标签:android des style blog http java
AppWidget不知道大家使用这个多不多,这个在手机上也叫做挂件,挂件也就是放在桌面方便用户进行使用的,从android1.6开始挂件支持一些简单的lauout和view,到了android4.0之后谷歌在挂件上也是加上了更为丰富的view支持,下面我们就从头开始来介绍一下这些挂件吧。
如何添加一个简单的AppWidget挂件
添加一个挂件很简单,分为四部,只要按照这四部来弄就很容易添加上一个挂件:
(1)添加AppWidgetProviderInfo信息,这个信息是一个以xml文件形式出现的,这个文件是描述的是这个挂件的属性信息,比如大小和布局文件等等。那么这个xml文件定义在哪里呢?它就定义在res目录在xml目录中,看下图
看上面的图片中在xml目录下创建一个itchq_info.xml文件,这个文件里面就是描述挂件的属性,来看看这个里面的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:minWidth="70dp" android:minHeight="120dp" android:initialLayout="@layout/activity_main" > </appwidget-provider>
上面的都是基本的属性,android:minWidth和android:minHeight这个两个分别是表示挂件的宽和高,android:initialLayout这个就是设置这个挂件的布局文件,这个布局文件就是在layout下的。
(2)添加布局信息,从上面中已经看到挂件的布局文件是Activity_main,看一下这个布局文件,这一步估计就很简单的,
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:id="@+id/txt" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <Button android:layout_below="@id/txt" android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> </RelativeLayout>
上面的布局很简单,就是显示一个简单的TextView和Button,这个就不多做介绍了。
(3)创建一个类继承于AppWidgetProvider,这个类类似于我们的Activty类,定义Appwidget的生命周期,我们来看看系统中AppWidgetProvider是一个啥样的类

从上面的图片我们就可以看出这个AppWidgetProvider是继承于广播的类,所以这个AppwidgetProvider就是一个广播,当是它又有自己的生命周期函数,来看看这个我们定义这个类的代码:
package com.itchq.appwidgetactivity; import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager; import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; public class itchqAppWidget extends AppWidgetProvider{ @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onReceive(context, intent); } @Override public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds); } @Override public void onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds); } @Override public void onEnabled(Context context) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onEnabled(context); } @Override public void onDisabled(Context context) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onDisabled(context); } }
上面这五个方法就是AppWidgetProvider经常使用到的一些函数,它们分别的意义是:
onReceive(Context context, Intent intent):
这个大家都知道是接受广播的方法,因为我们的AppWidgetProvider就是一个广播类,每一次对挂件的添加和删除这个方法都会接受到一个广播,都会跑一次这个方法
onEnabled(Context context)
这个是刚开始添加的挂件的时候跑的方法,注意在android机制中同一个挂件可以添加多次,这个只有第一次添加该挂件时才会跑的方法,
onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,int[] appWidgetIds)
根据AppWidgetProviderInfo 中updatePeriodMillis 属性描述的时间间隔来调用此方法对 Widget 进行更新和每一次添加挂件时都会调用这个方法,注意这个方法和onEnabled()区别是每一次添加挂件都会调用,而onEnabled()只有第一次添加挂件的时候才会调用,还有一个是关于android:updatePeriodMillis这个属性好像没有作用,就算你设置了1分钟更新一次没过一分钟也不会取调用这个方法也就是没有更新(这个好像一直都是这样的,不知道是为什么)。
onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds)
这个方法是每删除一次挂件就会调用,注意前面有说过同一个挂件可以添加多次,所以当有多个挂件在桌面上时每删除一个挂件就就会调用上面的方法。
onDisabled(Context context)
这个是删除桌面上最后一个挂件的时候才会调用,注意不要和onDeleted()方法搞混淆了,onDisabled()表示的是一个桌面上添加了多个相同的挂件当我们删除完最后一个时就会调用这个方法。
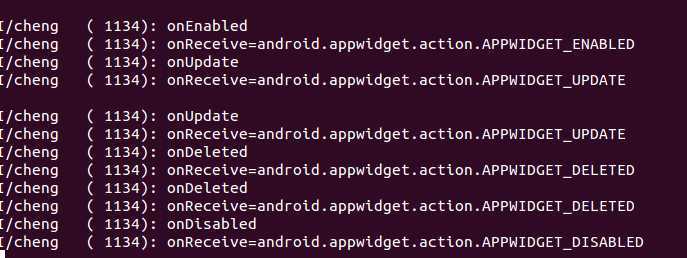
看上面的log,第一次添加挂件时先是跑了onEnabled()方法之后就接受到android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_ENABLED的广播,之后又调用了opUpdate()方法以及接受到android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE的广播,这些广播都是系统发的,我们再看下面的log,在添加第二次相同的挂件的时候我们发现直接就调用onUpdate()以及接受到android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE的广播,没有调用了onEnabled()方法了,这个就是因为该挂件不是第一次添加所以就不会再调用onEnabled()方法了。
接下来我们看看删除的时候,在第一次删除时调用了onDeleted()方法以及接受到android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_DELETED的广播,但是没有调用onDisabled()这个方法,因为该挂件添加了两次,我们在删除第一个的时候还有一个在桌面上,当我们再把最后一个给删除的时候就发现先调用onDeleted()方法之后就调用onDisabled()方法,
上面每一次调用方法之后都会接受相应的广播,这个就是android系统发来的。
(4)最后一步是在AndroidManifest.xml中声明,AppWidgetProvider本身是一个广播,那么既然是广播我们就需要在AndroidManifest.xm进行注册,来看看这个是如何注册的:
