,依次回查调用栈中的方法,直至找到含有合适异常处理器的方法并执行。当运行时系统遍历调用栈而未找到合适 的异常处理器,则运行时系统终止。同时,意味着Java程序的终止。
1.3 定义自己的异常类
在程序中使用自定义异常类,大体可分为以下几个步骤。
(1)创建自定义异常类。
(2)在方法中通过throw关键字抛出异常对象。
(3)如果在当前抛出异常的方法中处理异常,可以使用try-catch语句捕获并处理;否则在方法的声明处通过throws关键字指明要抛出给方法调用者的异常,继续进行下一步操作。
(4)在出现异常方法的调用者中捕获并处理异常。
24. }
25. class MyException extends Exception { // 创建自定义异常类
34. }
2、Java IO流
【案例1】创建一个新文件
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import java.io.*;
class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { File f=new File("D:\\hello.txt"); try{ f.createNewFile(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
运行结果:
程序运行之后,在d盘下会有一个名字为hello.txt的文件。
【案例2】File类的两个常量
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(File.separator); System.out.println(File.pathSeparator); } } |
【运行结果】:
\
;
现在我们使用File类中的常量改写上面的代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); try{ f.createNewFile(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
建议使用File类中的常量。
删除一个文件
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
/** * 删除一个文件 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); if(f.exists()){ f.delete(); }else{ System.out.println("文件不存在"); }
} } |
创建一个文件夹
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
/** * 创建一个文件夹 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello"; File f=new File(fileName); f.mkdir(); } } |
【运行结果】:
D盘下多了一个hello文件夹
列出指定目录的全部文件(包括隐藏文件):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
/** * 使用list列出指定目录的全部文件 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator; File f=new File(fileName); String[] str=f.list(); for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { System.out.println(str[i]); } } } |
【运行结果】:
$RECYCLE.BIN
360
360Downloads
360Rec
360SoftMove
Config.Msi
da
Downloads
DriversBackup
eclipse
java web整合开发和项目实战
Lenovo
MSOCache
Program
Program Files
python
RECYGLER.{8F92DA15-A229-A4D5-B5CE-5280C8B89C19}
System Volume Information
Tomcat6
var
vod_cache_data
新建文件夹
(你的运行结果应该和这个不一样的,呵呵)
但是使用list返回的是String数组,。而且列出的不是完整路径,如果想列出完整路径的话,需要使用listFiles.他返回的是File的数组
列出指定目录的全部文件(包括隐藏文件):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
/** * 使用listFiles列出指定目录的全部文件 * listFiles输出的是完整路径 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator; File f=new File(fileName); File[] str=f.listFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { System.out.println(str[i]); } } } |
【运行结果】:
D:\$RECYCLE.BIN
D:\360
D:\360Downloads
D:\360Rec
D:\360SoftMove
D:\Config.Msi
D:\da
D:\Downloads
D:\DriversBackup
D:\eclipse
D:\java web整合开发和项目实战
D:\Lenovo
D:\MSOCache
D:\Program
D:\Program Files
D:\python
D:\RECYGLER.{8F92DA15-A229-A4D5-B5CE-5280C8B89C19}
D:\System Volume Information
D:\Tomcat6
D:\var
D:\vod_cache_data
D:\新建文件夹
通过比较可以指定,使用listFiles更加方便、
判断一个指定的路径是否为目录
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
/** * 使用isDirectory判断一个指定的路径是否为目录 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator; File f=new File(fileName); if(f.isDirectory()){ System.out.println("YES"); }else{ System.out.println("NO"); } } } |
【运行结果】:YES
搜索指定目录的全部内容
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
/** * 列出指定目录的全部内容 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName="D:"+File.separator; File f=new File(fileName); print(f); } public static void print(File f){ if(f!=null){ if(f.isDirectory()){ File[] fileArray=f.listFiles(); if(fileArray!=null){ for (int i = 0; i < fileArray.length; i++) { //递归调用 print(fileArray[i]); } } } else{ System.out.println(f); } } } } |
【运行结果】:
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\framepages\web4welcome_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\help_005fhome_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\help_005fhome_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\home_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\home_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\index_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\index_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\login_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\login_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\modify_005fuser_005finfo_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\modify_005fuser_005finfo_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\register_005fnotify_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\register_005fnotify_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\sign_005fup_jsp.class
