标签:
一个APP肯定不单单由一个Activity构成,我们在使用过程中,经常需要在多个Activity中跳转,Android中Intent可以帮我们来完成在各个Activity中跳转的功能。
Intent翻译为中文为“意图,目的”,在Android中提供了Intent机制来协助应用之间的交互和通讯,Intent负责对应用中一次操作的动作、动作涉及的数据、附加数据进行描述,Android则根据此Intent的描述,负责找到对应的组件,将Intent传递给调用的组件,并完成组件的调用。
Intent不仅可以用于程序之间,也可以用于程序内部。
Intent分为隐式Intent和显式Intent。
明确指出了目标组件名称的Intent,被称之为显式Intent。显式Intent直接用组件的名称定义目标组件,这种方式很直接。但是开发人员往往并不清楚别的应用程序的组件名称,因此,显示Intent更多用于应用程序内部传递消息。
在显式Intent消息中,决定目标组件的唯一要素就是组件名称,因此,如果你的Intent中已经明确定义了目标组件的名称,那么你就完全不用再定义其他Intent内容。
1. 新建一个工程LearnIntent
2. MainActivity.java
package cn.lixyz.learnintent; import android.content.Intent; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); //找到button组件设置点击事件 findViewById(R.id.btnStartMyAty).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { //显式方式声明Intent,并启动 startActivity(new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyAty.class)); } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); return true; } @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. int id = item.getItemId(); //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement if (id == R.id.action_settings) { return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } }
3. MyAty.java
package cn.lixyz.learnintent; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; /** * Created by LGB on 2015/8/6. */ public class MyAty extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.myaty); } }
4. acitivity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start MyAty" android:id="@+id/btnStartMyAty"/> </RelativeLayout>
5. myaty.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="New Text" android:id="@+id/textView" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="New Button" android:id="@+id/button" /> </LinearLayout>
6. AndroidManiFest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="cn.lixyz.learnintent" > <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".MyAty" > </activity> </application> </manifest>
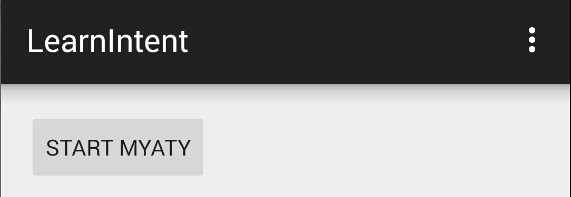
运行结果,点击“Start MYATY”,会转跳到MyAty中去

隐式Intent在创建时候并不指定要启动的activity,而是由Android系统帮助应用程序寻找与Intent请求意图最匹配的组件。
Android系统寻找与Intent请求意图最匹配的组件具体的选择方法是:Android将Intent的请求内容与一个叫做intent-filter的过滤器比较,intent-filter中包含系统中所有可能的待选组件。如果Intent-Filter中的某一组件隐式匹配Intent的请求,那么Android就选择该组件作为隐式Intent的目标组件。如果有多个组件满足该Intent请求,那么则会弹出提示,
1. 新建一个工程LearnIntent
2. MainActivity.java
package cn.lixyz.learnintent; import android.content.Intent; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); findViewById(R.id.button).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent("asdkfjalskd"); startActivity(intent); } }); } }
3. SecondActivity.java
import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; /** * Created by LGB on 2015/8/6. */ public class SecondActivity extends Activity{ @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.second_layout); } }
4. acitivity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="点击跳转到另一个页面" android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_alignParentStart="true" /> </RelativeLayout>
5. second_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第二个页面" android:id="@+id/second_view"/> </LinearLayout>
6. AndroidManiFest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="cn.lixyz.learnintent" > <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="asdkfjalskd" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
运行程序,点击按钮,成功转跳到第二个activity中
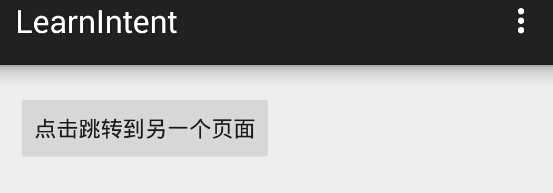

在上面的代码中,MainActivity.java中Intent请求内容为“asdkfjalskd”,这时候会在AndroidManiFest中的Intent-Filter寻找最匹配的activity,恰好SecondActivity满足,所以会跳转到SecondActivity上面去
上面说了,那个请求字符串可以是任意字符串,假如说两个activity的Intent-Filter中的action相同呢?
7.ThirdActivity.java
import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; /** * Created by LGB on 2015/8/6. */ public class ThirdActivity extends Activity{ @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.third_layout); } }
8.third_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第三个页面" android:id="@+id/third_view" /> </LinearLayout>
9. AndroidManiFest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="cn.lixyz.learnintent" > <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="asdkfjalskd" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".ThirdActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="asdkfjalskd" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
运行我们会发现,当点击按钮时候,会提示用户选择跳转到哪个activity
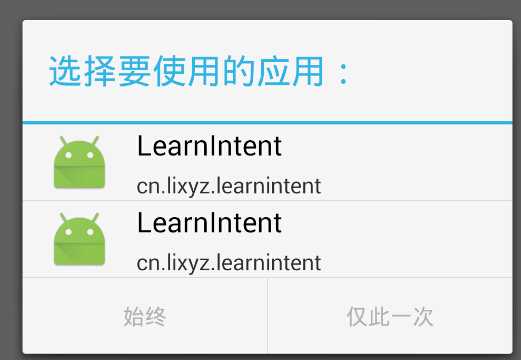
选择之后,跳转成功
在实际开发中,我们约定俗成的使用“包名.intent.action.类名”来代替那个字符串,以免发生混乱
Android笔记(三) 使得Activity之间可以跳转---Intent
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xs104/p/4708086.html