<receiver android:name="com.itchq.appwidgetactivity.itchqAppWidget" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"/> </intent-filter> <meta-data android:name="android.appwidget.provider" android:resource="@xml/itchq_info"/> </receiver>
看上面的代码,这个广播要记得需要静态的注册android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE广播,如果你不添加这个就无法在挂件栏里面看到这个挂件,也就无法添加新的挂件,在meta-data标签里面android:name是固定的,来看看android:resource这个就是我们在第一步添加AppWidgetProviderInfo信息
我们来看看界面的显示效果
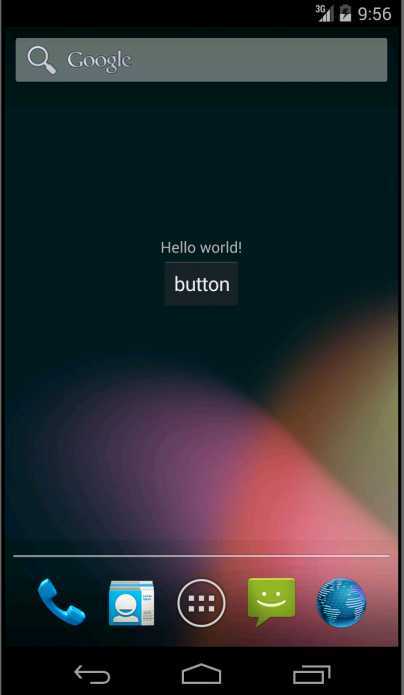
上面就是显示效果,一个textView和一个button
挂件的交互事件
我们在上面定义一个按钮和一个文本,那边在挂件中如何设置按钮的点击事件以及给文本框设置文本呢?这个跟我们在Activity的处理是完全不一样的,这个涉及到一个RemoteViews类的使用,RemoteViews类描述了一个View对象能够显示在其他进程中,可以融合从一个 layout资源文件实现布局。虽然该类在android.widget.RemoteViews而不是appWidget下面但在Android Widgets开发中会经常用到它,我们先来看看按钮的点击事件是如何设置的,
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int[] appWidgetIds) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main);
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setAction("btn.itchq.com");
PendingIntent pendingIntent=PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intent, 0);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btn, pendingIntent);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds, remoteViews);
Log.i("cheng", "onUpdate");
}
我们看到这个RemoteViews对象的构造函数中第二个参数就是我们的初始化布局文件,即就是在第一步中添加AppWidgetProviderInfo信息的中的 android:initialLayout这个布局,当然如何我们在这里指定其它布局也可以,如果在这里指定其它布局那么这个布局就会调换掉默认的初始化布局文件,上面的代码可以看到按钮的点击事件通过设置想要的intent来实现的,在设置好的intent中通过PendingIntent包装之后,remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent()就是设置的按钮的点击事件,这个方法中第一个参数指定的是这个button的id,第二个方法指定的就是已经设置好的PengingIntent,我们可以看到这个是一个广播事件,当然我们也可以设置按钮的来开启一个Activity和一个服务,如何修改看下面的代码:
RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main); Intent intent=new Intent(context,MainActivity.class); //intent.setAction("btn.itchq.com"); PendingIntent pendingIntent=PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0, intent, 0); remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btn, pendingIntent); appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds, remoteViews);
很容易了,说白了就是这个PendingIntent的使用方法了,好了我们再来看看还有最好一句话appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds, remoteViews);
这个是挂件的更新,这个很重要,我们要记住每一个使用RemoteViews设置完相应的动作之后一定要更新一下挂件,如果不更新那么我们所有设置都是无效的,比如上面没有更新的话那么我们点击按钮是没有任何效果的,由于这个是在onUpdate()方法里面设置的,所以更新这个直接那appWidgetManager这个对象来更新就行,那么如果不是在onUpdate()里面更新的话在外面又是如何来更新的呢?,我们直接来看下面的代码
ComponentName thisName=new ComponentName(context, itchqAppWidget.class); AppWidgetManager manager=AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context); manager.updateAppWidget(thisName, remoteViews);
这个就是直接获取的AppWidgetManager对象,通过这个就可以更新挂件,itchqAppWidget.class是继承AppWidgetProvider的类名,这里还有另外一个方法:
AppWidgetManager manager=AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context); int[] appids=manager.getAppWidgetIds(new ComponentName(context, itchqAppWidget.class)); manager.updateAppWidget(appids, remoteViews);
这两个更新的方法都是一样的,很简单吧,好了回到按钮的点击事件,上面中我们设置一个按钮的点击事件,其实是一个发送广播的方式,这个广播是btn.itchq.com,那要让一个挂件接受这个广播我们就必须进行注册,这个和广播的机制是一样的
<intent-filter> <action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"/> <action android:name="btn.itchq.com"/> </intent-filter>
看上面的代码就很容易理解了,那么我们再看看接受广播之后做哪些事件呢
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onReceive(context, intent); Log.i("cheng", "onReceive="+intent.getAction()); if(intent.getAction().equals("btn.itchq.com")){ RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main); remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.txt, "Success"); ComponentName thisName=new ComponentName(context, itchqAppWidget.class); AppWidgetManager manager=AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context); manager.updateAppWidget(thisName, remoteViews); }
remoteViews.setTextViewText()就是更新文本,第一个参数就是文本的id,第二个参数就是要更新的文件内容,很容易理解吧,最后不要忘了更新一些挂件