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\sign_005fup_jsp.java
D:\Tomcat6\work\Catalina\localhost\nevel\org\apache\jsp\transit_jsp.class
……
【使用RandomAccessFile写入文件】
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
/** * 使用RandomAccessFile写入文件 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); RandomAccessFile demo=new RandomAccessFile(f,"rw"); demo.writeBytes("asdsad"); demo.writeInt(12); demo.writeBoolean(true); demo.writeChar(‘A‘); demo.writeFloat(1.21f); demo.writeDouble(12.123); demo.close(); } } |
如果你此时打开hello。txt查看的话,会发现那是乱码。
字节流
【向文件中写入字符串】
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
/** * 字节流 * 向文件中写入字符串 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); OutputStream out =new FileOutputStream(f); String str="你好"; byte[] b=str.getBytes(); out.write(b); out.close(); } } |
查看hello.txt会看到“你好”
当然也可以一个字节一个字节的写。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
/** * 字节流 * 向文件中一个字节一个字节的写入字符串 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); OutputStream out =new FileOutputStream(f); String str="你好"; byte[] b=str.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { out.write(b[i]); } out.close(); } } |
结果还是:“你好”
向文件中追加新内容:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
/** * 字节流 * 向文件中追加新内容: * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); OutputStream out =new FileOutputStream(f,true); String str="Rollen"; //String str="\r\nRollen"; 可以换行 byte[] b=str.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { out.write(b[i]); } out.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:
你好Rollen
【读取文件内容】
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
/** * 字节流 * 读文件内容 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; in.read(b); in.close(); System.out.println(new String(b)); } } |
【运行结果】
你好Rollen
Rollen_
但是这个例子读取出来会有大量的空格,我们可以利用in.read(b);的返回值来设计程序。如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/** * 字节流 * 读文件内容 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; int len=in.read(b); in.close(); System.out.println("读入长度为:"+len); System.out.println(new String(b,0,len)); } } |
【运行结果】:
读入长度为:18
你好Rollen
Rollen
我们预先申请了一个指定大小的空间,但是有时候这个空间可能太小,有时候可能太大,我们需要准确的大小,这样节省空间,那么我们可以这样干:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/** * 字节流 * 读文件内容,节省空间 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f); byte[] b=new byte[(int)f.length()]; in.read(b); System.out.println("文件长度为:"+f.length()); in.close(); System.out.println(new String(b)); } } |
文件长度为:18
你好Rollen
Rollen
将上面的例子改为一个一个读:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
/** * 字节流 * 读文件内容,节省空间 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f); byte[] b=new byte[(int)f.length()]; for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { b[i]=(byte)in.read(); } in.close(); System.out.println(new String(b)); } } |
输出的结果和上面的一样。
上面的几个例子都是在知道文件的内容多大,然后才展开的,有时候我们不知道文件有多大,这种情况下,我们需要判断是否独到文件的末尾。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
/** * 字节流 *读文件 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; int count =0; int temp=0; while((temp=in.read())!=(-1)){ b[count++]=(byte)temp; } in.close(); System.out.println(new String(b)); } } |
【运行结果】
你好Rollen
Rollen_
提醒一下,当独到文件末尾的时候会返回-1.正常情况下是不会返回-1的
字符流
【向文件中写入数据】
现在我们使用字符流
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
/** * 字符流 * 写入数据 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); Writer out =new FileWriter(f); String str="hello"; out.write(str); out.close(); } } |
当你打开hello。txt的时候,会看到hello
其实这个例子上之前的例子没什么区别,只是你可以直接输入字符串,而不需要你将字符串转化为字节数组。
当你如果想问文件中追加内容的时候,可以使用将上面的声明out的哪一行换为:
