标签:
边看源码边参考别人的博客等,做一下学习笔记。
要了解View的绘制,首先得知道View树的结构:(可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7226787)
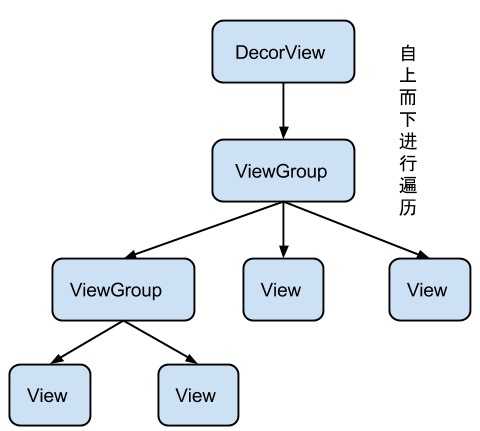
整个 View 树的绘图流程在ViewRoot.java类的performTraversals()函数展开,其绘制流程如下:
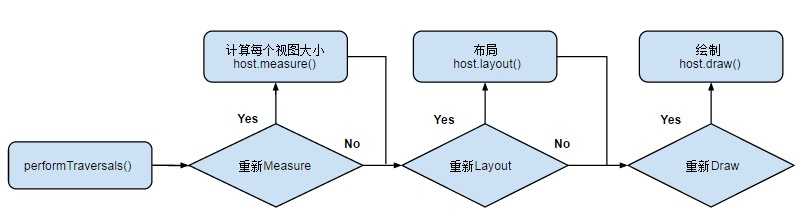
我们从最基本的思路来理解绘图流程:先确定所有View的大小,然后根据布局决定每个View的位置,然后开画!
这里着重关注具体绘图的Draw方法,其绘制流程为:
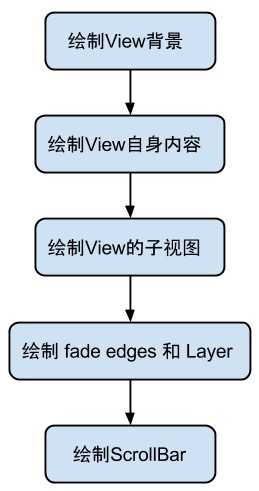
View.draw(Canvas) 方法:
/** * Manually render this view (and all of its children) to the given Canvas. * The view must have already done a full layout before this function is * called. When implementing a view, implement * {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} instead of overriding this method. * If you do need to override this method, call the superclass version. * * @param canvas The Canvas to which the View is rendered. * * 根据给定的 Canvas 自动渲染 View(包括其所有子 View)。在调用该方法之前必须要完成 layout。当你自定义 view 的时候, * 应该去是实现 onDraw(Canvas) 方法,而不是 draw(canvas) 方法。如果你确实需要复写该方法,请记得先调用父类的方法。 */ public void draw(Canvas canvas) { / * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed * in the appropriate order: * * 1. Draw the background if need * 2. If necessary, save the canvas‘ layers to prepare for fading * 3. Draw view‘s content * 4. Draw children (dispatchDraw) * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) */ // Step 1, draw the background, if needed if (!dirtyOpaque) { drawBackground(canvas); } // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case) final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) { // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) onDrawScrollBars(canvas); if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) { mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas); } // we‘re done... return; } // Step 2, save the canvas‘ layers ... // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) onDrawScrollBars(canvas); }
ViewGroup.dispatchDraw()方法:
dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas){ ... if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) {//处理 ChildView 的动画 final boolean buildCache = !isHardwareAccelerated(); for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) { final View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {//只绘制 Visible 状态的布局,因此可以通过延时加载来提高效率 final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams(); attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, childrenCount);// 添加布局变化的动画 bindLayoutAnimation(child);//为 Child 绑定动画 if (cache) { child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true); if (buildCache) { child.buildDrawingCache(true); } } } } final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController; if (controller.willOverlap()) { mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE; } controller.start();// 启动 View 的动画 } // 绘制 ChildView for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) { int childIndex = customOrder ? getChildDrawingOrder(childrenCount, i) : i; final View child = (preorderedList == null) ? children[childIndex] : preorderedList.get(childIndex); if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); } } ... } protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) { return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime); } /** * This method is called by ViewGroup.drawChild() to have each child view draw itself. * This draw() method is an implementation detail and is not intended to be overridden or * to be called from anywhere else other than ViewGroup.drawChild(). */ boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) { ... }
参考资料:
http://codekk.com/blogs/detail/54cfab086c4761e5001b253f
http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7110211
http://blog.csdn.net/xyz_lmn/article/details/20385049
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/albert1017/p/4730906.html