其实在RomteViews类里面有一系列的setXXX()方法,我们可以 这些set设置相应的功能,比如可以切换ImageView的图片
android:configure
<appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:minWidth="70dp" android:minHeight="120dp" android:initialLayout="@layout/activity_main" android:configure="com.itchq.appwidgetactivity.MainActivity" > </appwidget-provider>
这个是在appwidgetproviderInfo中定义的(就是我们的res目录下xml文件中),如果用户在添加一个App Widget时需要配置设置,那么可以创建一个app widget configuration Activity。这个Activity由App Widget host自动启动,并且允许用户在创建的时候配置可能的设置,不如挂件的大小呀,一些需要的参数呀等等,这个Activity和我们普通的Avtivity是一样需要在在Android manifest文件中进行声明,但是要注意这个activity必须能接收这样的Intent “android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_CONFIGURE“,因为只有接受这个才会被它会被App Widget host中的ACTION_APPWIDGET_CONFIGUREaction启动
<activity android:name="com.itchq.appwidgetactivity.MainActivity" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_CONFIGURE" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
我们再看看这个Avtivity中的代码
package com.itchq.appwidgetactivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.RemoteViews; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private int mAppWidgetId = AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID; private EditText text; private Button btn; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setResult(RESULT_CANCELED); setContentView(R.layout.main); Intent intent = getIntent(); Bundle extras = intent.getExtras(); if (extras != null) { mAppWidgetId = extras.getInt( AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID); } if (mAppWidgetId == AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID) { Log.i("cheng", "aaaaa"); finish(); } text=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.test); btn=(Button) findViewById(R.id.ok); btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub click(); } }); } public void click(){ RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main); remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.txt, text.getText()); AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(this); appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(mAppWidgetId, remoteViews); Intent resultValue = new Intent(); resultValue.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, mAppWidgetId); setResult(RESULT_OK, resultValue); finish(); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true; } }
这个MainActivity中布局中显示一个EditText和Button,setResult(RESULT_CANCELED);这句话说明的就是配置Activity第一次打开时,设置Activity result为RESULT_CANCLED。这样,用户在未完成配置设置而退出时,App Widget被告知配置取消,将不会添加App Widget。
Intent intent = getIntent(); Bundle extras = intent.getExtras(); if (extras != null) { mAppWidgetId = extras.getInt( AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID); }
这段代码从启动Activity的Intent中获取App Widget ID。我们后面会通过这个ID来更新挂件
if (mAppWidgetId == AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID) { finish(); }
这句话表示的就是这个给定的app widget ID无效的时候就直接结束这个Activity,最后我们来看看这个按钮的点击事件中的代码:
RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main); remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.txt, text.getText()); AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(this); appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(mAppWidgetId, remoteViews);
这段代码表示当我们点击了按钮之后,挂件外面的TextView就显示成我们在这里设置的Text,之后还不要忘了要更新一下挂件
Intent resultValue = new Intent(); resultValue.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, mAppWidgetId); setResult(RESULT_OK, resultValue); finish();
最后,创建返回Intent,设置给Activity返回结果,并且结束Activity。
这个整体的效果就是在添加挂件之后就会先弹出一个Activity界面,设置好Text之后点击按钮就返回挂件外面,挂件的TextView控件显示的就是我们刚刚开始设置的Text。
android 4.0之后挂件的变化
谷歌在android 4.0对挂件进行了大修改,添加了不少的新功能,在这里我说一下我们在res/layout所定义的widget布局使用的组件必须是RemoteViews所支持的,我们先来看看在android4.0之前挂件能支持的控件是哪些?