Writer out =new FileWriter(f,true);
这样,当你运行程序的时候,会发现文件内容变为:
hellohello如果想在文件中换行的话,需要使用“\r\n”
比如将str变为String str=”\r\nhello”;
这样文件追加的str的内容就会换行了。
从文件中读内容:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/** * 字符流 * 从文件中读出内容 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); char[] ch=new char[100]; Reader read=new FileReader(f); int count=read.read(ch); read.close(); System.out.println("读入的长度为:"+count); System.out.println("内容为"+new String(ch,0,count)); } } |
【运行结果】:
读入的长度为:17
内容为hellohello
hello
当然最好采用循环读取的方式,因为我们有时候不知道文件到底有多大。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
/** * 字符流 * 从文件中读出内容 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName="D:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File f=new File(fileName); char[] ch=new char[100]; Reader read=new FileReader(f); int temp=0; int count=0; while((temp=read.read())!=(-1)){ ch[count++]=(char)temp; } read.close(); System.out.println("内容为"+new String(ch,0,count)); } } |
运行结果:
内容为hellohello
hello
关于字节流和字符流的区别
实际上字节流在操作的时候本身是不会用到缓冲区的,是文件本身的直接操作的,但是字符流在操作的 时候下后是会用到缓冲区的,是通过缓冲区来操作文件的。
读者可以试着将上面的字节流和字符流的程序的最后一行关闭文件的代码注释掉,然后运行程序看看。你就会发现使用字节流的话,文件中已经存在内容,但是使用字符流的时候,文件中还是没有内容的,这个时候就要刷新缓冲区。
使用字节流好还是字符流好呢?
答案是字节流。首先因为硬盘上的所有文件都是以字节的形式进行传输或者保存的,包括图片等内容。但是字符只是在内存中才会形成的,所以在开发中,字节流使用广泛。
文件的复制
其实DOS下就有一个文件复制功能,比如我们想把d盘下面的hello.txt文件复制到d盘下面的rollen.txt文件中,那么我们就可以使用下面的命令:
copy d:\hello.txt d:\rollen.txt
运行之后你会在d盘中看见hello.txt.,并且两个文件的内容是一样的,
下面我们使用程序来复制文件吧。
基本思路还是从一个文件中读入内容,边读边写入另一个文件,就是这么简单。、
首先编写下面的代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
/** * 文件的复制 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { if(args.length!=2){ System.out.println("命令行参数输入有误,请检查"); System.exit(1); } File file1=new File(args[0]); File file2=new File(args[1]);
if(!file1.exists()){ System.out.println("被复制的文件不存在"); System.exit(1); } InputStream input=new FileInputStream(file1); OutputStream output=new FileOutputStream(file2); if((input!=null)&&(output!=null)){ int temp=0; while((temp=input.read())!=(-1)){ output.write(temp); } } input.close(); output.close(); } } |
然后在命令行下面
javac hello.java
java hello d:\hello.txt d:\rollen.txt
现在你就会在d盘看到rollen。txt了,
OutputStreramWriter 和InputStreamReader类
整个IO类中除了字节流和字符流还包括字节和字符转换流。
OutputStreramWriter将输出的字符流转化为字节流
InputStreamReader将输入的字节流转换为字符流
但是不管如何操作,最后都是以字节的形式保存在文件中的。
将字节输出流转化为字符输出流
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
/** * 将字节输出流转化为字符输出流 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName= "d:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File file=new File(fileName); Writer out=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file)); out.write("hello"); out.close(); } } |
运行结果:文件中内容为:hello
将字节输入流变为字符输入流
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
/** * 将字节输入流变为字符输入流 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String fileName= "d:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"; File file=new File(fileName); Reader read=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)); char[] b=new char[100]; int len=read.read(b); System.out.println(new String(b,0,len)); read.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:hello
前面列举的输出输入都是以文件进行的,现在我们以内容为输出输入目的地,使用内存操作流
ByteArrayInputStream 主要将内容写入内容
ByteArrayOutputStream 主要将内容从内存输出
使用内存操作流将一个大写字母转化为小写字母
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
/** * 使用内存操作流将一个大写字母转化为小写字母 * */ import java.io.*; class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String str="ROLLENHOLT"; ByteArrayInputStream input=new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes()); ByteArrayOutputStream output=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int temp=0; while((temp=input.read())!=-1){ char ch=(char)temp; output.write(Character.toLowerCase(ch)); } String outStr=output.toString(); input.close(); output.close(); System.out.println(outStr); } } |
【运行结果】:
rollenholt
内容操作流一般使用来生成一些临时信息采用的,这样可以避免删除的麻烦。
管道流
管道流主要可以进行两个线程之间的通信。
PipedOutputStream 管道输出流
PipedInputStream 管道输入流
验证管道流
