标签:
1.表插入排序只是求得一个有序的链表,它是修改指针的值来代替移动记录,操作过程如下
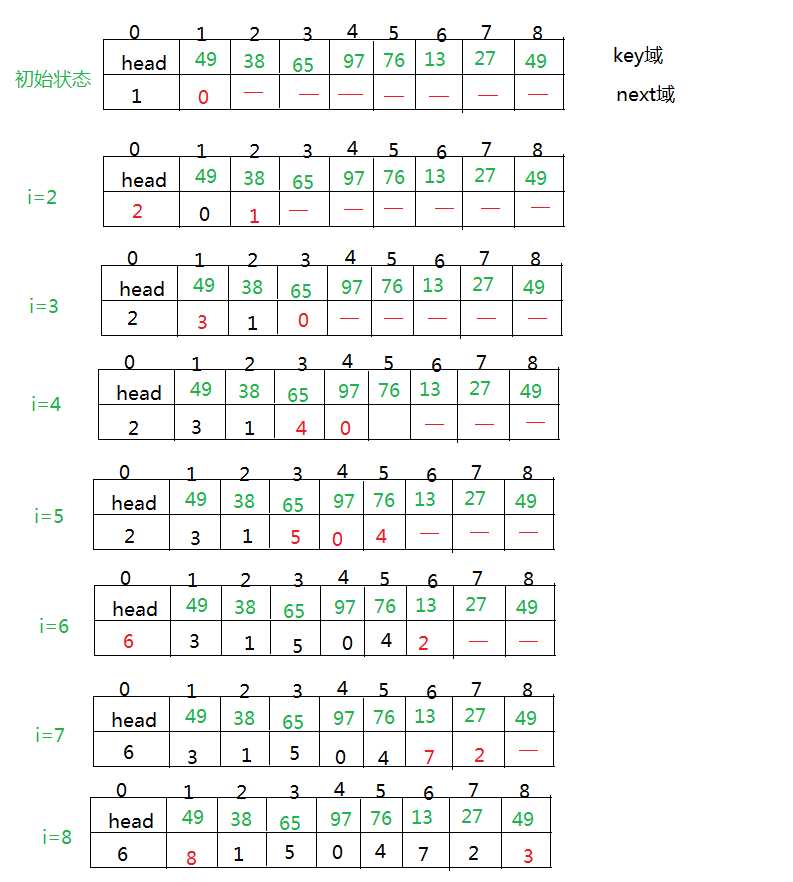
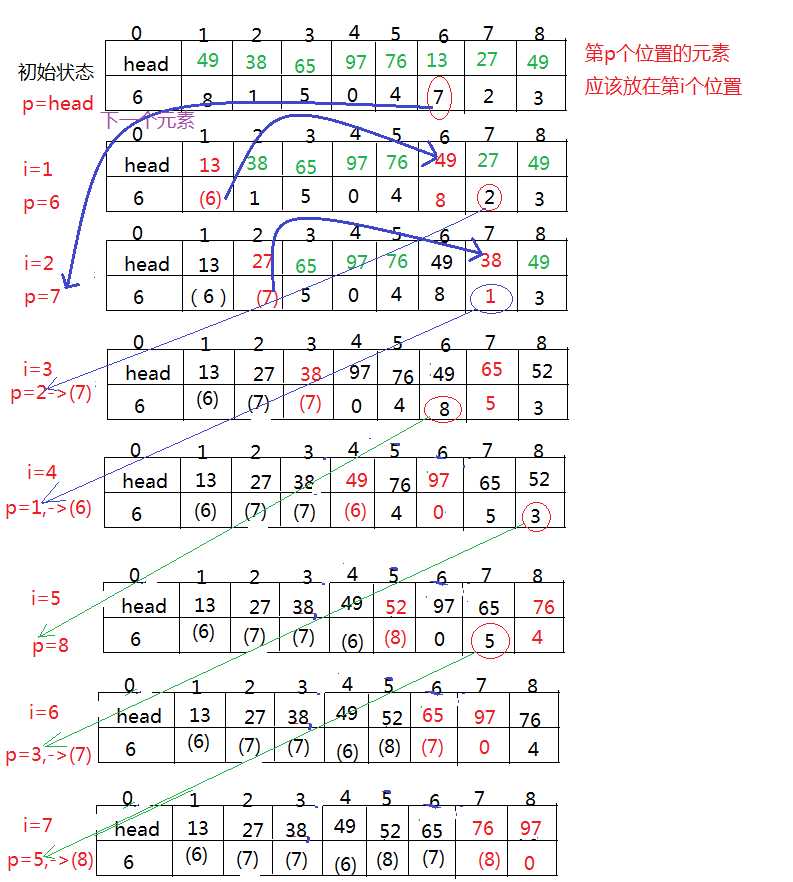
2.但是这样只能进行顺序查找,不能进行随机查找,为了能实现有序表的折半查找,需要对记录进行重新排列。操作过程如下:
3.测试程序如下:
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; typedef struct xxx{ int head;//头结点 int a[100]; int next[100];//记录下一个元素的位置 int len; xxx(){ head = 1; memset(next, 0, sizeof(next)); } void outList(){ for(int i=1; i<=len; ++i){ cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } }Listx; Listx Lx; void table_insertion_sort(){//表插入排序,相当于静态链表 for(int i=2; i<=Lx.len; ++i){ int pre, p; for(p=Lx.head; p && Lx.a[p]<Lx.a[i]; pre=p, p=Lx.next[p]); if(p==0){ Lx.next[pre] = i; } else if(p==Lx.head){ Lx.next[i] = Lx.head; Lx.head = i; } else { Lx.next[pre] = i; Lx.next[i] = p; } } //输出 for(int i=Lx.head; i; i = Lx.next[i]) cout<<Lx.a[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; } void arrang_table() { int p = Lx.head, q; for(int i=1; i<Lx.len; ++i){ while(p < i) p = Lx.next[p];//第i个记录在表中的位置不应该小于 i,如果小于i,说明该元素已经被交换位置了,可以通过next继续寻找 q = Lx.next[p];//指向下一个节点 if(p!=i){//第p个元素应该在第i个位置 swap(Lx.a[i], Lx.a[p]); swap(Lx.next[i], Lx.next[p]); Lx.next[i] = p;//该元素之前的位置 p,指向被移走的记录,使得以后可由while循环找回 } p = q; } for(int i=1; i<=Lx.len; ++i) cout<<Lx.a[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; } int main() { int i; scanf("%d", &Lx.len); for(i=1; i<=Lx.len; i++) scanf("%d", &Lx.a[i]); table_insertion_sort(); arrang_table(); return 0; }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hujunzheng/p/4677484.html