标签:
FlowLayout应该是Swing布局管理器学习中最简单、最基础的一个。所谓流式,就是内部控件像水流一样,从前到后按顺序水平排列,直到达到容器的宽度时跳转到第二行。既然是水平排列,那么就存在三种基本的对齐方式:居中对齐(CENTER )、左对齐(LEFT )和右对齐(RIGHT )。然而,FlowLayout还提供两种对齐方式:LEADING,表示控件与容器方向开始边对应;TRAILING,控件与容器方向结束边对应。setAlignment(int align)用于设置对齐方式。在一般情况下,LEADING就是左对齐,TRAILING就是右对齐。除此之外,FlowLayout还可以对内部控件之间、内部控件与容器之间的间距进行设置,setHgap(int hgap)用于指定水平间距;setVgap(int vgap)用于指定垂直间距。
FlowLayout常用方法如下:
|
构造函数 |
||
|
名称 |
用途 |
|
|
FlowLayout() |
构造一个新的 FlowLayout,它是默认居中对齐的,默认的水平和垂直间隙是5个像素 |
|
|
FlowLayout(int align) |
构造一个新的 FlowLayout,它具有指定的对齐方式,默认的水平和垂直间隙是 5 个像素 五个参数值及含义如下: 0或FlowLayout.lEFT ,控件左对齐 1或FlowLayout.CENTER ,居中对齐 2或FlowLayout.RIGHT ,右对齐 3或FlowLayout.LEADING,控件与容器方向开始边对应 4或FlowLayout.TRAILING,控件与容器方向结束边对应 如果是0、1、2、3、4之外的整数,则为左对齐 |
|
|
FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap) |
创建一个新的流布局管理器,它具有指定的对齐方式以及指定的水平和垂直间隙。 |
|
|
基本方法 |
||
|
名称 |
用途 |
|
|
Void setAlignment(int align) |
设置此布局的对齐方式。 |
|
|
void setHgap(int hgap) |
设置组件之间以及组件与 Container 的边之间的水平间隙。 |
|
|
void setVgap(int vgap) |
设置组件之间以及组件与 Container 的边之间的垂直间隙。 |
|
测试用例如下:
package LayoutDemo; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import javax.swing.AbstractAction; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JTextField; /* * @功能:演示FlowLayout布局管理器的用法 * @版本:20150609 */ public class FlowLayoutDemo extends JFrame { FlowLayout contentPanelLayout = new FlowLayout(); Map<String, Integer> alignmentMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); JPanel configPanel = new JPanel(); JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel(); JComboBox<String> alignmentComboBox = new JComboBox<String> (); JTextField textHgap = new JTextField("10"); JTextField textVgap = new JTextField("20"); MyListener myListener = new MyListener(); public FlowLayoutDemo() { //init alignmentMap.put("LEFT", 0); alignmentMap.put("CENTER", 1); alignmentMap.put("RIGHT", 2); alignmentMap.put("LEADING", 3); alignmentMap.put("TRAILING", 4); //设置面板 configPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); configPanel.add(new JLabel("对齐方式")); for (String alignment : alignmentMap.keySet()) { alignmentComboBox.addItem(alignment); } configPanel.add(alignmentComboBox); configPanel.add(new JLabel("水平间距")); configPanel.add(textHgap); configPanel.add(new JLabel("垂直间距")); configPanel.add(textVgap); JButton actionBtn = new JButton("Action!!!"); actionBtn.addActionListener(myListener); configPanel.add(actionBtn); //展示面板 contentPanel.setLayout(contentPanelLayout); contentPanel.add(new JButton("Button 1")); contentPanel.add(new JButton("Button 2")); contentPanel.add(new JButton("Button 3")); contentPanel.add(new JButton("Button 4")); //主窗体 setLayout(new BorderLayout()); add("North",configPanel); add("South", contentPanel); } class MyListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String alignmentStr = alignmentComboBox.getSelectedItem().toString(); int alignment = alignmentMap.get(alignmentStr); contentPanelLayout.setAlignment(alignment); int hgap = Integer.valueOf(textHgap.getText()); int vgap = Integer.valueOf(textVgap.getText()); contentPanelLayout.setHgap(hgap); contentPanelLayout.setVgap(vgap); contentPanel.updateUI(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub FlowLayoutDemo window = new FlowLayoutDemo(); window.setTitle("FlowLayoutDemo"); // 该代码依据放置的组件设定窗口的大小使之正好能容纳你放置的所有组件 window.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(500, 200)); window.pack(); window.setVisible(true); window.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); window.setLocationRelativeTo(null); // 让窗体居中显示 } }
运行效果如下:
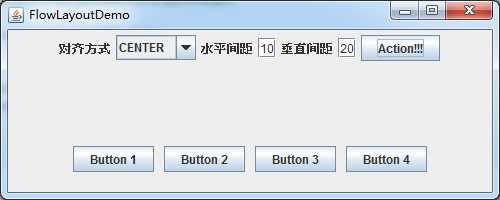
居中对齐
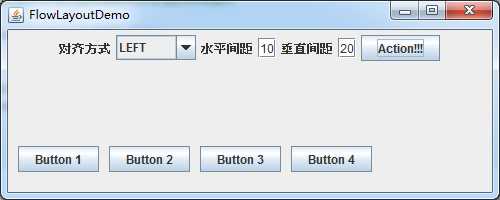
左对齐
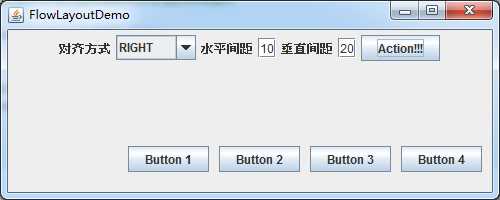
右对齐
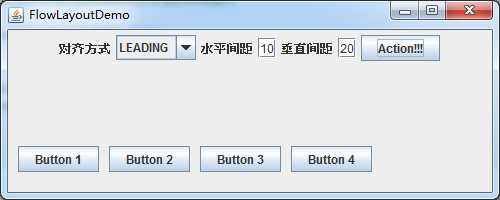
Leading对齐
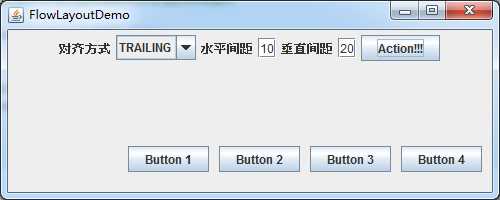
Trailing对齐
Swing-布局管理器之FlowLayout(流式布局)-入门
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/pzy4447/p/4696703.html