上图就是在android4.0之后挂件布局里面所支持的控件,也就是说我们只能使用上面的控件,如果在android4.0之前使用除上面之外的控件添加挂件就会报错,而且这个还不能说继承来使用,比如 不能像下面这样使用
public class widgetImage extends ImageView
这个也是不行的,所以这样直接导致android4.0之前挂件的功能都是很简单,没有listview等负责的控件,很多挂件都是显示图片,如果想自定widget的view也行,但是这个只能是在framework里面进行修改,这个只有厂家能使用,第三方就不好修改了。
我们再来看看android4.0所带来的appWidget的变化,首先我们来对比在控件上android4.0又添加哪些直接看下图:
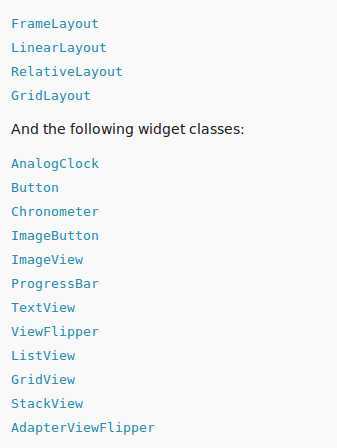
从这个图中可以看出谷歌在4.0之后对widget的支持添加了很多控件,这里有listView还有gridview等等,这样也使我们的挂件显示更加丰富。
除了上面的变化之外,android4.0之后还加入了一个可以变大小的功能,在我们长按挂件之后如果没有删除时就会出现这个效果,先来看看图片
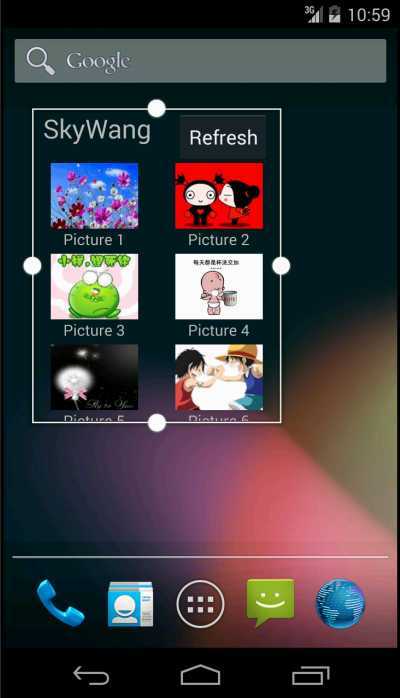
看上面的挂件左右上面都有一个点,这个表示可以改变改挂件的大小,我们手动放到对应的点上进行拉动就可以改变挂件的大小,那这个是什么实现的呢?
要实现这个效果就需要在AppWidgetProviderInfo(就是在res/xml目录下那个xml文件)中加上android:resizeMode属性,该属性一共有三个值分别设置,分别是:
android:resizeMode="horizontal"这个表示在水平方向可以进行大小的改变,也就是挂件的宽度
android:resizeMode="vertical"这个表示在垂直方向可以进行大小的改变,这个也就是可以改变挂件的高度
android:resizeMode="none"这个就是指定该挂件不可改变大小,不管是宽度还是高度都不能改变大小
如果我们想同时改变的宽度和高度的大小的话可以这样设置android:resizeMode="horizontal|vertical"
android4.0中还添加了一个挂件的预览图,同样也是在AppWidgetProviderInfo里面android:previewImage来指定挂件的预览图,
android:previewImage="@drawable/preview"这个就是我指定一个预览图片,那么这个有什么作用呢?

