标签:
由于一次面试被问到压缩算法,然后就没有然后了,所以自己深度学习一下哈夫曼压缩算法.
最简单的理解就是将出现次数多的字符,用尽量短的字符来代替.例如某个字节为‘11111111‘,用‘0‘或者‘1‘来代替,这样压缩率达到了1/8.
如何构建映射关系,成为压缩算法的关键,其中最常见的哈夫曼压缩算法.本文通过简单的java代码来实现哈夫曼压缩算法
1.如何构建哈夫曼树
首先需要统计压缩数据中,每一个byte出现的频率.
try { Map<Byte, Integer> map = new HashMap<Byte, Integer>();//统计每一个byte在数据中出现的次数 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);int n = 1; byte buffer[] = new byte[n]; while ((fis.read(buffer, 0, n) != -1) && (n > 0)) { fos.write(buffer); for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) { if (!map.containsKey(buffer[i])) { map.put(buffer[i], 1); } else { int count = map.get(buffer[i]) + 1; map.put(buffer[i], count); } } } fis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
构建哈夫曼树:
首先对统计的结果放到list中进行排序
List<HFnode> nodes = new ArrayList<HFnode>(); for (Byte key : map.keySet()) { HFnode node = new HFnode(key, map.get(key)); nodes.add(node); } Collections.sort(nodes);
生成哈夫曼树的原理很简单,给定n个权值作为n的叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。.
举一个简单例子,下面是已经排好顺序的list
| 字符 | a | b | c | d | e |
| 出现次数 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
第一步:
取出现频率最小节点d和e,de合并插入list队列,进行排序
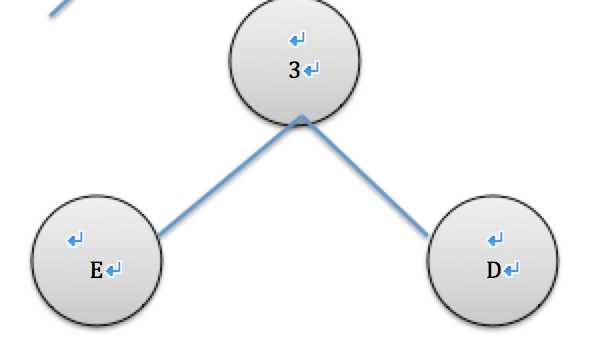
| 字符 | a | b | c | de |
| 出现次数 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
第二步:
取出现频率最小的节点c和de生成树,cde合并插入list队列,进行排序
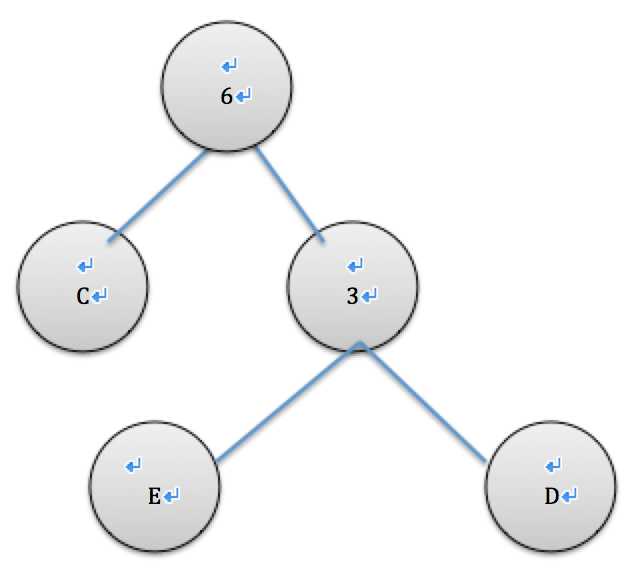
| 字符 | cde | a | b |
| 出现次数 | 6 | 5 | 4 |
第三步:
取出现频率最小的节点a和b生成树,ab合并插入list队列,进行排序
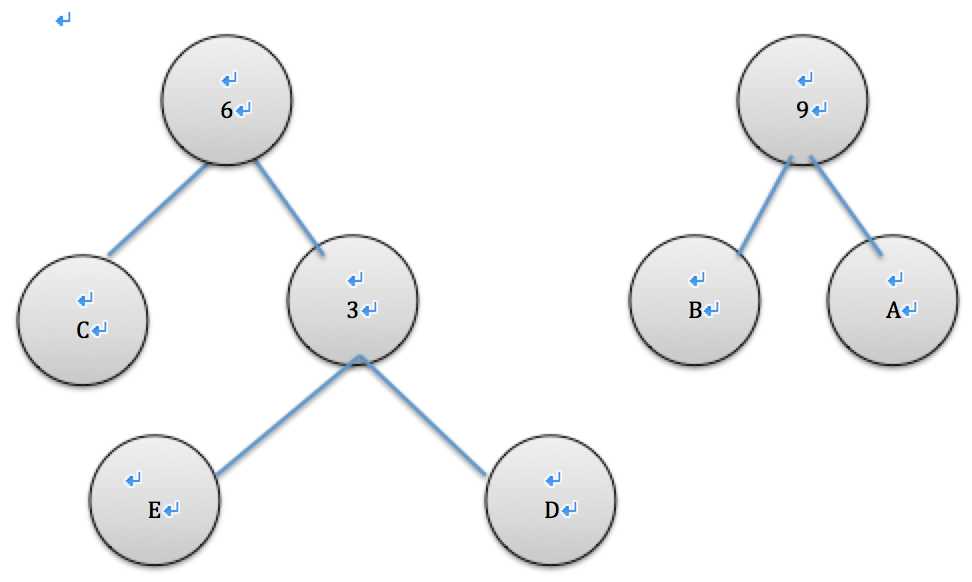
| 字符 | ab | cde |
| 出现次数 | 9 | 6 |
第四步:
取出现频率最小的节点cde和ab生成树
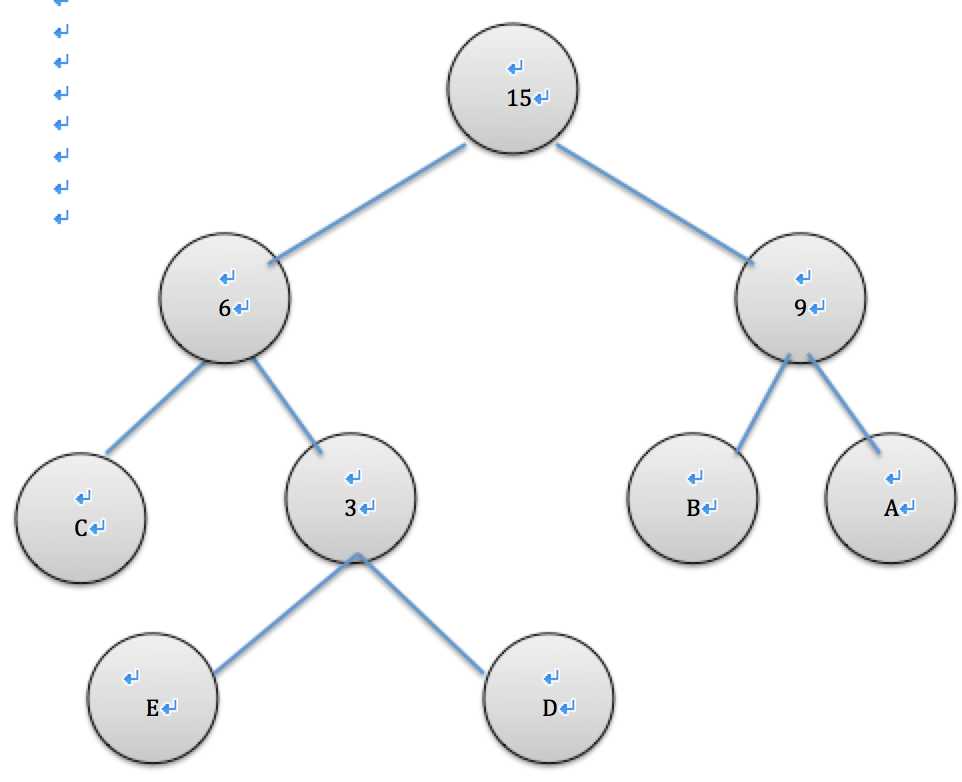
即所以各字符对应的编码为:A->11,B->10,C->00,D->011,E->010
哈夫曼树构建成功,代码实现上述逻辑即可.