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
/** * 验证管道流 * */ import java.io.*;
/** * 消息发送类 * */ class Send implements Runnable{ private PipedOutputStream out=null; public Send() { out=new PipedOutputStream(); } public PipedOutputStream getOut(){ return this.out; } public void run(){ String message="hello , Rollen"; try{ out.write(message.getBytes()); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }try{ out.close(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
/** * 接受消息类 * */ class Recive implements Runnable{ private PipedInputStream input=null; public Recive(){ this.input=new PipedInputStream(); } public PipedInputStream getInput(){ return this.input; } public void run(){ byte[] b=new byte[1000]; int len=0; try{ len=this.input.read(b); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }try{ input.close(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("接受的内容为 "+(new String(b,0,len))); } } /** * 测试类 * */ class hello{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Send send=new Send(); Recive recive=new Recive(); try{ //管道连接 send.getOut().connect(recive.getInput()); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(send).start(); new Thread(recive).start(); } } |
【运行结果】:
接受的内容为 hello , Rollen
打印流
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
/** * 使用PrintStream进行输出 * */ import java.io.*;
class hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintStream print = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"))); print.println(true); print.println("Rollen"); print.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:
true
Rollen
当然也可以格式化输出
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
/** * 使用PrintStream进行输出 * 并进行格式化 * */ import java.io.*; class hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintStream print = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"))); String name="Rollen"; int age=20; print.printf("姓名:%s. 年龄:%d.",name,age); print.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:
姓名:Rollen. 年龄:20.
使用OutputStream向屏幕上输出内容
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
/** * 使用OutputStream向屏幕上输出内容 * */ import java.io.*; class hello { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { OutputStream out=System.out; try{ out.write("hello".getBytes()); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try{ out.close(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
【运行结果】:
hello
输入输出重定向
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream;
/** * 为System.out.println()重定向输出 * */ public class systemDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){ // 此刻直接输出到屏幕 System.out.println("hello"); File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); try{ System.setOut(new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file))); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("这些内容在文件中才能看到哦!"); } } |
【运行结果】:
eclipse的控制台输出的是hello。然后当我们查看d盘下面的hello.txt文件的时候,会在里面看到:这些内容在文件中才能看到哦!
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream;
/** * System.err重定向 这个例子也提示我们可以使用这种方法保存错误信息 * */ public class systemErr{ public static void main(String[] args){ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); System.err.println("这些在控制台输出"); try{ System.setErr(new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file))); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.err.println("这些在文件中才能看到哦!"); } } |
【运行结果】:
你会在eclipse的控制台看到红色的输出:“这些在控制台输出”,然后在d盘下面的hello.txt中会看到:这些在文件中才能看到哦!
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException;
/** * System.in重定向 * */ public class systemIn{ public static void main(String[] args){ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ return; }else{ try{ System.setIn(new FileInputStream(file)); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; try{ len = System.in.read(bytes); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("读入的内容为:" + new String(bytes, 0, len)); } } } |
【运行结果】:
前提是我的d盘下面的hello.txt中的内容是:“这些文件中的内容哦!”,然后运行程序,输出的结果为:读入的内容为:这些文件中的内容哦!