看图片的右边就是添加了一个预览图片,这个就是在添加挂件显示界面看到的图片,这个也是很容易了。

这个是我直接从谷歌上面截取过来的,从这段文字中我们也可以看出在android4.2中谷歌对挂件进行一个小变动,LockSreen锁机挂件,意思就是说这个挂件可以添加到我们的桌面同时也可以设置这个挂件添加到锁机界面上去,这个设置就是通过android:widgetCategory来设置的,这个一共有两个值:
android:widgetCategory="home_screen"表示添加到桌面中
android:widgetCategory="keyguard"表示添加到锁机界面中
我来看下面的代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:minWidth="180dp" android:minHeight="180dp" android:previewImage="@drawable/preview" android:initialLayout="@layout/widget_layout" android:resizeMode="horizontal|vertical" android:widgetCategory="keyguard |home_screen" android:initialKeyguardLayout="@layout/widget_layout"> </appwidget-provider>
这段是appWidgetProviderInfo信息,我们在段信息中发现android:initialLayout和android:initialKeyguardLayout都是设置布局文件的,那么这两个的区别主要是在于android:initialLayout中布局是设置挂件在桌面中显示的布局,android:initialKeyguardLayout这个就是指定挂件在锁机界面显示的布局文件。当时在谷歌说明中也指定了可以在代码中动态来判断创建不同的layout文件。就是在运行时检测widget category进行响应。调用getAppWidgetOptions()获取widget放置位置的Bundle数据。返回的Bundle将会包括 key值OPTION_APPWIDGET_HOST_CATEGORY,它的值为WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN或者 WIDGET_CATEGORY_KEYGUARD。然后在AppWidgetProvider中检测widget category。例如:
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager;
int widgetId;
Bundle myOptions = appWidgetManager.getAppWidgetOptions (widgetId);
// Get the value of OPTION_APPWIDGET_HOST_CATEGORY
int category = myOptions.getInt(AppWidgetManager.OPTION_APPWIDGET_HOST_CATEGORY, -1);
// If the value is WIDGET_CATEGORY_KEYGUARD, it‘s a lockscreen widget
boolean isKeyguard = category == AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_KEYGUARD;
一旦知道了widget的category,就可以有选择的装载baselayout,设置不同的属性等。例如
int baseLayout = isKeyguard ? R.layout.keyguard_widget_layout :R.layout_widget_layout;
好的,除了上面的这些之外,我们就重点来介绍有关于android4.0所添加的stackView ,gridview,listview等一些用法,这个stackview也是android4.0之后才添加到手机上的,之前一直是在android3.0中使用也就是平板电脑,我们可以先来看看StackView显示的效果
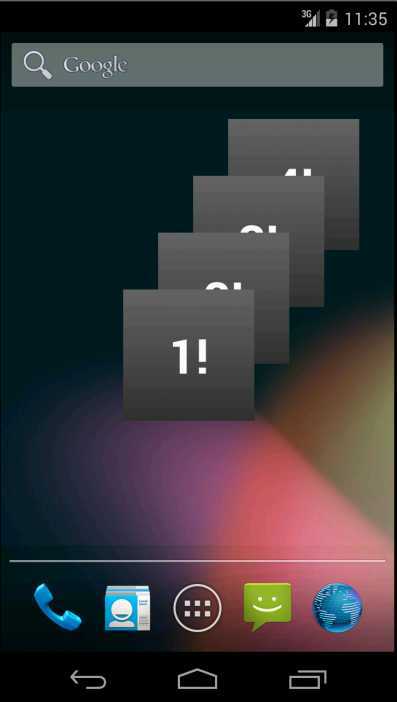
看上面这个挂件的效果是不是很酷呀,这个就是stackview的效果,这个是使用谷歌的列子,想这中stackView ,gridview,listview控件,我们平时使用的时候都需要一个adpater适配器来设置相应的数据,那么在挂件当中如何给这些来设置数据呢?这个就引入RemoteViewsService这个类和RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory这个接口,
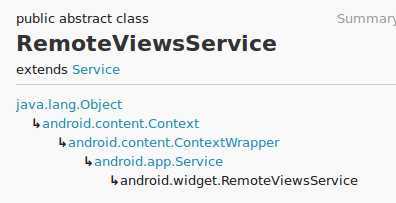
从上图中可以看出这个RemoteViewsService是继承于Service类,所以这个RemoteViewsService就是一个服务,它管理RemoteViews的服务,我们在RemoteViewsService这个类中主要是实现onGetViewFactory这个方法,返回一个RemoteViewsFactory的实现类,看下面的代码:
public class StackWidgetService extends RemoteViewsService { @Override public RemoteViewsFactory onGetViewFactory(Intent intent) { return new StackRemoteViewsFactory(this.getApplicationContext(), intent); } }
StackRemoteViewsFactory就是实现了RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory接口。
RemoteViewsFactory是RemoteViewsService中的一个接口。RemoteViewsFactory提供了一系列的方法管理“集合视图”中的每一项,也就是相当于我们adpater适配器作用,
class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory { private static final int mCount = 10; private List<WidgetItem> mWidgetItems = new ArrayList<WidgetItem>(); private Context mContext; private int mAppWidgetId; public StackRemoteViewsFactory(Context context, Intent intent) { mContext = context; mAppWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID); } public void onCreate() { // In onCreate() you setup any connections / cursors to your data source. Heavy lifting, // for example