标签:
In the Java programming language, every class implicitly or explicitly provides a hashCode() method, which digests the data stored in an instance of the class into a single hash value (a 32-bit signed integer). Technically, in Java, hashCode() by default is a native method, meaning, it has the modifier ‘native‘, as it is implemented directly in the native code in the JVM. (使用native关键字说明这个方法是原生函数,也就是这个方法是用C/C++语言实现的,并且被编译成了DLL,由java去调用。native关键字介绍)
All the classes inherit a basic hash scheme from the fundamental base class java.lang.Object, but instead many override this to provide a hash function that better handles their specific data. Classes which provide their own implementation must override the object method public int hashCode().
public int hashCode()
java.util.Hashtable 提供的哈希表)的性能。
hashCode 的常规协定是:
hashCode 方法都必须生成相同的整数结果。equals(java.lang.Object) 方法,两个对象不相等,那么对这两个对象中的任一对象上调用 hashCode 方法不 要求一定生成不同的整数结果。但是,程序员应该意识到,为不相等的对象生成不同整数结果可以提高哈希表的性能。实际上,由 Object 类定义的 hashCode 方法确实会针对不同的对象返回不同的整数。(这一般是通过将该对象的内部地址转换成一个整数来实现的,但是 JavaTM 编程语言不需要这种实现技巧。) 附equals方法和hashCode方法的详解。
java.lang.Object
java.lang.Number
java.lang.Integer
public int hashCode()
覆盖:类 Object 中的 hashCode
返回:该对象的哈希码值,它的值即为该Integer对象表示的基本 int 类型的数值。
java.lang.Object
java.lang.String
public int hashCode()
覆盖:类 Object 中的 hashCode
返回:该对象的哈希码值。String 对象的哈希码根据以下公式计算:
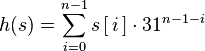
即:h(s)=s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1];
使用int算法,这里s[i]是字符串的第i个字符,n是字符串的长度,^表示求幂。(空字符串的哈希值为0)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/nightowc/p/4674111.html