BufferedReader的小例子
注意: BufferedReader只能接受字符流的缓冲区,因为每一个中文需要占据两个字节,所以需要将System.in这个字节输入流变为字符输入流,采用:
|
1 2 |
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); |
下面给一个实例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/** * 使用缓冲区从键盘上读入内容 * */ public class BufferedReaderDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){ BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String str = null; System.out.println("请输入内容"); try{ str = buf.readLine(); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("你输入的内容是:" + str); } } |
运行结果:
请输入内容
dasdas
你输入的内容是:dasdas
Scanner类
其实我们比较常用的是采用Scanner类来进行数据输入,下面来给一个Scanner的例子吧
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
import java.util.Scanner;
/** * Scanner的小例子,从键盘读数据 * */ public class ScannerDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in); // 读一个整数 int temp = sca.nextInt(); System.out.println(temp); //读取浮点数 float flo=sca.nextFloat(); System.out.println(flo); //读取字符 //...等等的,都是一些太基础的,就不师范了。 } } |
其实Scanner可以接受任何的输入流
下面给一个使用Scanner类从文件中读出内容
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.util.Scanner;
/** * Scanner的小例子,从文件中读内容 * */ public class ScannerDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); Scanner sca = null; try{ sca = new Scanner(file); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } String str = sca.next(); System.out.println("从文件中读取的内容是:" + str); } } |
【运行结果】:
从文件中读取的内容是:这些文件中的内容哦!
数据操作流DataOutputStream、DataInputStream类
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException;
public class DataOutputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); char[] ch = { ‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘ }; DataOutputStream out = null; out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file)); for(char temp : ch){ out.writeChar(temp); } out.close(); } } |
A B C
现在我们在上面例子的基础上,使用DataInputStream读出内容
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException;
public class DataOutputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); char[] ch = new char[10]; int count = 0; char temp; while((temp = input.readChar()) != ‘C‘){ ch[count++] = temp; } System.out.println(ch); } } |
【运行结果】:
AB
合并流 SequenceInputStream
SequenceInputStream主要用来将2个流合并在一起,比如将两个txt中的内容合并为另外一个txt。下面给出一个实例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
/** * 将两个文本文件合并为另外一个文本文件 * */ public class SequenceInputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file1 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello1.txt"); File file2 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello2.txt"); File file3 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); InputStream input1 = new FileInputStream(file1); InputStream input2 = new FileInputStream(file2); OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file3); // 合并流 SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(input1, input2); int temp = 0; while((temp = sis.read()) != -1){ output.write(temp); } input1.close(); input2.close(); output.close(); sis.close(); } } |
【运行结果】
结果会在hello.txt文件中包含hello1.txt和hello2.txt文件中的内容。
文件压缩 ZipOutputStream类
先举一个压缩单个文件的例子吧:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.zip.ZipEntry; import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class ZipOutputStreamDemo1{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); File zipFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.zip"); InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file); ZipOutputStream zipOut = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( zipFile)); zipOut.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file.getName())); // 设置注释 zipOut.setComment("hello"); int temp = 0; while((temp = input.read()) != -1){ zipOut.write(temp); } input.close(); zipOut.close(); } } |
【运行结果】
运行结果之前,我创建了一个hello.txt的文件,原本大小56个字节,但是压缩之后产生hello.zip之后,居然变成了175个字节,有点搞不懂。
不过结果肯定是正确的,我只是提出我的一个疑问而已。
上面的这个例子测试的是压缩单个文件,下面的们来看看如何压缩多个文件。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.zip.ZipEntry; import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
/** * 一次性压缩多个文件 * */ public class ZipOutputStreamDemo2{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 要被压缩的文件夹 File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "temp"); File zipFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + "zipFile.zip"); InputStream input = null; ZipOutputStream zipOut = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( zipFile)); zipOut.setComment("hello"); if(file.isDirectory()){ File[] files = file.listFiles(); for(int i = 0; i < files.length; ++i){ input = new FileInputStream(files[i]); zipOut.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file.getName() + File.separator + files[i].getName())); int temp = 0; while((temp = input.read()) != -1){ zipOut.write(temp); } input.close(); } } zipOut.close(); } } |
【运行结果】
先看看要被压缩的文件吧:
接下来看看压缩之后的:
既然能压缩,自然能解压缩,在谈解压缩之前,我们会用到一个ZipFile类,先给一个这个例子吧。java中的每一个压缩文件都是可以使用ZipFile来进行表示的
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.zip.ZipFile;