downloading or creating content etc, should be deferred to onDataSetChanged() // or getViewAt(). Taking more than 20 seconds in this call will result in an ANR. for (int i = 0; i < mCount; i++) { mWidgetItems.add(new WidgetItem(i + "!")); } // We sleep for 3 seconds here to show how the empty view appears in the interim. // The empty view is set in the StackWidgetProvider and should be a sibling of the // collection view. try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void onDestroy() { // In onDestroy() you should tear down anything that was setup for your data source, // eg. cursors, connections, etc. mWidgetItems.clear(); } public int getCount() { return mCount; } public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position) { // position will always range from 0 to getCount() - 1. // We construct a remote views item based on our widget item xml file, and set the // text based on the position. RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(mContext.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item); rv.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, mWidgetItems.get(position).text); // Next, we set a fill-intent which will be used to fill-in the pending intent template // which is set on the collection view in StackWidgetProvider. Bundle extras = new Bundle(); extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position); Intent fillInIntent = new Intent(); fillInIntent.putExtras(extras); rv.setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent); // You can do heaving lifting in here, synchronously. For example, if you need to // process an image, fetch something from the network, etc., it is ok to do it here, // synchronously. A loading view will show up in lieu of the actual contents in the // interim. try { System.out.println("Loading view " + position); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // Return the remote views object. return rv; } public RemoteViews getLoadingView() { // You can create a custom loading view (for instance when getViewAt() is slow.) If you // return null here, you will get the default loading view. return null; } public int getViewTypeCount() { return 1; } public long getItemId(int position) { return position; } public boolean hasStableIds() { return true; } public void onDataSetChanged() { // This is triggered when you call AppWidgetManager notifyAppWidgetViewDataChanged // on the collection view corresponding to this factory. You can do heaving lifting in // here, synchronously. For example, if you need to process an image, fetch something // from the network, etc., it is ok to do it here, synchronously. The widget will remain // in its current state while work is being done here, so you don‘t need to worry about // locking up the widget. } }
这个就是实现RemoteViewsFactory这个接口的类,从这个类中所实现的方法和BaseAdapter差不多是一样的,
public int getCount()
通过getCount()来获取“集合视图”中所有子项的总数。
RemoteViews getViewAt(int position)
通过getViewAt()来获取“集合视图”中的第position项的视图,视图是以RemoteViews的对象返回的。
public RemoteViews getLoadingView()
This allows for the use of a custom loading view which appears between the time that getViewAt(int) is called and returns.
public void onDataSetChanged()
Called when notifyDataSetChanged() is triggered on the remote adapter.