构建哈夫曼树java代码实现
public static void makeHFTree(List<HFnode> nodes) {
while (true) {
int size = nodes.size();
if (size <= 1) {
break;
}
HFnode node1 = nodes.get(size - 1);
HFnode node2 = nodes.get(size - 2);
HFnode newNode = new HFnode();
newNode.setCount(node1.getCount() + node2.getCount());
newNode.setLeft(node2);
newNode.setRight(node1);
nodes.add(newNode);
nodes.remove(node1);
nodes.remove(node2);
Collections.sort(nodes);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
print(nodes.get(0), sb);
}
2.压缩
根据构建的哈夫曼树,对文件进行压缩:
// 根据哈夫曼树写文件 try {
//将哈夫曼树写到文件开头,文件解压时使用 File file = new File(fileName + suffix2); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); StringBuilder dicStr = new StringBuilder(); for (Byte b : dic.keySet()) { dicStr.append(b).append(":").append(dic.get(b)).append(";"); } bw.write(dicStr.toString()); bw.newLine(); bw.close();
//根据哈夫曼树写文件,本代码需要注意,当末尾字节bit不足8位时,需要补齐,否则解压时会有缺省 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos); int n = 1; byte buffer[] = new byte[n]; int errorCount = 0; StringBuilder value = new StringBuilder(); while ((fis.read(buffer, 0, n) != -1) && (n > 0)) { if (dic.containsKey(buffer[0])) { String temp = dic.get(buffer[0]); for (int j = 0; j < temp.length(); j++) { value.append(temp.charAt(j)); if (value.length() == 8) { dos.write(changeString(value.toString())); value = new StringBuilder(); } } } else { errorCount++; } } if (!value.toString().equals("")) { String waiteString = "";// 清空要转化的的码 for (int t = 0; t < 8; t++) { if (t < value.length()) { waiteString = waiteString + value.charAt(t); } else { waiteString = waiteString + ‘0‘; fillzero++; } } dos.write(changeString(waiteString)); } System.out.println("error count:" + errorCount); dos.flush(); dos.close(); fis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
3.解压
根据哈夫曼树进行解压
// 解压缩文件 try { File file = new File(fileName + suffix2); dic2 = new HashMap<String, Byte>(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String line = br.readLine(); String[] dicArray = line.split(";"); for (int i = 0; i < dicArray.length; i++) { String value = dicArray[i]; if (value != null && value.length() > 0) { String[] keys = value.split(":"); if (keys.length == 2) { dic2.put(keys[1], Byte.parseByte(keys[0])); } } } br.close(); file = new File("op" + fileName); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName + suffix2); DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis); StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder(); dis.skip(line.length() + 1); // 哈夫曼码+补0+占位符 while (dis.available() > 0) { int c = dis.read(); if (dis.available() > 0) { temp.append(changeInt(c)); } else { String value = changeInt(c); temp.append(value.substring(0, value.length() - fillzero)); } } String str = ""; for (int i = 0; i < temp.length(); i++) { str += temp.charAt(i); if (dic2.containsKey(str)) { fos.write(dic2.get(str)); str = ""; } } fos.flush(); fos.close(); dis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
完整实现代码

import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * 哈夫曼压缩算法的实现 * @author zilong.li * * */ public class HF { public static Map<Byte, String> dic = new HashMap<Byte, String>(); public static Map<String, Byte> dic2 = new HashMap<String, Byte>(); public static String suffix = ".txt"; public static String suffix2 = ".myzip"; public static int fillzero = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { // String str = // "hello world,show me the money,food for thought,I love you"; // 读文件,生成哈夫曼树 String fileName = "gif.gif"; if (!new File(fileName).isFile()) { return; } try { Map<Byte, Integer> map = new HashMap<Byte, Integer>(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); int n = 1; byte buffer[] = new byte[n]; while ((fis.read(buffer, 0, n) != -1) && (n > 0)) { for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) { if (!map.containsKey(buffer[i])) { map.put(buffer[i], 1); } else { int count = map.get(buffer[i]) + 1; map.put(buffer[i], count); } } } List<HFnode> nodes = new ArrayList<HFnode>(); for (Byte key : map.keySet()) { HFnode node = new HFnode(key, map.get(key)); nodes.add(node); } Collections.sort(nodes); // System.out.println(nodes); makeHFTree(nodes); fis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 根据哈夫曼树写文件 try { File file = new File(fileName + suffix2); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); StringBuilder dicStr = new StringBuilder(); for (Byte b : dic.keySet()) { dicStr.append(b).append(":").append(dic.get(b)).append(";"); } bw.write(dicStr.toString()); bw.newLine(); bw.close(); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos); int n = 1; byte buffer[] = new byte[n]; int errorCount = 0; StringBuilder value = new StringBuilder(); while ((fis.read(buffer, 0, n) != -1) && (n > 0)) { if (dic.containsKey(buffer[0])) { String temp = dic.get(buffer[0]); for (int j = 0; j < temp.length(); j++) { value.append(temp.charAt(j)); if (value.length() == 8) { dos.write(changeString(value.toString())); value = new StringBuilder(); } } } else { errorCount++; } } if (!value.toString().equals("")) { String waiteString = "";// 清空要转化的的码 for (int t = 0; t < 8; t++) { if (t < value.length()) { waiteString = waiteString + value.charAt(t); } else { waiteString = waiteString + ‘0‘; fillzero++; } } dos.write(changeString(waiteString)); } System.out.println("error count:" + errorCount); dos.flush(); dos.close(); fis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 解压缩文件 try { File file = new File(fileName + suffix2); dic2 = new HashMap<String, Byte>(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String line = br.readLine(); String[] dicArray = line.split(";"); for (int i = 0; i < dicArray.length; i++) { String value = dicArray[i]; if (value != null && value.length() > 0) { String[] keys = value.split(":"); if (keys.length == 2) { dic2.put(keys[1], Byte.parseByte(keys[0])); } } } br.close(); file = new File("op" + fileName); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName + suffix2); DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis); StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder(); dis.skip(line.length() + 1); // 哈夫曼码+补0+占位符 while (dis.available() > 0) { int c = dis.read(); if (dis.available() > 0) { temp.append(changeInt(c)); } else { String value = changeInt(c); temp.append(value.substring(0, value.length() - fillzero)); } } String str = ""; for (int i = 0; i < temp.length(); i++) { str += temp.charAt(i); if (dic2.containsKey(str)) { fos.write(dic2.get(str)); str = ""; } } fos.flush(); fos.close(); dis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void makeHFTree(List<HFnode> nodes) { while (true) { int size = nodes.size(); if (size <= 1) { break; } HFnode node1 = nodes.get(size - 1); HFnode node2 = nodes.get(size - 2); HFnode newNode = new HFnode(); newNode.setCount(node1.getCount() + node2.getCount()); newNode.setLeft(node1); newNode.setRight(node2); nodes.add(newNode); nodes.remove(node1); nodes.remove(node2); Collections.sort(nodes); } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); print(nodes.get(0), sb); } public static void print(HFnode node, StringBuilder sb) { if (node.getLeft() == null && node.getRight() == null) { node.setValue(sb.toString()); dic.put(node.getB(), node.getValue()); dic2.put(node.getValue(), node.getB()); // System.out.println(node.getB() + ":" + node.getValue() + ":" // + node.getChangeString()); } if (node.getLeft() != null) { print(node.getLeft(), new StringBuilder(sb.toString()).append("0")); } if (node.getRight() != null) { print(node.getRight(), new StringBuilder(sb.toString()).append("1")); } } public static int changeString(String s) { int result = 0; result += ((int) s.charAt(0) - 48) * 128 + ((int) s.charAt(1) - 48) * 64 + ((int) s.charAt(2) - 48) * 32 + ((int) s.charAt(3) - 48) * 16 + ((int) s.charAt(4) - 48) * 8 + ((int) s.charAt(5) - 48) * 4 + ((int) s.charAt(6) - 48) * 2 + ((int) s.charAt(7) - 48); return result; } public static String changeInt(int i) { String value = Integer.toBinaryString(i); String waiteString = "";// 清空要转化的的码 for (int t = 0; t < 8; t++) { if (t < value.length()) { waiteString = waiteString + value.charAt(t); } else { waiteString = ‘0‘ + waiteString; } } return waiteString; } } class HFnode implements Comparable<HFnode> { private byte b; private int count; private HFnode left; private HFnode right; private String value; public HFnode() { } public HFnode(byte b, int count) { this.b = b; this.count = count; } public String getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(String value) { this.value = value; } public byte getB() { return b; } public void setB(byte b) { this.b = b; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } public HFnode getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(HFnode left) { this.left = left; } public HFnode getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(HFnode right) { this.right = right; } @Override public int compareTo(HFnode node) { if (node != null) { return node.count - this.count; } return 0; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); return sb.append(this.b).append(":").append(this.count).toString(); } public int getChangeString() { return changeString(this.getValue()); } private int changeString(String s) { int result = 0; for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { result = result * 2 + (c == ‘1‘ ? 1 : 0); } return result; } }
代码比较简单,压缩的文件叫gif.gif,压缩后为gif.gif.myzip,解压文件为opgif.gif
Haffman integration by java(Algorithm)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lizilong/p/4702617.html