标签:
流与文件的操作在编程中经常遇到,与C语言只有单一类型File*即可工作良好不同,Java拥有一个包含各种流类型的流家族,其数量超过60个!当然我们没必要去记住这60多个类或接口以及它们的层次结构,理解和掌握其中比较常用的类和接口即可,必要的时候查询文档或API。我们把流家族成员按照它们的使用方法来进行划分,就形成了处理字节和字符的两个单独的层次结构。 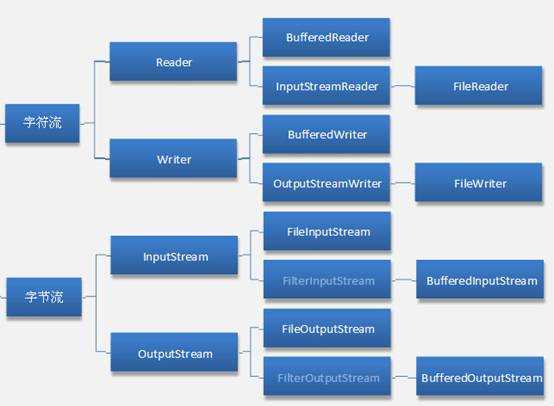
常用的字节字符流
本文主要总结了如何使用流对文件进行相应的操作。
createFile(String path, String name)方法在指定路径path下创建文件,如果路径不存在,就创建路径,如果文件已存在,不做操作。
createDir(String name)方法创建指定的目录name。
createDir(String path, String name)方法在指定路径path下创建文件夹name。
1 /** 2 * @description 根据路径创建文件 3 * @param path 路径 e.g. F:\temp 4 * @param name 文件名 e.g. hello.txt 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public File createFile(String path, String name) { 8 File file = new File(path); 9 try { 10 if(!file.exists()) { 11 file.mkdirs(); 12 } 13 file = new File(path + File.separator + name); 14 if(!file.exists()) { 15 file.createNewFile(); 16 } 17 } catch (IOException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 return file; 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * @description 创建文件目录 25 * @param name e.g. F:\temp\hello\world 26 * @return 27 * @throws IOException 28 */ 29 public File createDir(String name) throws IOException { 30 File file = new File(name); 31 if(!file.exists()) { 32 file.mkdirs(); 33 } 34 return file; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * @description 根据路径创建文件夹 39 * @param path 路径 e.g. F:\temp 40 * @param name 文件夹名 e.g. hello 41 * @return 42 * @throws IOException 43 */ 44 public File createDir(String path, String name) throws IOException { 45 File file = new File(path + File.separator + name); 46 if(!file.exists()) { 47 file.mkdirs(); 48 } 49 return file; 50 }
删除指定文件或文件夹,如果传入的参数是文件,则直接删除,如果是目录,递归调用方法,删除该目录下所有文件和目录。
1 /** 2 * @description 删除文件(夹) 3 * @param file 4 * @throws IOException 5 */ 6 public void deleteFile(File file) throws IOException { 7 if(file.exists()) { 8 if(file.isFile()) { 9 file.delete(); 10 }else if(file.isDirectory()){ 11 File[] files = file.listFiles(); 12 for(File item : files) { 13 deleteFile(item); 14 } 15 file.delete(); 16 } 17 }else { 18 throw new FileNotFoundException(); 19 } 20 }
文件的读操作,使用带缓冲的字节流,以字节的形式读取文件,并写到参数指定的输出流out。
文件的写操作,使用带缓冲的字节流,从参数指定的输入流in读取,并以字节形式写到目标文件。
1 /** 2 * @description 读文件 3 * @param name 源文件 4 * @param out 输出流 5 * @throws FileNotFoundException 6 */ 7 public void readFile(File name, OutputStream out) throws FileNotFoundException { 8 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(name)); 9 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out); 10 int len = 0; 11 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; 12 try { 13 while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) { 14 bos.write(buffer, 0, len); 15 } 16 } catch (IOException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } finally { 19 try { 20 bos.close(); 21 bis.close(); 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * @description 写文件 30 * @param name 目标文件 31 * @param in 输入流 32 * @throws FileNotFoundException 33 */ 34 public void writeFile(File name, InputStream in) throws FileNotFoundException { 35 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in); 36 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(name)); 37 int len = 0; 38 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; 39 try { 40 while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) { 41 bos.write(buffer, 0, len); 42 } 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } finally { 46 try { 47 bos.close(); 48 bis.close(); 49 } catch (IOException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 } 53 }
文件拷贝,源文件src可以是文件或是目录,目标文件desc为目录。如果src是文件,直接拷贝到desc路径下;如果src是目录,首先在desc目录下创建该目录,然后遍历src目录下所有文件和目录,递归调用拷贝方法,最终实现整个文件的拷贝。
1 /** 2 * @description 拷贝文件 3 * @param src 源文件(夹) e.g. F:\hello 4 * @param desc 目标文件夹 e.g. F:\world 5 */ 6 public void copyFile(File src, File desc){ 7 BufferedInputStream in = null; 8 BufferedOutputStream out = null; 9 try { 10 if(src.isFile()) { 11 desc = createFile(desc.getCanonicalPath(), src.getName()); 12 in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); 13 out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(desc)); 14 int len = 0; 15 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; 16 while((len = in.read(buffer)) != -1) { 17 out.write(buffer, 0, len); 18 out.flush(); 19 } 20 } else if (src.isDirectory()) { 21 desc = createDir(desc.getCanonicalPath(), src.getName()); 22 File[] files = src.listFiles(); 23 for(File item : files) { 24 copyFile(item, desc); 25 } 26 } else { 27 throw new FileNotFoundException(); 28 } 29 } catch (IOException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } finally { 32 try { 33 if(out != null) { 34 out.close(); 35 } 36 if(in != null) { 37 in.close(); 38 } 39 } catch(IOException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 }
遍历参数指定目录下的所有文件和目录,感兴趣可以做成树形结构。
1 /** 2 * @description 遍历文件目录 3 * @param file 4 * @throws IOException 5 */ 6 public void traverseFile(File file) throws IOException { 7 if(file.isFile()) { 8 //do something you like 9 } else if(file.isDirectory()) { 10 File[] list = file.listFiles(); 11 for(File item : list) { 12 traverseFile(item); 13 } 14 } else { 15 throw new FileNotFoundException(); 16 } 17 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/coderworld/p/4681664.html