下面两个都是使用谷歌原话不难理解,实在不行就在线翻译一下咯,哈哈。
下面介绍一下如何使用RemoteViewsService的过程,先来看下面的代码:
@Override public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) { // update each of the widgets with the remote adapter for (int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; ++i) { // Here we setup the intent which points to the StackViewService which will // provide the views for this collection. Intent intent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class); intent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]); // When intents are compared, the extras are ignored, so we need to embed the extras // into the data so that the extras will not be ignored. intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME))); RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_layout); rv.setRemoteAdapter(appWidgetIds[i], R.id.stack_view, intent); // The empty view is displayed when the collection has no items. It should be a sibling // of the collection view. rv.setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view);//@1 // Here we setup the a pending intent template. Individuals items of a collection // cannot setup their own pending intents, instead, the collection as a whole can // setup a pending intent template, and the individual items can set a fillInIntent // to create unique before on an item to item basis. Intent toastIntent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetProvider.class); toastIntent.setAction(StackWidgetProvider.TOAST_ACTION); toastIntent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]);//@2 intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME))); PendingIntent toastPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, toastIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); rv.setPendingIntentTemplate(R.id.stack_view, toastPendingIntent); appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], rv); } super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds); }
从上面的代码中我们发现是通过 rv.setRemoteAdapter来设置对应的RemoteViewsService,这个Intent定义 Intent intent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class)中StackWidgetService就是我们继承与RemoteViewsService的类,上面我们也可以这样写,不需要第一个参数的
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class); rv.setRemoteAdapter(R.id.stack_view, serviceIntent);
很容易理解的,是不是很像我们Activity之间的跳转呀,rv.setPendingIntentTemplate(R.id.stack_view, toastPendingIntent);设置的就是这个Item的相应事件,这里要说明一下:“集合控件(如GridView、ListView、StackView等)”中包含很多子元素,它们不能像挂件上普通的按钮一样通过 setOnClickPendingIntent 设置点击事件,必须先通过两步。
(01) 通过 setPendingIntentTemplate 设置 “intent模板”,这是比不可少的!
在上面的代码中
Intent toastIntent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetProvider.class);
toastIntent.setAction(StackWidgetProvider.TOAST_ACTION);
这个原理和setOnClickPendingIntent一样发送一个广播,然后通过rv.setPendingIntentTemplate(R.id.stack_view, toastPendingIntent)来设置intent模板
(02) 最后在处理该“集合控件”的RemoteViewsFactory类的getViewAt()接口中 通过 setOnClickFillInIntent 设置“集合控件的某一项的数据”
这个在下面会讲解到。
代码中还有 rv.setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view)这么一句话,这句话的意思是当这个没有Item的时候就是显示这个控件,R.id.empty_view布局如下
<TextView android:id="@+id/empty_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:background="@drawable/widget_item_background" android:textColor="#ffffff" android:textStyle="bold" android:text="@string/empty_view_text" android:textSize="20sp" />
那么我们从前面中我们知道这个RemoteViewsService是一个继承于Service的,既然是一个服务就必须要在AndroidManifast,xml文件中进行声明。下面这段代码就是声明一个RemoteViewsService
<service android:name="StackWidgetService" android:permission="android.permission.BIND_REMOTEVIEWS" android:exported="false" />
上面的RemoteViewsService设置好之后我们返回来看看这个Item,也就是实现RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory 接口中 public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position)方法里面的设置。
public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position) { // position will always range from 0 to getCount() - 1. // We construct a remote views item based on our widget item xml file, and set the // text based on the position. RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(mContext.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item); rv.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, mWidgetItems.get(position).text); // Next, we set a fill-intent which will be used to fill-in the pending intent template // which is set on the collection view in StackWidgetProvider. Bundle extras = new Bundle(); extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position); Intent fillInIntent = new Intent(); fillInIntent.putExtras(extras); rv.setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent); // You can do heaving lifting in here, synchronously. For example, if you need to // process an image, fetch something from the network, etc., it is ok to do it here, // synchronously. A loading view will show up in lieu of the actual contents in the // interim. try { System.out.println("Loading view " + position); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // Return the remote views object. return rv; }