/** * ZipFile演示 * */ public class ZipFileDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.zip"); ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file); System.out.println("压缩文件的名称为:" + zipFile.getName()); } } |
【运行结果】:
压缩文件的名称为:d:\hello.zip
现在我们是时候来看看如何加压缩文件了,和之前一样,先让我们来解压单个压缩文件(也就是压缩文件中只有一个文件的情况),我们采用前面的例子产生的压缩文件hello.zip
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.util.zip.ZipEntry; import java.util.zip.ZipFile;
/** * 解压缩文件(压缩文件中只有一个文件的情况) * */ public class ZipFileDemo2{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.zip"); File outFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + "unZipFile.txt"); ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file); ZipEntry entry = zipFile.getEntry("hello.txt"); InputStream input = zipFile.getInputStream(entry); OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(outFile); int temp = 0; while((temp = input.read()) != -1){ output.write(temp); } input.close(); output.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:
解压缩之前:
这个压缩文件还是175字节
解压之后产生:
又回到了56字节,表示郁闷。
现在让我们来解压一个压缩文件中包含多个文件的情况吧
ZipInputStream类
当我们需要解压缩多个文件的时候,ZipEntry就无法使用了,如果想操作更加复杂的压缩文件,我们就必须使用ZipInputStream类
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.util.zip.ZipEntry; import java.util.zip.ZipFile; import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
/** * 解压缩一个压缩文件中包含多个文件的情况 * */ public class ZipFileDemo3{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "zipFile.zip"); File outFile = null; ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file); ZipInputStream zipInput = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); ZipEntry entry = null; InputStream input = null; OutputStream output = null; while((entry = zipInput.getNextEntry()) != null){ System.out.println("解压缩" + entry.getName() + "文件"); outFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + entry.getName()); if(!outFile.getParentFile().exists()){ outFile.getParentFile().mkdir(); } if(!outFile.exists()){ outFile.createNewFile(); } input = zipFile.getInputStream(entry); output = new FileOutputStream(outFile); int temp = 0; while((temp = input.read()) != -1){ output.write(temp); } input.close(); output.close(); } } } |
【运行结果】:
被解压的文件:
解压之后再D盘下会出现一个temp文件夹,里面内容:
PushBackInputStream回退流
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PushbackInputStream;
/** * 回退流操作 * */ public class PushBackInputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ String str = "hello,rollenholt"; PushbackInputStream push = null; ByteArrayInputStream bat = null; bat = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes()); push = new PushbackInputStream(bat); int temp = 0; while((temp = push.read()) != -1){ if(temp == ‘,‘){ push.unread(temp); temp = push.read(); System.out.print("(回退" + (char) temp + ") "); }else{ System.out.print((char) temp); } } } } |
【运行结果】:
hello(回退,) rollenholt
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
/** * 取得本地的默认编码 * */ public class CharSetDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("系统默认编码为:" + System.getProperty("file.encoding")); } } |
【运行结果】:
系统默认编码为:GBK
乱码的产生:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream;
/** * 乱码的产生 * */ public class CharSetDemo2{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); byte[] bytes = "你好".getBytes("ISO8859-1"); out.write(bytes); out.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:
??
一般情况下产生乱码,都是由于编码不一致的问题。
对象的序列化
对象序列化就是把一个对象变为二进制数据流的一种方法。
一个类要想被序列化,就行必须实现java.io.Serializable接口。虽然这个接口中没有任何方法,就如同之前的cloneable接口一样。实现了这个接口之后,就表示这个类具有被序列化的能力。
先让我们实现一个具有序列化能力的类吧:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import java.io.*; /** * 实现具有序列化能力的类 * */ public class SerializableDemo implements Serializable{ public SerializableDemo(){
} public SerializableDemo(String name, int age){ this.name=name; this.age=age; } @Override public String toString(){ return "姓名:"+name+" 年龄:"+age; } private String name; private int age; } |
这个类就具有实现序列化能力,
在继续将序列化之前,先将一下ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream这两个类
先给一个ObjectOutputStream的例子吧:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
import java.io.Serializable; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
/** * 实现具有序列化能力的类 * */ public class Person implements Serializable{ public Person(){
}
public Person(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; }
@Override public String toString(){ return "姓名:" + name + " 年龄:" + age; }
private String name; private int age; } /** * 示范ObjectOutputStream * */ public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( file)); oos.writeObject(new Person("rollen", 20)); oos.close(); } } |
【运行结果】:
当我们查看产生的hello.txt的时候,看到的是乱码,呵呵。因为是二进制文件。
虽然我们不能直接查看里面的内容,但是我们可以使用ObjectInputStream类查看:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
/** * ObjectInputStream示范 * */ public class ObjectInputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream( file)); Object obj = input.readObject(); input.close(); System.out.println(obj); } } |
【运行结果】
姓名:rollen 年龄:20
到底序列化什么内容呢?