看上面的代码我们看到RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(mContext.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item);这个里面的第二个参数就是Item中的Layout,我们再来看看这个布局文件是什么写的
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@drawable/widget_item_background" >" <TextView android:id="@+id/widget_item" android:layout_width="120dp" android:layout_height="120dp" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#ffffff" android:textStyle="bold" android:textSize="44sp" /> </LinearLayout>
这个就是只有这个简单的TextView,那么我们是如何来设置这个TextView相应的文本呢,rv.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, mWidgetItems.get(position).text);这句话就是设置TextView相应的文本,mWidgetItems.get(position).text是一个String字符串,第一个参数就是TextView的Id,这个理解起来也是很容易吧
接下来要处理的就是这个Item的点击事件了,
Bundle extras = new Bundle(); extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position); Intent fillInIntent = new Intent(); fillInIntent.putExtras(extras); rv.setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent);
这段代码中就是设置Item的点击事件,这个extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position);是传送一个参数,rv.setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent);中第一个参数就是响应点击事件的ID,这个就是我们上面所说的第(2)点内容。设置好之后我们来看看这个广播是如何来接受我们的信息的:
@Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { AppWidgetManager mgr = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context); if (intent.getAction().equals(TOAST_ACTION)) { int appWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID); int viewIndex = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_ITEM, 0); Toast.makeText(context, "Touched view " + viewIndex, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } super.onReceive(context, intent); }
TOAST_ACTION就是我们点击的时候发送的广播,intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_ITEM, 0);这个EXTRA_ITEM就是上面extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position);传进来的,哈哈这里看到就明白很多了吧。
让挂件支持复杂的View
这个地方一般来说很少有人去东这里的东西,这个可能只有手机制作厂家在要弄酷炫的挂件的时候可以取改这些东西,在这里我只是简单的介绍一些就可以了。
我们知道对于一个挂件来说,它所支持的View不管是在android2.3或者是在Android4.0中支持都是很少的,而且我们要注意到这些功能要是弄个简单的动画都是很麻烦的,你会发现有写东西根本就没法用,因为我们修改一切都必须是RemoteViews这个有的方法才行,不如修改修改文本呀或者设置点击事件呀都是通过RemoteViews类中的方法来实现的。这个时候如果想自定义挂件支持的View或者是ViewGroup,在这些里面做一些RemoteViews所不支持的的话,就可以使用自定义View的方法,如何自定义View呢?首先我们来在源码目录下添加我们自定义的View
Frameworks\base\core\java\android\widget这个目录就是我们存放view类的目录
在这个目录下我们随便打开一个挂件所支持的View看一下都会发现在挂件所支持的View当中类前面都会有@RemoteView这么一个注释,所以第一步就是
(1)在自定义的View或者ViewGroup类前面加上@RemoteView,并且将该类放到Frameworks\base\core\java\android\widget目录下面
第一步定义好之后在挂件外面添加该类是可以支持的,但是我们如何来进行传参数呢,就是从挂件外面把参数传到这个自定义的view中呢?注意这个传参数不能是简单的一个函数调用,这个我们可以看一下RemoteViews类,因为我们必须通过这个类进行传参数,那么如果查看源码就会发现这个类中的方法前面都是加上了@android.view.RemotableViewMethod声明,而且还有这些方法都是public公共方法。所以我们要记住第二点
(2)要想通过RemoteViews对象调用framework自定的方法,就要在自定义的类中声明一个public方法,该方法前面要加上@android.view.RemotableViewMethod注释
贴一段代码上来看看吧
@RemoteView public class widgetTest extends RelativeLayout{ public widgetTest(Context context) { super(context); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public widgetTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @android.view.RemotableViewMethod public void init(Bundle bundle){ } }
上面我定义了一个简单的ViewGroup类,这个类前面我添加了@RemoteView方法,说明这个类可以被挂件所支持,注意这里不能放在自己的应用程序中,必须放在framework路径下,public void init(Bundle bundle)就是我定义要在挂件中传入参数的方法,这个前面加上了@android.view.RemotableViewMethod注释,而且是public类的,我们再来看看onUpdate中是如何传参数的
RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main); Bundle bundle=new Bundle(); bundle.putInt("image", R.drawable.ic_launcher); remoteViews.setBundle(R.id.widgettest, "init", bundle);
注意看最后一句话remoteViews.setBundle(R.id.widgettest, "init", bundle);,这个里面第一个参数就是我们上面自定义ViewGroup在挂件布局中的ID,第二个就是方法名,这个方法名也是我们上面所定义的public void init(Bundle bundle),第三个参数就是传进来的bundle,上面的代码就是传一张图片进去。
在这里还要说一下我们自定义的方法中的参数必须是remoteViews这个类可以设置的参数,打个比方吧,我们上面传进来的参数是Bundle对象可以,因为remoteViews对象中有setBundle()这个方法可以传Bundle对象,如何我们修改自定义的方法参数为public void init(int a)参数是int类型的也是可以的,因为这个remoteViews中有setInt()方法,但是如果我们参数也是一个自定义的View类,那这个就不行,因为remoteViews没有相应的setView方法,无法给View传参数,这个问题就是说我们自定义的方法中参数还要受到remoteViews的影响。
代码地址:
http://files.cnblogs.com/itchq/AppWidgetActivity.zip
Android AppWidget,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:android des style blog http java
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/itchq/p/3817411.html