其实只有属性会被序列化。
Externalizable接口
被Serializable接口声明的类的对象的属性都将被序列化,但是如果想自定义序列化的内容的时候,就需要实现Externalizable接口。
当一个类要使用Externalizable这个接口的时候,这个类中必须要有一个无参的构造函数,如果没有的话,在构造的时候会产生异常,这是因为在反序列话的时候会默认调用无参的构造函数。
现在我们来演示一下序列化和反序列话:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 |
package IO;
import java.io.Externalizable; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInput; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutput; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
/** * 序列化和反序列化的操作 * */ public class ExternalizableDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ser(); // 序列化 dser(); // 反序列话 }
public static void ser() throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( file)); out.writeObject(new Person("rollen", 20)); out.close(); }
public static void dser() throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream( file)); Object obj = input.readObject(); input.close(); System.out.println(obj); } }
class Person implements Externalizable{ public Person(){
}
public Person(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; }
@Override public String toString(){ return "姓名:" + name + " 年龄:" + age; }
// 复写这个方法,根据需要可以保存的属性或者具体内容,在序列化的时候使用 @Override public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException{ out.writeObject(this.name); out.writeInt(age); }
// 复写这个方法,根据需要读取内容 反序列话的时候需要 @Override public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ this.name = (String) in.readObject(); this.age = in.readInt(); }
private String name; private int age; } |
【运行结果】:
姓名:rollen 年龄:20
本例中,我们将全部的属性都保留了下来,
Serializable接口实现的操作其实是吧一个对象中的全部属性进行序列化,当然也可以使用我们上使用是Externalizable接口以实现部分属性的序列化,但是这样的操作比较麻烦,
当我们使用Serializable接口实现序列化操作的时候,如果一个对象的某一个属性不想被序列化保存下来,那么我们可以使用transient关键字进行说明:
下面举一个例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
package IO;
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.Serializable;
/** * 序列化和反序列化的操作 * */ public class serDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ser(); // 序列化 dser(); // 反序列话 }
public static void ser() throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( file)); out.writeObject(new Person1("rollen", 20)); out.close(); }
public static void dser() throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream( file)); Object obj = input.readObject(); input.close(); System.out.println(obj); } }
class Person1 implements Serializable{ public Person1(){
}
public Person1(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; }
@Override public String toString(){ return "姓名:" + name + " 年龄:" + age; }
// 注意这里 private transient String name; private int age; } |
【运行结果】:
姓名:null 年龄:20
最后在给一个序列化一组对象的例子吧:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.Serializable;
/** * 序列化一组对象 * */ public class SerDemo1{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Student[] stu = { new Student("hello", 20), new Student("world", 30), new Student("rollen", 40) }; ser(stu); Object[] obj = dser(); for(int i = 0; i < obj.length; ++i){ Student s = (Student) obj[i]; System.out.println(s); } }
// 序列化 public static void ser(Object[] obj) throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( file)); out.writeObject(obj); out.close(); }
// 反序列化 public static Object[] dser() throws Exception{ File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt"); ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream( file)); Object[] obj = (Object[]) input.readObject(); input.close(); return obj; } }
class Student implements Serializable{ public Student(){
}
public Student(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; }
@Override public String toString(){ return "姓名: " + name + " 年龄:" + age; }
private String name; private int age; } |
【运行结果】:
姓名: hello 年龄:20
姓名: world 年龄:30
姓名: rollen 年龄:40
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/math-sushu/p/4644434.html